Vocabulary Practice - Science With Ms. Ortiz
advertisement
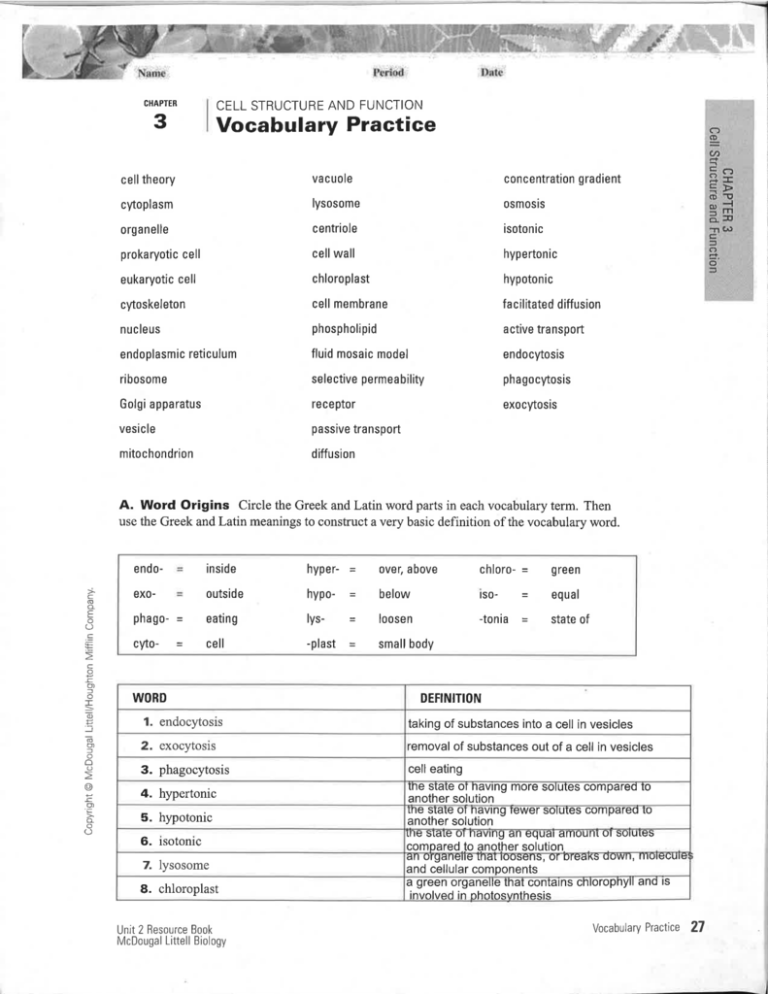
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHAPTER 3 Vocabulary Practice concentration gradient cuole celltheory va cytoplasm lysosome osmosis organelle centriole isotonic prokaryotic cell cellwall hypertonic eukaryotic cell chloroplast hypotonic cytoskeleton cell membrane facilitated diffusion nucleus phospholipid active transpoft endoplasmic reticulum fluid mosaic model endocytosis ribosome selective permea bility phagocytosis Golgi apparatus receptor exocytosis vesicle passive transport mitochondrion diffusion A. Word Origins Circle the Greek and Latin word parts in each vocabulary term. Then use the Greek and Latin meanings to construct a very basic definition of the vocabulary word. endo- inside hyper- = over, above chloro- = green exo- outside hypo- = below ISO- = equal (_) o Phago- = eating lys- = loosen -tonia = state of .c E + CYIO- cell -plast = small body c o o E = =co E o) l -o õÞ : õõ) = o oO o T .9 o o (_) WORD DEFINITION 1. endocytosis taking of substances into a cell in vesicles 2. exocytosis 3. phagocytosis 4. hypertonic 5. hypotonic 6. isotonic removal of substances out of a cell in vesicles 7, lysosome 8. chloroplast Unit 2 Besource Book McDougal Littell Biology cell eating Ine state ol navrng more solutes compared Io another solution rne srare or navrng rewer sotules compareo ro another solution ure 5ta[e ot ililvtf t9 aft equat arltuuilt ur lturutË5 compared to another solution afl organelle InaI loosens, or oreaKs uowl l, llluluuulc and cellular components a green organelle that conta¡ns chloropnyll ano ls involved in nhofosvnfhesis Vocabulary Practice 27 Period Name Date VOCABULARY PRACTICE, CONTINUED WORD 9, lt cytoplasm DEFINITION rv JgÍyil^ç ùuuùrdt tr,v iJLI I tPt.rÐvv vr vvorgr or ru utÐùu molecu]es and ions lhat fills much of a cpll trt9 10. cytoskeleton ongrglvrr q vgil, vt qtI Ittgtvv¡iltgwtgv Itgtvvvt^ vt a cell strenqth, the abilitv to move. and the abilitv to I 1 ns that gives nsport organelles B, Analogies Read each analogy. Decide which term is most like it. active transport exocytosis passive transport cellwall Golgi apparatus ribosomes concentration gradient nucleus selective permeability ribosomes 1. Chips in a chocolate chip cookie 2, Skin of a grape 3. Allowing 4. cellwall only invited guests in to your party selective permeability Floating on a raft through a tunnel 5. A cab driving you to the party 6. without paddling passive transport through heavy traffic active transport exocytosis Spitting out watermelon seeds 7. Thick fog in one area, clearin another 8. An accordion 9. golgi apparatus The chewy center of a candy > c nucleus 6 oE o O .c V/rite your own analogies to show the meaning of these terms: 10. cytoskeleton Sam answer: The =c eton is sort of like the und structure of a buildi that holds noP I =o else up and provides a structure for elevators to run up and down. .E -J õO) 11. phagocytosis f Sample answer: Phagocytosis is sort of like a person who hovers over the food, shoveling in huge bites. oo o E O) .E o o 28 Vocabulary Practice Unit 2 