Matter Test: Review
advertisement

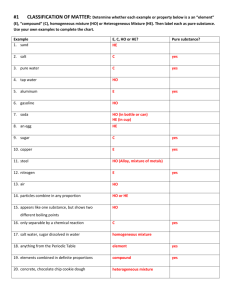
Name: Date Due: Matter Physical Science Chapter 8 What is Matter? 1. Define the following terms: a. matter= a. physical property= b. physical change= c. chemical change= d. reactivity= e. flammability= f. change of color= g. production of gas= h. production of a precipitate= 2. How can you recognize a physical change? 3. True or False: In a physical change, some of the substances in a material change, but the properties of the material stay the same. 4. How can we use physical properties to identify materials? 5. When can chemical properties be observed? 2 6. How is a chemical change different from a physical change? 7. Give an example of each of the following: Flammability Reactivity Example Change in Color Production of Gas Formation of Precipitate Example 8. Use a dictionary or internet to define the following properties: Term Definition Viscosity Conductivity Malleability Melting Point Boiling Point Density 3 9. A pat of butter melts and then burns in a hot frying pan. Which of these changes is physical and which is chemical? 10. Compare the properties of a raw egg to those of a hard-boiled egg. 11. If you spill household bleach on denim jeans, you will observe that the area of the spill no longer has a blue color. Is this change chemical or physical? Give a reason for your answer. 12. What do you think a reversible change means? 13. What do you think an irreversible change means? 4 Pure Substances 14. Define the following terms: a. pure substance= i. element= j. atom= k. compound= l. crystal= m. molecule= 15. What are the two categories that substances can be classified? 16. Why does every sample of a given pure substance have the same properties? 17. Why do chemists use symbols to represent the elements? 18. How many symbols are used for each element? 19. If there is a second letter, is it capitalized? 20. What does a compound always contain? 21. Properties of a compound are the (same or different). 22. How is water different that the Hydrogen and Oxygen that make up water? 5 Mixtures 23. Define the following terms: a. mixture= b. heterogeneous= c. homogeneous= d. solution= e. suspension= f. colloid= 24. What are the properties of a mixture like? 25. What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures? 26. What determines if a mixture is a solution, suspension or colloid? 6 27. What are two processes are used to separate mixture? Explain them. 28. Homogenized milk is a colloid. It has been treated to prevent its different components from separating when it stands. When non-homogenized milk stands, the cream rises to the top because it is less dense than the rest of the milk. Which type of mixture is non-homogenized milk? Explain your answer. 29. How could you use water and a coffee filter to separate a mixture of salt and sand? 30. Use the Internet to help you answer the following question. Explain how filtration separates materials based on the size of their particles. 7 States of Matter 31. Define the following terms: a. solid= b. liquid= c. gas= d. phase change= e. freezing= f. melting= g. vaporization= h. condensation= i. sublimation= j. deposition= k. endothermic change= l. exothermic change= 32. How can materials be classified? 33. What is kinetic theory? 8 34. Complete the table about the different states of matter using Definite and Not Definite: Shape Solids Volume Definite Liquids Gases Not Definite 35. How is a gas able to fill a container of any size or shape? 36. Use kinetic theory and attractive forces to explain why liquid has a definite volume and shape that can vary. 37. Explain why a solid has a definite shape and volume. Term Phase Change 38. Freezing a. Solid to Gas 39. Sublimation b. Liquid to Gas 40. Condensation c. Gas to Solid 41. Melting d. Liquid to Solid 42. Deposition e. Gas to Liquid 43. Vaporization f. Solid to Liquid 44. What happens to the temperature of a substance during a phase change? 9 45. What happens to the energy during a phase change? 46. How does endothermic phase change differ from exothermic phase change? 47. Complete the table: Endothermic Change Exothermic Change Sublimation (solid to gas) Deposition (gas to solid) Use the table to complete the next two questions Substances Melting Point Boiling Point Hydrogen -259.3°C -252.9°C Nitrogen -210.0°C -195.8°C Ammonia -77.7°C -33.3°C Octane -56.8°C 125.6°C Water 0.0°C 100.0°C Acetic acid 16.6°C 117.9°C 48. Which of the substance in the table above are solids at -40°C? 49. Which of the substances in the table above are gases at room temperature (22°C)? 10