chapter 3 - UiTM Kedah
advertisement

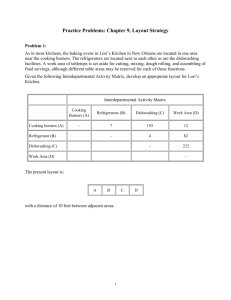
CHAPTER 3 Plant/Facility Layout 1 Definition • The overall arrangement of machines, departments, work centers, equipment, material handling, service facilities and aisles to facilitate the movement of work, customers or materials through the system. • Objective of Plant Layout Reduce Bottlenecks in moving people or material Bottleneck – an operation that limits output in the production sequence. Bottleneck centre has less capacity than the prior and following work centers. 2 Minimize Material Handling Cost Reduce Hazard To Personnel Utilize Labor Efficiently Increase Morale Utilize Available Space Effectively and Efficiently. Provide Flexibility 3 1 Factors That Influence Layout 1. Type of product – good of services, the aspect of product design and quality standard and whether for stock or made to order products. 2. Volume of production – capacity utilization, provision for expansion. 3. Type of production process – technology used, types of material handled and the process of producing the goods, service creation and delivery. 4 Types of Production/Operation • Continuous/Flow shop • Intermittent/Job shop • Project 5 Types of Production Continuous/Flow shop Intermittent/Job shop High product volume Low product volume Use special purpose equipment Use general purpose equipment Capital intensive operations Labor intensive Few schedule changes due to few Frequent schedule changes due to highly standardize output large variety of outputs Small product mix Large product mix Standardize product made to inventory Made to order products and not stored Operators are less broadly skilled Operators are broadly skilled Fixed cost high and variable cost low Fixed costs tend to be low and variable cost high 6 2 Types of Layout • 1. 2. 3. 3 basic types of layouts Product layout Process layout Fixed layout 7 Product Layout • Product layout is defined as the arrangement of facilities according to the needs processing requirement and in the same sequence as the operations necessary for producing the products or service. • Also known as line layout or assembly layout • It is appropriate for producing one standard product, in large volume • Suitable for products that require continuous production operations. Eg television sets, washing machines and automobiles assembly. 8 Advantages and Disadvantages of Product Layout Advantages Disadvantages Reduce material handling cost Lack of process flexibility Low work in progress inventory Expensive equipment – special purpose equipment Reduced total processing time – high output, low unit cost The operation are too interdependent Task is simplified – low training cost and time Low workers’ morale and productivity Simple production planning and control 9 3 Process Layout • Process layout is the arrangement of facilities and equipment in groups according to the function performed. • It is appropriate for intermittent operations when work flow is not consistent for all output. • Variable of workflow occurs when a variety of products or variations on single product are produced. • Work centers or department are grouped together according to functional type • Prevalent in banks, hospital and department store. 10 Process-Oriented Layout Patient A - broken leg ER triage room Emergency room admissions Patient B - erratic heart pacemaker Surgery Laboratories Radiology ER Beds Pharmacy Billing/exit Figure 9.3 11 Advantages/Disadvantages of Process Layout Advantages Disadvantages Flexibility of equipment and personnel High material handling cost Smaller investment in equipment High work in process inventory Workers are more knowledgeable Large storage space Less vulnerable to equipment failure Large aisles required High production cost per unit Long processing time Complex requirement for scheduling and control 12 4 Comparison Between Product and Process Layout Product layout Process Layout Efficiency Flexibility Machines are arranged in a sequence manner Machines are arranged in groups according to functions Continuous production process Intermittent production process, jobshop, batch production Standardize product made to stock Varied, product made to order Stable demand Fluctuating demand High Volume Low volume Special purpose equipment General purpose equipment Workers have limited skillsperform special tasks Workers have varied skills – perform diverse tasks. 13 Fixed Position layout • Fixed position layout is the arrangement of facilities and equipment so that resources needed in the form of workers, equipment and materials flow to the item being produced or serviced. • Also referred to as project layout • Eg. Home plumbing , construction of dams, bridges, ships and home building. 14 Product Layout Analysis • Three important requirements in designing an effective and efficient production line. 1. It meets the required capacity of demand – able to generate the desired number of output 2. The sequence is technically feasible – in sequence to facilitate the production flow 3. It is an efficient line – reduce cost of idleness and increase capacity 15 5 Important definitions Precedence diagram It shows the elemental task to be performed and sequence requirements. Task time The amount of time required to perform a task. Could be in minutes or seconds. Productive times per hour Number in the minutes in each hour that a work station is working. Cycle time The longest task time. Work station Physical location where particular set of task are performed 16 Important definitions Minimum numbers of work stations The least number of workstations that can provide the required production. Actual number of work stations The total number of workstations required on the entire production line, calculated as the next higher integer value of the number of workstations working. Bottleneck station The workstation that has the longest task time. Line balancing The process of assigning tasks to workstation in order to equalize the performance time at all workstations in such a way that 17 idle time is minimized Production Layout Analysis 1. 2. 3. 4. Cycle time Capacity Efficiency and Idleness Assembly Line Balancing 18 6