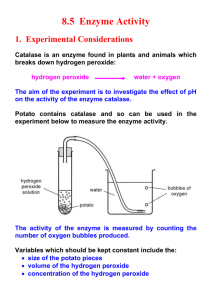
Catalase and Oxidase Test Lab Protocol
advertisement

CATALASE AND OXIDASE TEST PURPOSE: In this laboratory investigation, students will learn the steps in performing the catalase and oxidase tests. BACKGROUND INFORMATION: Catalase Test During aerobic respiration, hydrogen atoms may combine with oxygen, forming hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which is lethal to the cell. Most aerobic organisms produce the enzyme catalase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen as shown here: Catalase 2H2O2 2H2O + O2 A positive reaction is indicated by a continuous bubble formation when the hydrogen peroxide is introduced to bacterial colonies. Oxidase Test Some aerobic bacterial species contain cytochrome C, a component of the cytochrome oxidase system. When the oxidase reagent is added to a colony of bacteria containing cytochrome C, a dark blue to purple color is formed. PRELAB: 1. Research Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas fluorescens and list the colony characteristics. 2. Why does hydrogen peroxide bubble when it is poured on a skin cut? 3. Differentiate between aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. MATERIALS: Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA) plate with 18 – 24 hour growth of the following bacteria:. Staphylococcus aureus Pseudomonas fluorescens 3% Hydrogen Peroxide Microscope slides Oxidase reagent (6% tetramethylphenylenediamine hydrochloride in dimethyl sulfoxide) Eye dropper Inoculating loops PROCEDURE: Preparation-DAY 1 1. Wash hands and put on gloves and goggles. 2. Assemble equipment and materials. 3. Prepare work area. 4. Prepare 2 TSA plates 5. Streak each organism on individual plates, parafilm the sides and incubate the plate, inverted at 35°C for 24 to 48 hours. Catalase procedure: DAY 2 1. Flame and cool the inoculating loop. 2. Place a small amount of a bacterial colony (18 to 24 hours old) on a clean glass slide. 3. Flame and cool the inoculating loop. 4. Add one to two drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide. 5. Record observations: Positive: Rapid bubble formation Negative: No bubble formation 6. Dispose of the slide in the bleach solution 7. Petri dishes can be placed in the biohazard bag. Oxidase procedure: 1. Flame and cool the inoculating loop. 2. Place a small amount of a bacterial colony (18 to 24 hours old) on a clean glass slide. 3. Place one drop of oxidase reagent on the colony 4. Observe for color change: Positive: blue to dark purple color Negative: no color change 5. Dispose of the slide in the bleach solution 6. Clean work area with surface disinfectant. Remove goggles and gloves and wash hands. DATA: Record the results of your testing in a chart in your lab journal. CONCLUSION: Write an analysis of the lab in your lab journal. What do your results tell you?