Photosynthesis Q & A
advertisement
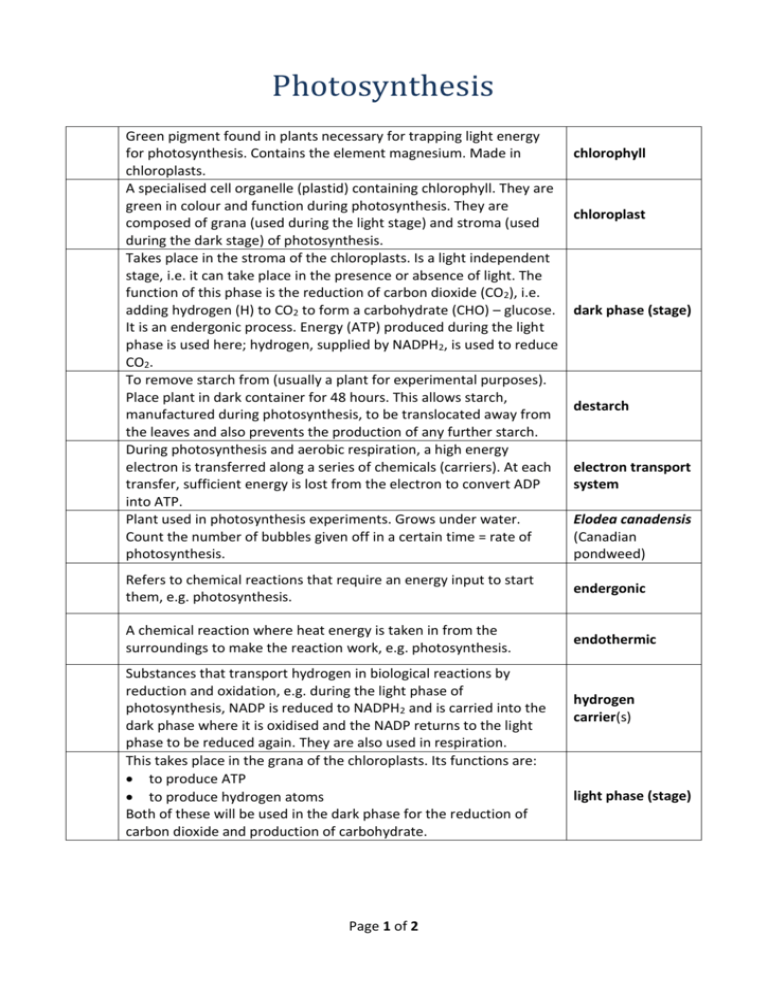
Photosynthesis Green pigment found in plants necessary for trapping light energy for photosynthesis. Contains the element magnesium. Made in chloroplasts. A specialised cell organelle (plastid) containing chlorophyll. They are green in colour and function during photosynthesis. They are composed of grana (used during the light stage) and stroma (used during the dark stage) of photosynthesis. Takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. Is a light independent stage, i.e. it can take place in the presence or absence of light. The function of this phase is the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2), i.e. adding hydrogen (H) to CO2 to form a carbohydrate (CHO) – glucose. It is an endergonic process. Energy (ATP) produced during the light phase is used here; hydrogen, supplied by NADPH2, is used to reduce CO2. To remove starch from (usually a plant for experimental purposes). Place plant in dark container for 48 hours. This allows starch, manufactured during photosynthesis, to be translocated away from the leaves and also prevents the production of any further starch. During photosynthesis and aerobic respiration, a high energy electron is transferred along a series of chemicals (carriers). At each transfer, sufficient energy is lost from the electron to convert ADP into ATP. Plant used in photosynthesis experiments. Grows under water. Count the number of bubbles given off in a certain time = rate of photosynthesis. chlorophyll chloroplast dark phase (stage) destarch electron transport system Elodea canadensis (Canadian pondweed) Refers to chemical reactions that require an energy input to start them, e.g. photosynthesis. endergonic A chemical reaction where heat energy is taken in from the surroundings to make the reaction work, e.g. photosynthesis. endothermic Substances that transport hydrogen in biological reactions by reduction and oxidation, e.g. during the light phase of photosynthesis, NADP is reduced to NADPH2 and is carried into the dark phase where it is oxidised and the NADP returns to the light phase to be reduced again. They are also used in respiration. This takes place in the grana of the chloroplasts. Its functions are: to produce ATP to produce hydrogen atoms Both of these will be used in the dark phase for the reduction of carbon dioxide and production of carbohydrate. Page 1 of 2 hydrogen carrier(s) light phase (stage) An oxidising and reducing co-enzyme necessary in photosynthesis. It traps and transfers hydrogen ions in cell activities. NADP nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate A chemical reaction in which oxygen combines with another substance. OR A reaction which involves the removal of hydrogen from a compound. OR A reaction that involves the loss of electrons. oxidation The addition of phosphorus (phosphate), i.e. ADP + P = ATP. phosphorylation The process in plants that makes food using light energy. It occurs in the chloroplasts of green plants in which carbon dioxide and water, in the presence of light energy and chlorophyll, are converted into simple sugars and oxygen. The light energy is converted to chemical energy and is stored in the sugar molecule. A chemical reaction in which hydrogen combines with another substance. OR A reaction which involves the removal of oxygen from a compound. OR A reaction that involves the gain of electrons. Emitted from the sun as electromagnetic waves . It is capable of being absorbed by the pigment chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of plant cells. Combining separate small units to form a more complex structure, e.g. elements to molecules; amino acids to proteins; monosaccharides to polysaccharides; etc. Page 2 of 2 photosynthesis reduction solar energy / radiation synthesis(e)








