egypt - Sepulveda Middle School
advertisement

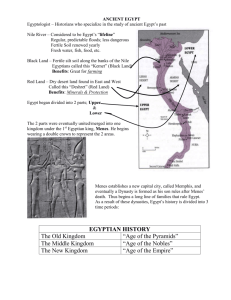
Name ___________________________________ __________________ EGYPT TIME PERIOD O______ Kingdom 2686-______ BC M_________ Kingdom 2061-______ BC N_______ Kingdom 1570-______ BC GrecoRoman period 305-282 BC 51-30 BC Egypt.doc Kings/Pharaohs Worksheet SYMBOL/ DISTINCTION Great P__________ KINGS/PHARAOHS King Z_______ 2630-______ BC god of the N________, K_________, spoke to him in a d_________. 2551-2528 K________ 2520-2494 – K____________ 2490-______ Menkaure Egypt became s_________. Cult of Isis and O_____________ began. Great achievements in Egypt invaded Palestine because Palestine attacked their t________ l__________, a____, caravans. architecture 2061-2_____ Mentuhotpe 1991-_______ Amenemhet I 1971-_______ Senwsret I 1787-________ Nefrusobk Egypt became a w_______ Kings called Pharoahs, seen as gods. power - Queen H__________ (1500-1480), 1st female Pharaoh. Renewed Egypt’s prosperity and p________. -Akhenaton (1350-1334) destroyed old gods. Set up Aton, s___ god, as o____ god. This was the first _____theistic time in Egypt. Capital moved to Akhetaton, meaning “Horizon of A_____”. -King Tut (1343-1325) ruled from ages 9-___. Went back to old g_____. T______ became the capital again. -Ramses I, II, III (1291-______. Moved royal capital to M______. Built great temples. Alexander the Great of Ptolemy I. One of Alexander the Great’s g___________. He held Greece rules most of the p__________ in Egypt after Alexander’s d________. world Rome rules the known Cleopatra VII. The last Pharaoh. She wanted to restore Egypt’s world e_________. She tried to make alliances with J_________ Caesar and Mark Antony. She and Mark Antony committed s_________ when Emperor Augustus declared w_______ on Egypt. Answers: Old Kingdom: 2181, Pyramids, Zoser, 2611, Nile, Khnum, dream, Khufu, Khephren, 2472 Middle Kingdom: 1650, stronger, literature, art, Osiris, trade, 2010, 1962, 1926, 1783 New Kingdom: 1070, world, Hatshepsut, peace, sun, only, mono, Aton, 18, gods, Thebes, 1510, Memphis Greco-Roman period: generals, power, death, empire, Julius, suicide, war. Name ___________________________________ __________________ EGYPT TIME PERIOD O______ Kingdom 2686-______ BC M_________ Kingdom 2061-______ BC Kings/Pharaohs Worksheet SYMBOL/ DISTINCTION Great P__________ KINGS/PHARAOHS King Z_______ 2630-______ BC god of the N________, K_________, spoke to him in a d_________. 2551-2528 K________ 2520-2494 – K____________ 2490-______ Menkaure Egypt became s_________. Cult of Isis and O_____________ began. Great achievements in Egypt invaded Palestine because Palestine attacked their t________ l__________, a____, caravans. architecture N_______ Kingdom 1570-______ BC Egypt became a w_______ power GrecoRoman period 305-282 BC Alexander the Great of Greece rules most of the world Rome rules the known world 51-30 BC 2061-2_____ Mentuhotpe 1991-_______ Amenemhet I 1971-_______ Senwsret I 1787-________ Nefrusobk Kings called Pharoahs, seen as gods. - Queen H__________ (1500-1480), 1st female Pharaoh. Renewed Egypt’s prosperity and p________. -Akhenaton (1350-1334) destroyed old gods. Set up Aton, s___ god, as o____ god. This was the first _____theistic time in Egypt. Capital moved to Akhetaton, meaning “Horizon of A_____”. -King Tut (1343-1325) ruled from ages 9-___. Went back to old g_____. T______ became the capital again. -Ramses I, II, III (1291-______. Moved royal capital to M______. Built great temples. Ptolemy I. One of Alexander the Great’s g___________. He held p__________ in Egypt after Alexander’s d________. Cleopatra VII. The last Pharaoh. She wanted to restore Egypt’s e_________. She tried to make alliances with J_________ Caesar and Mark Antony. She and Mark Antony committed s_________ when Emperor Augustus declared w_______ on Egypt. Egypt.doc Answers: Old Kingdom: 2181, Pyramids, Zoser, 2611, Nile, Khnum, dream, Khufu, Khephren, 2472 Middle Kingdom: 1650, stronger, literature, art, Osiris, trade, 2010, 1962, 1926, 1783 New Kingdom: 1070, world, Hatshepsut, peace, sun, only, mono, Aton, 18, gods, Thebes, 1510, Memphis Greco-Roman period: generals, power, death, empire, Julius, suicide, war. Name_______________________ Date________________________ Period_______________________ Egyptian Gods and Goddesses PowerPoint Project Either alone or with a partner, look over the list on the back, and choose the names of at least three Egyptian gods and three goddesses that you might like to research. Rate them as your 1st, 2nd and 3rd choices. The teacher will randomly call your name. If your 1st choice is taken, choose your 2nd or 3rd choice, or else a god and goddess will be assigned to you. When everyone (or group of 2) has been assigned one god and one goddess, begin your research as explained below. Project Objectives: Working either alone or with one other person, students