US History Fort Burrows Government, Citizenship, and the
advertisement

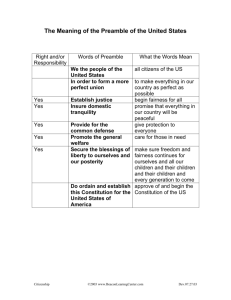
US History Fort Burrows Government, Citizenship, and the Constitution, 1787 - Present 8.1 -- Goals and Principles of the Constitution READ pgs 246 - 251 Time Line: 1787 1789 1830 1870 1920 1951 1971 - US Constitution written George Washington becomes the 1st US President ( for two terms ) male land owners over 21 years old and white can vote 15th Amendment African American males can legally vote 19th Amendment allows women to vote 22nd Amendment limits Presidents to two terms 26th Amendment extends right to vote to 18 -21 years of age George Washington, 1st President of the United States of America. Born at Pope’s Creek, Virginia on February 22, 1732 and died December 14, 1799. He was considered a Federalist. As our nation’s 1st President, GW is known as the ‘Father of Our Country.” Through his leadership, the American colonies won independence from Great Britain and became the United States of America. Washington grew up on a farm in Virginia but inherited an estate, Mount Vernon, from his half-brother. In his early 20s, GW joined the Virginia militia and fought in the French & Indian War. His military skills earned him an appointment as commander of the colony’s militia. After the war, Virginia’s voters elected GW to the colony’s legislature, where he served for 15 years. When the American Revolution broke out, GW was called to lead the Continental Army against the British troops. As General Washington, he led the poorly equipped colonial soldiers through six years of battle. The Continental Army was often short of ammunition, food, clothing, and other supplies. GW’s courage inspired his men. He kept their spirits up through his disciplined leadership and by sharing their hardships. The Continental Army finally triumphed in 1781, when the British surrendered. Main Idea: The goals and principles of the Constitution have guided the United States for more than 222 years. Vocabulary: ( Gov’t - government ) preamble - introduction to a declaration, constitution, or official document domestic tranquility - peace and order at home (from the Preamble) civilian - nonmilitary general welfare - well-being of all the citizens of a nation (from the Preamble) liberty - freedom 1 of 8.1 Printer Copy US History Fort Burrows Articles - the main body of the Constitution that establishes the framework for the US government popular sovereignty - principle of the US Constitution that states the people have a right to create, alter, and abolish their gov’t limited government - principle of the US Constitution that states the gov’t has only the powers that the Constitution gives it checks and balances - principle of the US Constitution that safeguards against abuse of power by giving each branch of gov’t the power to check the other branches federalism - principle of the US Constitution that establishes the division of power between the federal gov’t and the states Setting the Scene: On Election Day, 2000, some 100 million Americans went to the polls to elect a new President. But they woke up the next morning to learn that the election was not over. Across the nation, the vote was split almost down the middle. Neither the Democratic candidate, Albert Gore, nor the Republican candidate, George W. Bush, had the 270 electoral votes needed to become President. The result would depend on the vote in Florida—a race that was too close to call! For 36 days, Americans watched and argued as the candidates battled for Florida’s 25 electoral votes. Teams of lawyers, local election officials, state legislators, and state and federal judges all became involved in the battle. At last, a ruling by the Supreme Court of the United States allowed Bush to claim victory. Gore offered his opponent best wishes for a successful presidency. The election of 2000 raised some troubling issues. In the end, though, the election showed the strength of our constitutional system. The electoral battle was fierce but not violent. The candidates fought bitterly to win, but they fought in courts not in the streets. As in the past, Americans relied on the system established by their Constitution. The Preamble Sets Goals Constitution is divided into 3 main parts: Preamble, Articles and Amendments Preamble has 6 goals “We the people of the United States , in order to form a more perfect Union, establish justice, insure domestic tranquillity, provide for the common defense, promote the general welfare, and secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity, do ordain and establish this Constitution for the United States of America.” Preamble of the Constitution 2 of 8.1 Printer Copy US History Fort Burrows To Form a More Perfect Union when Constitution was written, states saw themselves as separate nations the framers wanted to work together as a unified nation To Establish Justice the framers knew the nation needed a unified system to settle legal disputes American justice system requires that the law be applied fairly to every American regardless of race, religion, gender or country of origin To Insure Domestic Tranquillity National government has the power to insure domestic tranquillity Example: National Guard providing assistance in a disaster area To Provide for the Common Defense every country has a duty to protect its citizens against foreign attack the framers gave the national gov’t the power to raise armies and navies they also placed the military under civilian, or nonmilitary control To Promote the General Welfare Constitution set out to give the national gov’t the means to promote the general welfare of its citizens Example: National Institutes of Health leads the fight against many diseases To Secure the Blessings of Liberty Colonists fought and died for liberty during Revolution the framers made liberty a major goal of the Constitution amendments have extended the “blessings of liberty” to more Americans ¿¿ What are the goals of the preamble of the Constitution ? