Science Investigatory Project (SIP) Guide
advertisement
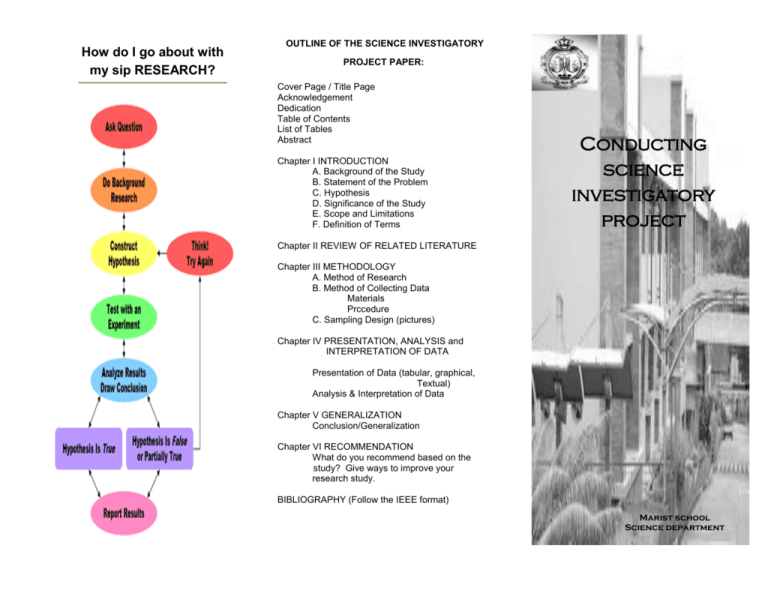
How do I go about with my sip RESEARCH? OUTLINE OF THE SCIENCE INVESTIGATORY PROJECT PAPER: Cover Page / Title Page Acknowledgement Dedication Table of Contents List of Tables Abstract Chapter I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study B. Statement of the Problem C. Hypothesis D. Significance of the Study E. Scope and Limitations F. Definition of Terms Conducting science investigatory project Chapter II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE Chapter III METHODOLOGY A. Method of Research B. Method of Collecting Data Materials Prccedure C. Sampling Design (pictures) Chapter IV PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS and INTERPRETATION OF DATA Presentation of Data (tabular, graphical, Textual) Analysis & Interpretation of Data Chapter V GENERALIZATION Conclusion/Generalization Chapter VI RECOMMENDATION What do you recommend based on the study? Give ways to improve your research study. BIBLIOGRAPHY (Follow the IEEE format) Marist school Science department What is a SCIENCE INVESTIGATORY PROJECT? WHAT KIND OF RESEARCH WILL I MAKE IN SIP? A Science Investigatory Project (some call it investigative project or IP) is like any other research work. It is a research undertaking that applies certain scientific principles or ideas with the purpose of determining possible solutions to a problem or possible explanations to existing phenomena. Two types of research one may undertake: a) Pure Research is conducted with no immediate objective in mind although the results may lead to solutions of problems in other fields. Problems in pure science may require more time. Projects under pure research can be accomplished by using data-gathering methods such as: survey, observations, case studies, statistical studies or experiment. Examples: Structure of nucleus, mass-energy relationship, DNA, structure of the atom, Phosphate content of Urine in Human Teenager b) Applied Research is conducted with an immediate purpose in mind. It is a project that makes use of scientific principles and the results would have immediate application or finished product. It requires less time and focuses on specific problem. Examples: Developing a new packaging material; studying the effect of temperature on a certain process, developing biodegradable plastic bag, Surgical Thread from Papaya Fiber, Dental floss from Pineapple Fiber What is a SCIENCE INVESTIGATORY What is a SCIENCE INVESTIGATORY PROJECT? PROJECT? SPECIFIC TYPES OF SCIENCE INVESTIGATORY PROJECTS: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Collection Project Designing & Building an apparatus, equipment or model Developing a process for testing products Improving/Developing a New product or new use for an existing product Finding new ways/improved ways of doing things Demonstrating a Scientific Principle in action or demonstrating an abstract principle in concrete terms Science in everyday life Survey Studies CRITERIA for grading PURE RESEARCH: a) b) c) d) e) Originality Degree of Difficulty Significance/Contribution to Science Scientific Treatment Clarity of Presentation CRITERIA for grading APPLIED RESEARCH: a) b) c) d) e) Originality Utilitarian Value (how useful is the study) Degree of Difficulty Scientific Treatment Clarity of Presentation TIPS in doing SIP research 1) In selecting a research problem, consider the following: Degree of difficulty: Examine this carefully in relation to your skills, knowledge, and experience level. Time available: Estimate the time you need for planning, literature research, setting up the project, executing it, assembling results, and drawing conclusions. Allow for a margin of safety for possible errors. Necessary resources & expenses: These include manpower, equipment, and materials needed. List them down and find out if these are all available. Collateral readings and availability of advice: This may be necessary on critical points in the experiments. You may consult knowledgeable people in your community, including your own parents if you are working on a local problem. 2) Keep a notebook for recording data Meticulously record all your observation, data, procedures, set-ups & questions. Even mistakes or failed experiments are important. Record your data using proper number of significant figures depending on the accuracy of the measuring instrument or device that you used.