Besource Book McDougal Littell BiologY Period Name Date VOCABU LARY PRACTICE, CONTINU ED C. Vector Vocabulary Define the words in the boxes. On the lines across each arrow, write a phrase that describes how the words ACTIVE TRANSPORT 1 the movement of molecules across a membrane through a tr@ in the boxes are related to each other. PASSIVE TRANSPORT 2. the movement of mol across a membrane without energy input from a cell. energy input from a cell. diffusion of molecules across the cell membrane is a type of passive transport. 0sM0srs the movement of mol 4. from a region of higher centration to a reqion of ower concentration tC a o DIFFUSION 5. the movement of water molecules from a region of 6. osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules higher water concentration to a region of lower water concentration. E o C) .c 5 c o E o) f o T 7. The relative concentrations of two solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane wtll determ¡ne the direction osmosis across the membrane. õ ) .E õo) l ôoo o c o) o_ o (_) ts0T0Ntc HYPOTONIC L having an equal amount of L solutes compared to another compared to another sol having fewer solutes HYPERTONIC 10. have more solutes compared to another sol solution. Unit 2 Resource Book McDougal Littell Biology Vocabulary Practice 29 Period Name Date VOCABULARY PRACTICE, CONTI NU ED D. Who Am l? Choose among these terms to answer the riddles below: cell membrane facilitated diffusion phospholipid cell theory fluid mosaic model prokaryotic cell centriole lysosome receptor endoplasmic reticulum mitochondrion vacuole eukaryotic cell organelle vesicle 1. I cary out special jobs in a cell: 2. l'm an important concept and I have three main points; the last is that all cells come celltheory from existing cells 3. organelles I make up the two layers of the cell membrane: 4. phospholipids it is flexible and could be compared to 5. I am the type of cell that has a nucleus; animal and plant cells are me: 6. I am the type of cell without a nucleus; bacteria are me: eukaryotic cell prokaryotic cell facilitated diffusion 7. I help molecules diffirse across a membrane through transport proteins: 8. I have two t¡res, endoplasmic reticulum smooth and rough; I help produce proteins and lipids: 9. I contain enzymes and defend cells from viruses and bacteria; animal cells have lots of me: lysosomes G o_ E 1O. I am an organelle shaped like a bean; I provide energy for a cell .E 11. I am a cylinder-shaped organelle in animal cells, and I help make flagella: 12. I am the outer edge that separates a cell from the outside environment; cell membrane goes in and out of a cell: 13. I receive signals from molecules and make right time: 14. I'm a sac receptor centriole =o I control what E o) ô sure the right cell gets the right signal at the filled with fluid inside a cell; I store materials the cell needs: 15. I'm a little o mitochondrion (J r E : 6o) oo vacuole organelle that carries materials from one part of the cell to another; vesicle live long, but I can be recycled: I don't o E o) 'Ë o- oo 30 Vocabulary Practice Unit 2 Besource Book McDougal Littell Biology