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________. Articles and Amendments The main body of the Constitution is a short document divided into 7 sections called Articles that establish the framework for our gov’t The Articles Articles I, II and III describe the 3 branches: legislative, executive, and judicial Article IV deals with relations between states – requires states to honor one another’s laws and legal decisions and system for admitting new states Article V provides a process to amend the Constitution Article VI states the Constitution is the “supreme law of the land” – states may not make laws that violate the Constitution Article VII sets up a procedure for the states to ratify the Constitution 3 of 8.1 Printer Copy US History Fort Burrows Amendments Only 27 formal changes have been made to the Constitution in 220 years The 1st 10 amendments were the Bill of Rights added in 1791 Amendments have changed the working of the gov’t or extended rights Seven Basic Principles Popular Sovereignty Declaration of Independence asserted that people “are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable rights” They have the right to alter or abolish their gov’t Constitution reflects this principle of popular sovereignty: gov’t gets its authority from the people Limited Government The framers made limited gov’t a principle of the Constitution In a limited gov’t, the gov’t has only the powers that the Constitution gives it Everyone from you to the President must obey the law Separation of Powers The framers provided for separation of powers to further limit the gov’t Constitution divides the gov’t into 3 branches Legislative, or Congress, makes the laws Executive, or President, carries out the laws Judicial, or Courts, interprets the laws Checks and Balances A system on checks and balances safeguards against abuse of power Each branch has the power to check, or limit, the actions of other 2 branches ¿¿ How does the US Constitution address the idea of limited gov’t? __________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________. Federalism Constitution establishes the principle of federalism, or division between the federal gov’t and the states Federal gov’t can coin money, declare war, & regulate trade between states States regulate trade inside state borders, make rules for state elections and establish schools Republicanism Constitution provides for a republican form of government Citizens elect representatives to carry out their will Representatives vote according to their own judgment but must remain open to the opinions of the people they represent 4 of 8.1 Printer Copy US History Fort Burrows Individual Rights Constitution protects individual rights Rights such as freedom of speech and religion and the right to trial by jury “The character of every act depends upon the circumstances in which it is done. The most [strict] protection of free speech would not protect a man in falsely shouting fire in a theatre and causing a panic… The question in every case is whether the words used are used in such circumstances and are of such a nature as to create a clear and present danger that they will bring about the [real] evils that Congress has a right to prevent.” Oliver Wendell Holmes, Jr., Schenck v. United States, 1919 1. How does the Preamble define the basic goals of the Constitution ? 1. _______________________________________________________________ 2. _______________________________________________________________ 3. _______________________________________________________________ 4. _______________________________________________________________ 5. _______________________________________________________________ 6. _______________________________________________________________ 2. What framework of government is established by the articles of the Constitution ? 1. _________________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________________ 4. _________________________________________________________________ 5. _________________________________________________________________ 3. What are the seven (7) principles of American government ? a. _______________________________________________ b. _______________________________________________ c. _______________________________________________ d. _______________________________________________ e. _______________________________________________ f. _______________________________________________ g. _______________________________________________ 4. Constitution of the United States Article I Section 1 “The House of Representatives shall be composed of members chosen every second year by the people of the several states…” Which principle of the Constitution is primarily reflected in the passage above ? A. Republicanism B. Federalism C. Checks and Balance D. Individual Rights 5 of 8.1 Printer Copy