will research one Egyptian god and one Egyptian goddess. Students will then create a PowerPoint presentation to display what they have learned about their god and goddess. Every slide must contain a picture. B sure to copy the URL of each picture and information source (books, Internet, encyclopedias, etc.) to the last slide, which will be a bibliography. Also include the following items: Slide 1: The first name and last initial of those working on the project, the name of the god and goddess studied, and a picture of each. Slide 2: An explanation of what the god stands for or represents, what symbols he holds or wears and why. Explain what his name means, if known, and what specific function he performs (like weighing the hearts of the dead), or what city is he connected with, or whom he is supposed to protect. (If this information needs more than one slide, that is fine. You must have a minimum of six slides, but you can have more than six.) Be sure to use your own words, and to use correct grammar and spelling. Slide 3: To whom is he related? (Married to what goddess, or father or son of what god or goddess.) Slide 4: An explanation of what the goddess stands for or represents, what symbols she holds or wears, and why. Explain what her name means, if known, and what specific function she performs (like weighing the hearts of the dead), or what city is she connected with, or whom she is supposed to protect. Slide 5: To whom is the goddess related? (Married to what god, or mother of or daughter of what god or goddess. Slide 6: Bibliography – center and bold this as the title of the last slide. Copy and paste any URL’s from which you obtain information or pictures. Next to the URL, explain what you found at that particular site. DO NOT use search engines as URL references in the bibliography (google, altavista, etc.). Give the exact URL where the information was found, such as: http://www.touregypt.net/gods1.htm Mythology information http://www.ancientegypt.co.uk/gods/home.html http://www.ancientegypt.co.uk/gods/explore/main.html (pictures) http://www.neferchichi.com/gods.html (pictures) http://sobek.colorado.edu/LAB/GODS/ (index and descriptions of gods and goddesses) http://www.angelfire.com/wi/egypt/gods.html http://www.angelfire.com/ca/pye/gods.html http://www.angelfire.com/wi/egypt/hiero.html (hieroglyphs) http://www.osirisweb.com/egypt/director.htm http://www.cmi.k12.il.us/Urbana/projects/AncientCiv/gods/gods.html (index) List of Egyptian Gods and Goddesses Circle and label your 1st, 2nd and 3rd choices. Pick the top 3 gods, and then pick the top 3 goddesses. When you or your partner’s name is called, you must choose one god and one goddess that have not already been chosen. When you receive your choice, circle the god and goddess on this sheet and keep this paper in the social studies section of your binder. As you answer the research questions on the front, check them off. Save your PowerPoint project to the server, sontag period 1/2 or sontag period 3/4 if working on a library computer, or to your period’s folder on the desktop of computers in the room. Name your project with your first name only and then the word god, such as Mattgod. Do not use commas, periods or hyphens in the file name when saving the PowerPoint. Amen - Egyptian god of the dead Anubis - a very ancient god of the dead. Bast - Egyptian cat goddess Bes- Egyptian dwarf god believed to guard against evil spirits and misfortune Chons -Egyptian moon god Dua - (god) Protector of the stomach of the deceased Geb - (god) God of the Earth Hathor - Egyptian cow goddess Horus - is the son of Osiris and Isis. He is identified with the pharaoh. Isis - Egyptian mother goddess Khepry - A divine scarab beetle which was the dawn manifestation of the sun god Khnum - is known as the creator god Maat - Egyptian goddess of truth and justice Meresger - A snake goddess of the mountain peak overlooking the royal tombs of Thebes (modern Luxor). She was generally benevolent and had the power to cure disease, but she could also inflict sickness on sinners. Min - (god) Egyptian fertility god Mut - Wife of Amen, mother of Khons Khnum - is known as the creator god Neith - The great mother goddess. According to one account, she emerged from the Nun, the primordial waters, and created deities and humans. Nekhbet - The vulture goddess of the Southern city of Nekheb (modern el-Kab) and the patron goddess of Upper Egypt. Nephthys -Egyptian goddess of the dead Nut - Egyptian goddess of the sky and of the heavens Osiris -Egyptian god of the underworld and of vegetation Ptah - is the god of artists and craftsmen Qetesh - Goddess of love and beauty. Re - (Ra, Amun-Re (or Amon-Ra, Sobk-Re Re-Harakhty) is the sun god. He is considered king of the gods. Egyptian sun god Selket - Scorpion goddess, helper of women in childbirth Set - Egyptian god of chaos, protector of Egypt Shu - Egyptian god