Food Web & Energy Pyramid Worksheet: Ecology Activity
advertisement
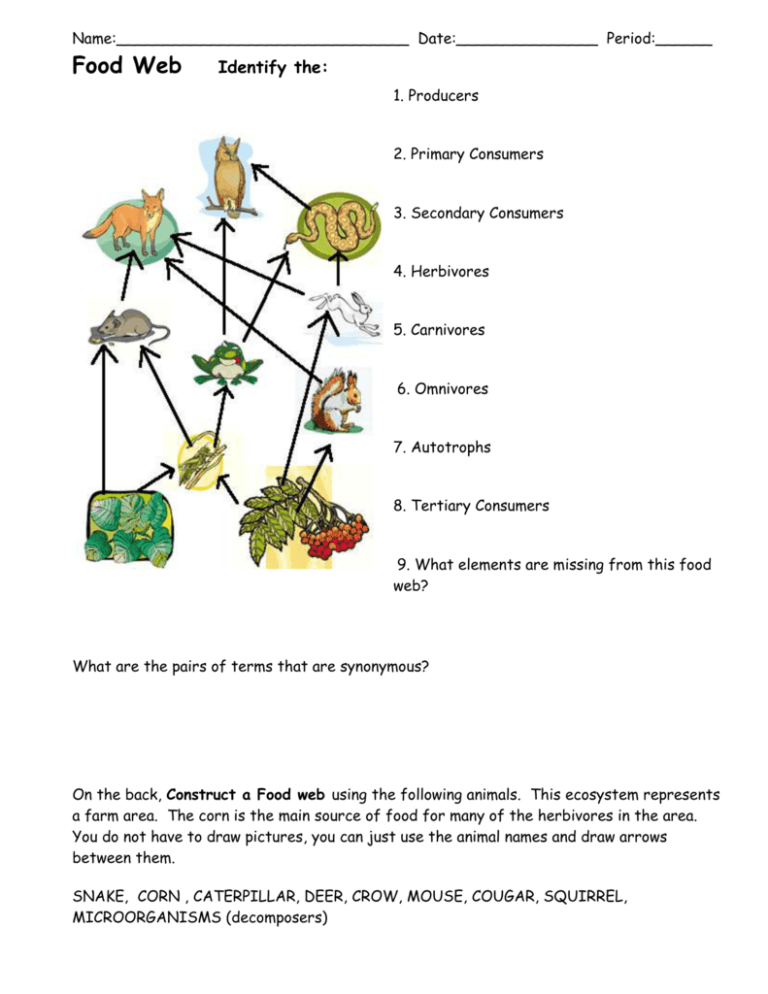
Name:_______________________________ Date:_______________ Period:______ Food Web Identify the: 1. Producers 2. Primary Consumers 3. Secondary Consumers 4. Herbivores 5. Carnivores 6. Omnivores 7. Autotrophs 8. Tertiary Consumers 9. What elements are missing from this food web? What are the pairs of terms that are synonymous? On the back, Construct a Food web using the following animals. This ecosystem represents a farm area. The corn is the main source of food for many of the herbivores in the area. You do not have to draw pictures, you can just use the animal names and draw arrows between them. SNAKE, CORN , CATERPILLAR, DEER, CROW, MOUSE, COUGAR, SQUIRREL, MICROORGANISMS (decomposers) Name:_______________________________ Date:_______________ Period:______ Constructing a Food Web and Energy Pyramid1 How is energy passed from organism to organism in an ecosystem? A food chain shows a single path for energy flow in an ecosystem. The overlapping relationships between food chains are shown in a food web. Food webs can be very complicated which makes ecological relationships very difficult to trace all the energy pathways between organisms. Ecologists have studied a low elevation meadow ecosystem and determined the dietary habits of several organisms in the community. Use the relationships below to construct a food web by first using the organism cards, then drawing the food web below. Identify the herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and detritivores (decomposers) in the food web. As a group identify community relationships (competition and predation) and whether the organism is an autotroph or a heterotroph. Once you have constructed the food web and energy pyramid, write a proof essay for the Muskrat scenario and be ready to share your analysis. Red foxes feed on raccoons, crayfishes, grasshoppers, red clover, meadow voles, and gray squirrels. Red clover is eaten by grasshoppers, muskrats, red foxes, and meadow voles. Meadow voles, gray squirrels, and raccoons all eat parts of the white oak tree. Crayfishes feed on green algae and detritus, and they are eaten by muskrats and red foxes. Raccoons feed on muskrats, meadow voles, gray squirrels, and white oak trees. Food Web 1 Adapted from Biology Glencoe Science – McGraw Hill (2007) Food Web Exercise – Member Cards Cut out each card and then arrange cards to show relationships, before drawing the web. Raccoons Red Foxes Grasshopper Red Clover Crayfishes Meadow Voles Grey Squirrel White Oak Detritus Muskrat Green Algae Constructing an Energy Pyramid2 The food web you constructed above details organism by organism energy transfers. Using the relationships shown, you will create an energy pyramid showing trophic levels and net energy transfer between levels. Practice paired reading of text (pg. 44) or RE (page 18). Before you get started on analyzing and interpreting your food web relationships, with your partner take time to go through the following examples using the OPTIC method. Recall that OPTIC stands • O is for Overview: Conduct a brief overview of the main subject of the visual. • P is for Parts: Scrutinize the parts of the visual. Note any details that seem important. • T is for Title: Read the title or caption of the visual (if present) for added information. • I is for Interrelationships: Use the words in the title or caption and the individual parts of the visual to determine connections and relationships within the graphic. • C is for Conclusion: Draw a conclusion about the meaning of the visual as a whole. Summarize the message in one or two sentences. Draw a simple food chain using information from the generalized energy pyramid. Use the diagram of the marine food web below to answer the following questions3. Which of these best describes the role of the krill in this food web? A. decomposer B. primary consumer C. producer D. secondary consumer Which of these best describes the role of the leopard seal in this food web? A. tertiary consumer B. primary consumer C. producer D. decomposer Which of these best describes the role of the phytoplankton in this food web? A. tertiary consumer B. primary consumer C. producer D. secondary consumer 2 3 http://www.mesa.edu.au/friends/seashores/energy_pyramid.html http://mdk12.org/instruction/clg/public_release/biology/G3_E5_I2.html Meadow Energy Pyramid When you are drawing your energy pyramid using the meadow food web, make sure to label the trophic levels: producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers. Draw an arrow showing the energy flow trend and relative percent available energy. What happens to the energy that is not transferred? It is lost as _______________. Analysis: The Muskrat Protection League is concerned that the muskrat population will be affected if the white oak tree disease is not controlled. Your job as the Regional Ecologist is to write a fact sheet (one paragraph proof) describing how the muskrat population would be affected if disease kills the white oak trees in the meadow. One paragraph proof consists of your answer – what you think will happen, followed by three or more sentences describing why.











