Pest analysis.doc
advertisement

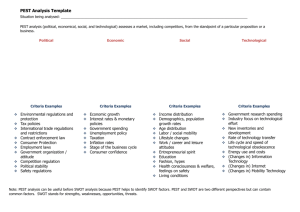
PEST Analysis Template Situation being analysed: Tourism is subject to a range of global influences, events and forces that impact on the sustainability of the industry at statewide and regional levels. The diagram below outlines some of the issues and trends in the macro environment that may have an impact on tourism in Queensland. ______________________________________________________________ PEST analysis (political, economical, social, technological) assesses a market, including competitors, from the standpoint of a particular proposition or a business. criteria examples Political Economical ecological/environmental current legislation future legislation international legislation regulatory bodies and processes government policies government term and change trading policies funding, grants and initiatives home market pressuregroups international pressuregroups wars and conflicts Political/legal trends criteria examples social lifestyle trends demographics consumer attitudes and opinions media views law changes affecting social factors brand, company, technology image consumer buying patterns fashion and role models major events and influences buying access and trends ethnic/religious factors advertising and publicity ethical issues criteria examples Economic trends Terrorism will be ‘top of mind’ and travellers will adjust Fluctuating global economies and variable exchange rates will continue to influence travel demand Security measures will be standardised around the world and their cost will increase airfares Variable fuel prices will influence transport supply and demand Technological Social & cultural trends • Growing urban and coastal populations • Ageing, affluent, active Western population • Emerging middle class in developing cities • Risk of a disease pandemic is growing • Growing concerns for safety and security home economy economy trends overseas economies general taxation taxation specific to product/services seasonality issues market/trade cycles specific industry factors market routes trends distribution trends customer/end-user drivers interest/ exchange rates international trade and monetary issues criteria examples competing technology development research funding associated/dependent Technology will technologies continue to replacement technology/solutions develop at a maturity of technology manufacturing maturity rapid pace and and capacity involve all information and communications sectors of the consumer buying industry mechanisms/technology technology legislation innovation potential Mobile phones will be technology access, used to plan and licencing, patents intellectual property issues organise global communications echnology trends holidays High-definition televisions and computers will provide virtual visits to a destination Innovations in transportation will affect range, speed, comfort and safety of travel Economic trends Fluctuating global economies and variable exchange rates will continue to influence travel demand Variable fuel prices will influence transport supply and demand Natural environment trends • Environmental and social awareness will increase • Natural disasters and geo-political events affect travel behaviour • Market trends • Increasing market fragmentation, and growth in special interest/niche markets • More frequent, shorter holidays • Travellers will have higher service expectations • More travellers will require customised holidays • Travellers will use new media technology more for information, booking and sales • Emerging travel markets in developing countries will influence travel demand • As baby boomers retire en masse from 2010 to 2020, they will shape demand • Trend towards the accumulation of leave entitlements • Increased price sensitivity Competitive trends Political/legal trends • Terrorism will be ‘top of mind’ and travellers will adjust • Security measures will be standardised around the world and their cost will increase airfares • Technology trends • Technology will continue to develop at a rapid pace and involve all sectors of the industry • Mobile phones will be used to plan and organise holidays • High-definition televisions and computers will provide virtual visits to a destination • Innovations in transportation will affect range, speed, comfort and safety of travel • Industry trends • Liberalisation of air transport and low cost travel will influence travel demand • With greater speed and capacity, remote and long haul destinations will be more accessible and affordable to many travellers • Oversupply of undifferentiated travel products and destinations will affect competitiveness • Social & cultural trends • Growing urban and coastal populations • Ageing, affluent, active Western population • Emerging middle class in developing cities • Risk of a disease pandemic is growing • Growing concerns for safety and security • Note: PEST analysis can be useful before SWOT analysis because PEST helps to identify SWOT factors. PEST and SWOT are two different perspectives but can contain common factors. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats. SWOT analysis explanation and templates are at www.businessballs.com/swotanalysisfreetemplate.htm www.businessballs.com/pestanalysisfreetemplate.htm www.businessballs.com Not to be sold or published. A free resource from