Chatfield Citation Guide
advertisement

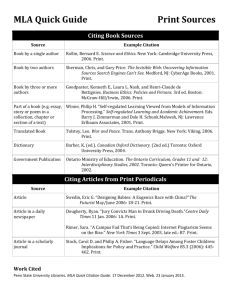
. Citing Internet Sources Chatfield Senior High School When you are citing information from a website, the site should be high quality. This means that you should evaluate a website for validity, relevance, currency, and authority. Avoid sites that end in .com. Look for sites that come from reputable sources. These sites usually end in one of the following; .edu, .gov, or .org. Website: Site Title. Last date updated day month year. Producers. Visitation day month year. URL address. Examples: The 100 Most Frequently Challenged Books of 1990-2000. 3 April 2003. American Library Association. 15 April 2004. <http://www.ala.org/ala/oif/bannedbooksweek/bbwlinks/100mostfrequently.htm> Helpguide: Fast Food Nutrition/Healthy Restaurants. 10 June 2004. Rotary Club of Santa Monica and Center for Healthy Aging. 24 May 2005. <http://www.helpguide.org/aging/fast_food_nutrition.htm>. If you use databases, the citations are already there!! Citing Other Sources Television or Radio Program “Subtitle of show.” Main title of show. Network. Local Network, City. Day Month Year. Example: “Greece behind in Summer Games.” 60 Minutes. CBS. KCNC, Denver. 11 April 2004. Video or DVD Title. Videocassette or DVD. Production Company, Date. Example: Of Mice and Men. Videocassette. MGM/ United Artist. 1992. Film Title. Dir.(Director) First and Last Name. Perf. (Performers) Production Company, date. Example: The Green Mile. Dir. Frank Darabont. Perf. Tom Hanks, David Morse, Bonnie Hunt, Michael Clark Duncan. Castle Rock Entertainment, 1999. Map or Chart Title. Map or Chart. City: Publisher, date. Example: The Heart of the Grand Canyon. Map. Washington Nation Geographic Society, 1978. Style Guide for Citing Resources CHS uses the citation format resources found in Writers, Inc.: A Student Handbook for Writing and Learning (2001) which is based on the Modern Language Association (MLA) style. The information contained here is based on the citations and definitions found in this addition and are meant to be used as a quick reference. It is your responsibility to cite sources in your research paper to give credit to those individuals considered to be experts in the field of study that you are researching. In a sense you are borrowing their expertise to gain knowledge, so you must give them credit. Not citing the source and using the expert’s information is called plagiarism and is illegal. In addition, citing your sources will show that you know how many sources you have referred to in order to complete your assignment. Looking at a number of sources instead of just one or two will allow you to develop a well-rounded paper. Finally, citing your resources will allow others to find additional information about their topic if they are interested in further study. If you need further help… The following are sources that can help you with citation examples that are not given here: Citation Machine http://citationmachine.net/ OWL Online Writing Lab - Purdue University http://owl.english.purdue.edu/handouts/research/r_mla.html Writers Workshop - University of Illinois http://www.english.uiuc.edu/cws/wworkshop/writer_resources/citation_st yles/mla/mla.htm If you use databases, the citations are already there!! Citing Articles The following examples give the format first, then an example of how the format is used. Please pay careful attention to how the citation is punctuated and underlined. Citing Book Sources Books with one author: Author’s Last name, First name. Title. City: Publisher, copyright. Example: Zienert, Karen. Those Incredible Women of World War II. Brookfield: Millbrook Press, 1994. Books with two or three authors: First author’s Last name, First name. and the second author’s first name last name. Title. City: Publisher, copyright. Example: Estell, Doug, Michele L. Satchwell and Patricia S. Wright. Reading Lists for College-Bound Students. 2nd Ed. New York: Macmillan, 1993. Books with more than three authors: This citation adds the phrase et al. which means and others. Author’s Last name, First name, et al. Title. City: Publisher, copyright. Example: Webster, Christopher, et al. Autism. New York: Pergamon Press, 1980. "Pyrrho." The Encyclopedia Americana. International ed. 1995. With author identification: Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of the article”. Title of the reference book. Edition number. Copyright. Examples: Augee, Michael. “Kangaroo”. World Book. 2002. Pettigrew, Thomas F. "Racism" The World Book Encyclopedia. 1998 ed. An article from a periodical (magazine): Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of the article”. Title of the magazine. Edition number. Publication date: page numbers. Examples: Hoffer, Richard. “Golden Oldie”. Sports Illustrated. Vol. 100, No. 14. April 5, 2004: 30-32. Gorn, Heather. “Fast Food Update”. Vegetarian Journal. Vol 24, No. 1. Jan-Feb 2005: 28-30. Books with an editor: This adds the phrase ed. which stands for editor Editor’s Last name, First name, ed. Title. City: Publisher, copyright. Example: Lanier, Robert, ed. The Photographic History of the Civil War: Armies and Leaders. New York: Fairfax Press, 1983. A single work from an anthology: Use the name of the author of the single piece you chose and then the editor after the title of the anthology. Author’s Last name, First name. “Title of the piece”. Title of the anthology. Editor. Edition Number of the anthology if appropriate. City: Publisher, copyright. Example: O’Neill, June. “ Poverty: Programs and Policies.” Thinking About America: The United States in the 1990’s. Annelise Anderson and Dennis L. Bark eds. Stanford: Hoover Institution Press, 1988. An article in a reference book without an author identification: “Title of the article”. Title of the reference book. Edition number. Copyright. Examples: “Cleopatra I”. Britannica. 15th Edition. 1993. An article from a newspaper: “Title of the article”. Title of the newspaper [city of publication] day Month year, Section: page. Examples: “Panel Oks College Voucher Bill”. The Denver Post [Denver] 15 April 2004, Sec. B: 2. “Restaurant Sales Climb With Bad-For-You Food”. USA Today 13 May 2005, Sec. A: 1. An article from a database service such as Gale Student Resource Center Gold, WorldBook, CQ Researcher, Culturegrams etc… “Title of the article”. Name of the source. Online. Database Host, Visited Date. Examples: “WTC Memorial Finalist; All 8 Designs Use Footprints of Twin Towers”. The Washington Times. Online. Infotrac Student Edition. Visited April 15, 2004. Henderson, Shirley. “Snack Attack: Replacing Junk Food With Nutritious Alternatives.” Ebony. April 2005, 60 :118-121. Gale Student Resource Center Gold. Chatfield Sr. High Library. 24 May 2005. <http://galenet.galegroup.com>.