Chapter 29 mosses and ferns
advertisement

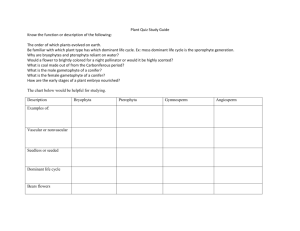
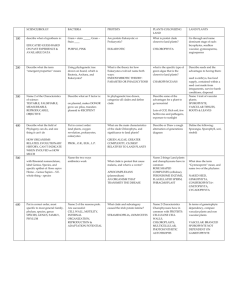
Figure 29.0 Ferns Figure 29.1 Some highlights of plant evolution Figure 29.12 Fossilized spores and sporophyte tissue Earliest fossils are 500 million years old Similarities between the Charophyceans and plants Why are plants thought to have evolved from Green Algae? Rosette complexes Peroxisome enzymes Flagellated sperm Phragmoplast formation 1 Apical Meristems Derived characters in plants Allow plants to elongate along all axes Spores are formed inside sporangia and have tough outer coverings formed from sporopollenin Alternation of Generations (does not occur in Charophyceans) Charophyceans) Multicellular Gametangia Specialized structures where gametes are formed Multicellular dependent embryos Zygotes are retained and develop in the maternal tissues Antheridia Archegonia 2 Terrestrial adaptations (derived characters in plants) Adaptations for water conservation Adaptations for transport Cuticle Stomata Xylem and phloem Adaptations for support They had to develop some new way of transporting sperm to eggs Non vascular plants Gametophyte is dominant stage of lifecycle Most lack conducting tissue Rhizoids anchor plants Reproduction: Spore germinates to become the protonema Male gametophyte contains Antheridia Female gametophyte contains Archegonia Nonvascular Plants: Phyla Bryophyta, Bryophyta, Hepatophyta and Anthocerophyta Mosses, liverworts, hornworts 3 Fig. 20.11 Fig. 20.12 The sporophyte in Bryophyta develops WITHIN the gametophyte Consists of a foot, seta and capsule Capsule Figure 29.16x Moss life cycle Is nutritionally dependent upon the gametophyte Calyptra peristome Figure 29.18 A moss sporangium with a “spore“spore-shaker” tip 4 Figure 29.19x A peat moss bog in Norway Phylum Hepatocyta Liverwort archegonia Female gameotphytes Gemmae cups Antheridia Male gametophytes 5 Anthocerophyta - Hornworts Vascular plants Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Seedless Vascular Plants (Pteridophytes): Vascular plants all share the following Vascular tissue with lignified cells for water and food transport Independent branched sporophytes Phyla Lycophyta and Pterophyta Cooksonia, Cooksonia, a vascular plant of the Silurian Age True roots with lignified vascular tissue Leaves Microphylls Megaphylls Sporophyte is dominant generation Evolution from homospory to heterspory Evolved about 400 mya Grew to 50 cm Figure 29.22 Hypotheses for the evolution of leaves 6 Lycophyta: Lycophyta: Lycopodium Pterophyta: Pterophyta: Psilotum Lycophyta Phylum Pterophyta: Pterophyta: Phylum Pterophyta: Pterophyta: Equisetum Polypodium Club mosses Have microphylls Have some shoots ending in sporophylls Figure 29.23 The life cycle of a fern Sphenophyta: Sphenophyta: the Horsetails Produce cones at tips Cones are clusters of sporophylls Have hollow stems for transport of Oxygen to rhizomes underground 7 Figure 29.23x7 Life cycle of a fern: archegonia Figure 29.25 Artist’s conception of a Carboniferous forest based based on fossil evidence 8