Ch 19 : Introduction to Ecology
advertisement

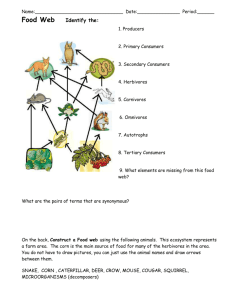
Ch 4 : Introduction to Ecology Ecology is the study of INTERACTIONS between organisms and the living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components of their environments. • Observations, data collection, explanation of trends and patterns. • Many/all areas of science – Taxonomy, biochemistry, cell type, etc. • Hunter – Gatherer societies 10,000 – 12,000 y.a. • Agricultural societies impact on Earth • Today’s exploding population > 6 billion Ecology Related Issues Think “ecosystem services” …. What service does each area do ? What job does it have ? Is it able to efficiently do that job? What is the overall impact? 1. Use of water, energy, food, space and other resources. 2. Disposal of waste is also a big issue 3. Mass extinctions – species are currently disappearing faster than dinosaurs 4. Thinning Ozone layer – related to CFC’s and pollution. Increases UV radiation 5. Green house gasses are increasing – creating global warming. Ecosystem Services • Resources that are produced by natural and artificial ecosystems…. Food we eat, oxygen we breathe, water we drink……. – – – – – – – – Purification of water and air Preservation of soil and renewal of soil fertility Prevention of drought and flood Regulation of climate Maintenance of biodiversity (food, cover, pollination) Movement and cycling of nutrients (H2O, C, N, etc) Detoxification and decomposition of wastes Aesthetic beauty ! • Biosphere : layer of Earth that supports life roughly 13 miles thick ( 7 miles into atmosphere and 7 miles down into the oceans !!!) • Ecosystems: All of the living organisms and the nonliving environment in a particular place – Biotic (all the living and once-living things) – Abiotic (physical features) • Biomes : large regions of the globe defined by similar climate and vegetation • Communities: All the living organisms that interact in a given area • Population: All the members of a given species in a defined area • Species: Organisms that are genetically similar enough to breed in nature and produce viable offspring. – Measure of biodiversity = variety of living organisms in a given area – D, K, P, C, O, F, G, Species (Scientific name) • Biotic factors: – living and once-living components in the environment - plants, animals, bacteria fungi and protista • Abiotic factors : – nonliving components in the environment; things Like wind, temperature precipitation, sunlight Succession • Change in an area’s physical features over time – new species are now better suited or less suited. Species themselves also change physical features. (needles from pine trees make the soil under the tree more acidic – different plants like acidic soil) • Primary succession – start from scratch • Secondary succession – change leads to more change leads to more change • Equilibrium Pioneer species changes climax community Energy Flow • Trophic levels….food chains and food webs – 10 % rule (Energy pyramid) • What else is the material and energy used for? • GO TO SOCRATIVE APP and answer ….. 701439 – Producers • Plants • Protista like algae – Consumers • • • • • • Herbivores Omnivores Carnivores Scavengers Decomposers Detritivores : eat detritus or ‘waste’ – crayfish chewing on dead fish is different than bacteria or fungi chemically digesting dead fish. Practice Web: Meadow • Construct the following food chains, they will overlap to create a Meadow Food Web • Identify (color code) all the herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and detritivores in the food web when you are finished 1. Red fox feed on raccoons, crayfishes, grasshoppers, red clover, meadow voles and gray squirrels 2. Red clover is eaten by grasshoppers, muskrats, red foxes and meadow voles 3. Meadow voles, gray squirrels and raccoons all eat parts of white oak trees 4. Crayfishes feed on algae and detritus and they are eaten by muskrats and red foxes 5. Raccoons feed on muskrats, meadow voles, gray squirrels and white oak trees.