Lesson Plans
advertisement

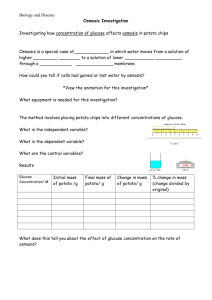
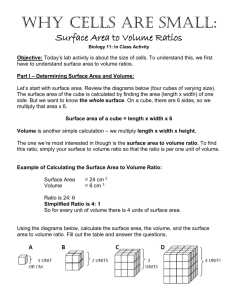
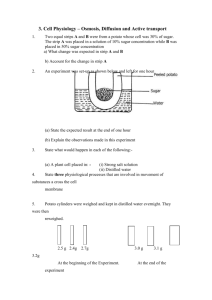
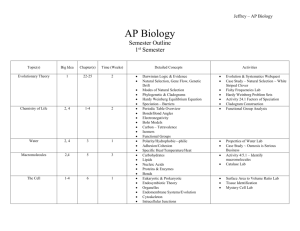
Science Pull-out Programmes Enhancing Analytical Thinking Skills through Scientific Enquiries Lesson 1, 2 and 3 (60 min. x 3) Level of Students: S.2 and S.3 Duration of Lessons: 3 hours Specific Objectives: Students should be able to (i) Students should be able to enhance self-analytical skills through the investigation of using the osmotic potential of potato and beet root. (ii) use logic and evidence to formulate scientific explanations and models to explain how water molecules pass through cell membranes during osmosis. Materials and Apparatuses for each group: (a) 1 Cork borer (b) Fresh potatoes and beet root (c) Beakers (d) Salt solution A (20 g sodium chloride in 1 L water = 0.02 g/mL) (e) Salt solution B (100 g sodium chloride in 1 L water = 0.1 g/mL) (f) Glucose solution (100 g glucose in 1 L water = 0.1 g/mL) (g) Salt solution Y (unknown salt concentration) (h) Petri dishes x 4 (i) Water (j) Stop watch or timer Prior knowledge of students: As students may mix up the structure cell wall and cell membrane, the teacher can ask a few simple questions about the cell structure and cell functions to consolidate their concept. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osmosis#Examples_of_osmosis Suggested Learning and Teaching Activities: Time allocation Remarks 5 min. Example of osmosis: Lesson 1 (60 min) Teacher uses an example of osmosis to motivate students to think about the movement of water from and into cells. - Roots of plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis. - A freshwater fish will die in high salinity water. Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osmosis#Examples_o f_osmosis Teacher discusses the basic features of a plant and animal cell with students. 10 min Teacher briefs the students the objectives of the 45 min investigation on the movement of water across the plants cells (potato and beet root). Teacher asks the students to discuss the methods to perform the investigation and compare the effect of osmosis in potato and beet root. This experiment focuses on enhancing analytical thinking skills of students (process skill). The terms isotonic, hypotonic, hypertonic may be difficult for many students, hence it is better to introduce these terms after the experiment. Osmosis can simply be introduced to students as a movement of water from and into cells. Students are required to use a mind map to answer the 'what', 'why' and 'how' questions relating to the scientific enquiry so as to work out an agreed experiment procedure. Students are encouraged to challenge others thoughts based on the scientific knowledge. Relevant questions may include: What would happen if the potato / beet root is immersed in water, salt solution or sugar solution? Students are required to predict the results. How should the experiment be started? What treatment should be done to the potato strips? How to cut identical potato strips? How to measure the strips? What variable should be kept constant? How the time should be measured? What data should be taken? What should be the result table looked like? How is the control set-up? One potato strip or more? Division of labour? Students are invited to present their mind maps and work flow. Other students may criticise and make suggestions. The teacher concludes the experimental design after the presentations. Lesson 2 (60 min) 1 hour Students’ presentations should include observation, result (How to plot the graph? Scaling? Extrapolation?), data interpretation, conclusion, source of error, and recommendation to modify the experiments. Students are required to present their data and results. 45 min. (10 min. for each group) All agree? Questions and further suggestion? Pool class data? Use of excel? Experimental technique? Teacher comments on students’ presentation and concludes the activity on osmosis. 15 min. Through this activity, students should focus more on the process skills needed in Students are required to perform the experiments in groups - record the result, analyze the data collected and discuss among themselves the conclusion, possible source of error and suggestion to improve the experimental design. Students are required to find out the concentration of the unknown solution. Lesson 3 (60 min) the experimental design, data analysis and interpretation, and drawing conclusion based on the evidence. Extension for very highly able students Assignme nt or activity (1-2 hours) More able students are encouraged to study the concepts of the terms Isotonic, hypertonic and hypotonic through researching in the library and on the Internet. They are also required to write a summary about these terms.