The effects of solution concentration on osmosis in carrot rings
advertisement

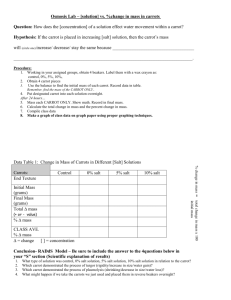
THE EFFECTS OF SOLUTION CONCENTRATION ON OSMOSIS IN CARROT RINGS Plant cells respond differently based on the types of solutions that surround their cells. Hypotonic solutions have fewer particles in the solutions than found in the cells so the cells take in water. Hypertonic solutions have more particles in the solution than in the cells so the cells lose water. Cells in an isotonic solution have the same concentration of particles in the cells as the solution so cells tend to remain the same size. Cells placed in a hypotonic solution swell and shrink in a hypertonic solution. In this lab you will determine the concentration of sucrose that is hypertonic, isotonic, and hypotonic for carrot cells. Procedure 1. Obtain 6 dixie cups put your groups’ names on the cups and label one of each cup 0, 0.2 M, 0.4 M, 0.6 M, 0.8 M, and 1.0 M. Place approximately 25 to 30 mL of each of the sucrose solutions into the cups. 2. Take 6 carrot rings of approximately the same size that have been pithed and a small section of the arc of the ring has been removed. On the outside edge of the carrots, measure the portion of the arc that is missing in millimeters. Record the missing arc for each carrot in the table. Carrot ring Measure distance sides are apart at edge 1 2 3 3. Place one carrot ring into each of the dixie cups with solution. Allow the rings to remain in solution for 24 hours. 4. After 24 hours, measure the arc of the missing section for each carrot in millimeters. Record your results in the table. 5. To calculate the change in the carrot rings, subtract the final arc measurement from the original measurement. Calculate the percent change for each ring. Change in carrot ring arc = final arc - original arc Percent change in carrot ring arc = change in carrot ring x 100 Original arc Sucrose Solution Concentration 0 0.2 M 0.4 M 0.6 M 0.8 M 1.0 M Original arc (mm) Final arc (mm) Change in arc Percent (mm) change Below, graph the percent change in the missing arc versus the concentration of sucrose. 1. What are the independent and dependent variables in this experiment? 2. Based on your findings, which sucrose solutions are hypertonic in relation to the carrot rings? 3. Which are hypotonic? 4. What solution in this lab is closest to an isotonic solution? 5. Use your graph to predict the molarity of sucrose that produces an isotonic solution for carrot cells? 6. Which molecules are moving into or out of the carrot cells? 7. What is the name of this process? 8. How does osmosis compare to simple diffusion? 9. Suppose the carrot ring on the left is in a 0.1 M solution. Draw the concentration of particles you would expect on the inside and outside of the cells. What kind of solution is this? What is happening to the cells? 10. Suppose the carrot ring on the left is in a 2.0 M solution. Draw the concentration of particles you would expect on the inside and outside of the cells. What kind of solution is this? What is happening to the cells?