of the air Sobek - Egyptian crocodile god Taweret -Hippopotamus goddess and protective deity of childbirth Thoth - Egyptian moon god Wepwawet - God of war and of the funerary cult Name __________________ Date____________________ Period__________________ Egyptian Vocabulary Worksheet Slide #1: Black Land: Dark soiled valley of fertile land near the ___________ ______________ . Red Land: __________ area in Egypt. cataracts: Rushing water forming ________________ and rapids as it rushes through stone ___________ and boulders. Delta: T______________ of muddy wetlands where a river divides into many small channels and streams. It has rich soil for farming. Dynasty: A series of ________________ from the same family. Slide #2: Book of the Dead: A book of hymns, prayers, and magic spells. These were placed with the dead in order to help them pass through the d____________ of the underworld and attain an afterlife of bliss in the Field of Reeds. Some of the texts are also found on the w_____________ of tombs and on c_______________ or written on papyrus, linen or vellum. Slide #3: Ra or Re: The Egyptian ___________ god, c_________________ god, great-grandfather of Osiris, and Isis, and great-greatgrandfather to Horus. Slide #4 Osiris: The chief god of the underworld, or home of the dead. He greeted the dead person when they reached the underworld and asked them q________________ about their life on earth. Slide #5 Anubis: He had the body of a human and the head of a jackal. He helped Osiris prepare the bodies of the dead for the afterlife. He was worshipped as the i_______________ of embalming. He held the s__________________ that weighed a person’s heart. Slide #6 Maat: The goddess whose feather of ______________ was placed on the scale opposite the dead person’s heart. Slide #7 Cartouche: An ____________- shaped inscription with a king or queen’s _________________ written in hieroglyphs. The cartouche was an elongated version of the ___________ rope within which two of the king's names (his birth name and his throne name) were written. Slide #8 Khnum: A god who controlled the flood_____________ of the Nile who was pictured as a ram-headed _________________. He was also seen as a creator-god who molded people on a potter’s w_________ from the mud of the Nile River. Slide #9 Papyrus: Long, thin ____________ that grew wild along the riverbanks of the Nile. We get our word _______________ from papyrus. Pharaoh: The term means “great _____________.” During the New Kingdom period Egyptians began to call their kings “pharaohs”. Before that, it only referred to the royal p____________. Slide #10 Upper Egypt: The ________________part of Egypt that stretched for over 500 miles from the first c________________ northward to the beginning of the Nile Delta. Lower Egypt: The northern part of Egypt, consisting of the Nile ____________. It was only ________ miles long, but many times wider than Upper Egypt. White Crown: The crown worn by the kings of ___________ Egypt. It was a white, pear-shaped crown. Red Crown: The crown worn by kings of _______________ Egypt. It was a short, boxy, red crown with a tall spike at the back and a curlicue at the front. Slide #11 King Menes: The king of ______________ Egypt around ________________ BC. He defeated the king of Lower Egypt, united the two lands and named himself King of both Upper and Lower Egypt. Supposedly, he designed a new crown to celebrate his victory. This d_______________ crown stood for the union of the two lands. Slide #12 Sarcophagus: A c______________. The outside of the Egyptian sarcophagus usually had the king or queen’s c__________________, a picture of their head and hands, symbols of their reign, and p______________ of gods and goddesses. Slide #13 Thebes: In 2134 BC Thebes became the r_____________ residence of the Pharaoh, and the site of worship for the god, Amon during the M______________ Kingdom Period. Today it is the site of Luxor, and K___________. It contains the Valley of the Tombs and great temples. As the Egyptian empire began to decay, the city of Thebes declined. Thebes was taken over by the Assyrians in 661 BC. SlideNew #14 Middle Kingdom Old Kingdom 2686-2181 BC 3000 BC 3100 BC 3300 BC 4000 BC Hieroglyphics i__________ Kingdom 1570-1070 BC 2055-1650 BC E_______ grew s____________ Great Pyramids at G_______ built Egypt became a w________ p_________ Upper Egypt conquers l_______ Egypt Separate kings in u_______ and lower Egypt Egypt began to f_______ Slide #15 Mesopotamia Both Rivers flow __________ to north Rivers give l______ F_______ plain, not protected from i___________ No predictable f____________ H_________ to farm than in Egypt Egypt Nile flows n_________ to south Rivers f__________ Built i___________ canals Boundaries are p____________ from invaders Life based on f____________ P_______________ flooding Mineral-rich __________ Easier to farm than in M________________