Human/Environmental Interaction
advertisement

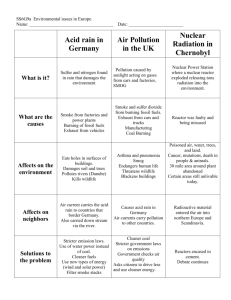
Human/Environmental Interaction Climate and weather affect people’s lives Farmers need rain Floods, storms, earthquakes destroy New technologies allow humans to influence their environment Some of this is good, some is bad Technology in Agriculture Fertilizers Can cause environmental side effects Mechanization Requires energy, usually fossil fuels Energy Technology Fossil Fuels Causes pollution; non-renewable resource Nuclear Energy Cleaner energy source; accidents can be catastrophic Transportation Technology Building roadways & Railways Destroys natural habitats; increases pollution Mountains and landscapes can create barriers to transportation patterns and cause problems Automotive Technology Parking lots Destroys natural habitats Suburbs People can afford to commute to cities to work; more pollution, more natural land destroyed as highways and subways are built In the U.S. the wealthy tend to live on the outskirts of the city in the suburbs because they can afford to commute in and out of the cities Aviation Technology Airport Expansion Natural land destroyed; pollution Noise Pollution Areas near airport lose value because of noise Environmental Impact on Humans Settlement Patterns People settle in an area that supports their lifestyle Ex: Fertile areas, moderate climates, adequate precipitation, proximity to water Housing Materials Housing depends on resources available Middle East: little or no forests; wood must be imported, rarely used to build Agricultural Activities Crops chosen according to what the climate will allow Certain crops need different temperatures and precipitation levels Ex: cotton, rice, sugarcane Types of Recreation Climate, land affect recreational opportunities Ex: skiing, watersports, golf Transportation Patterns Water transportation more popular in areas that can support it Natural Hazards to Humans Wind and Rain Hurricanes (in the Atlantic) Typhoons (hurricane in Pacific Ocean) Tornadoes Floods Monsoons (seasonal wind in South Asia that can bring heavy rain – flooding and mudslides) Erosion Earthquakes and Volcanoes Faults (cracks) in Earth’s surface are split by pressure from below California, Japan, Philippines are frequently in danger Use (and Misuse) of Land Deforestation—clearing forests for other uses of the land Forests filter air, provide habitats for wildlife, slow water runoff, and prevent erosion Deforestation taking place rapidly in Brazil and Malaysia Forests in North America and Europe have already been greatly reduced Desertification—destruction of the land’s fertility caused by overgrazing of goats and cattle and possibly drought Natural grasses die and are replaced by tougher plants that don’t cover soil; soil fails to hold moisture; sometimes land becomes desert Sahel region of Africa was grassland, now largely desert Water Diversion 1960s: Soviet Union diverted water toward farmland in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan Positives: stimulated cotton production Negatives: Aral Sea is drying up, rivers to it are polluted, thousands of people suffering chronic illness Aswan High Dam, Egypt, 1970: huge dam blocks flow of the Nile River in Egypt Positives--controls flooding, better navigation on lower Nile, and generate electricity Negatives: reduced silt (soft mud w/ nutrients) flow downstream, farmers now must use imported fertilizers, reduction of nutrients reduced fishing industry, parasites breed in irrigation canals Colorado River controlled by many dams Water distributed to California, Arizona, and Nevada Each state wants more water Success of cities and farms depend on good management of water Other Landscape Changes Polders *Netherlands: seawater drained from land creating 2,600 square miles (size of Delaware) of usable land *Farming, airport, housing now on these “polders” Terracing *South America, Asia (China, India, SE Asia): step-like fields are cut one above the other on sloping hillsides *Increases available farmland in mountainous regions *Reduces soil erosion Pollution Acid Rain: smoke from smokestacks, vehicle exhausts combine with water vapor and fall as acid rain o Kills fish, damages plants, makes soil useless for agriculture o Occurring mostly in Central Europe, Scandinavia, China, North America o Forests in Germany (Black Forest) and Appalachian Mountains have been badly damaged Smog: air pollution from vehicle and industries react with sunlight to form an irritant gas called ozone o Smog clouds worsen people’s breathing problems, raise cancer rates Greenhouse Effect: carbon dioxide created by vehicles and industries helps to trap the sun’s heat o Increase in world’s average temperature (global warming) o Antarctic ice melting or breaking away o Too much melting of icecaps will cause ocean levels to rise, flooding many coastal lands 1986—Chernobyl (Ukraine): nuclear accident released radioactive pollution equal to 750 atomic bombs like those dropped on Hiroshima o Area near plant is uninhabitable o Tens of thousands of lives endangered o Geographers call this a hazardscape Other hazardscapes: Oil spills—kill birds, plants, fish, makes the shoreline unusable for years (Alaska, Gulf Coast) People are continuing to put more and more pressure on the natural world