Movements/Characteristics/ Media: An Organizational Worksheet
advertisement
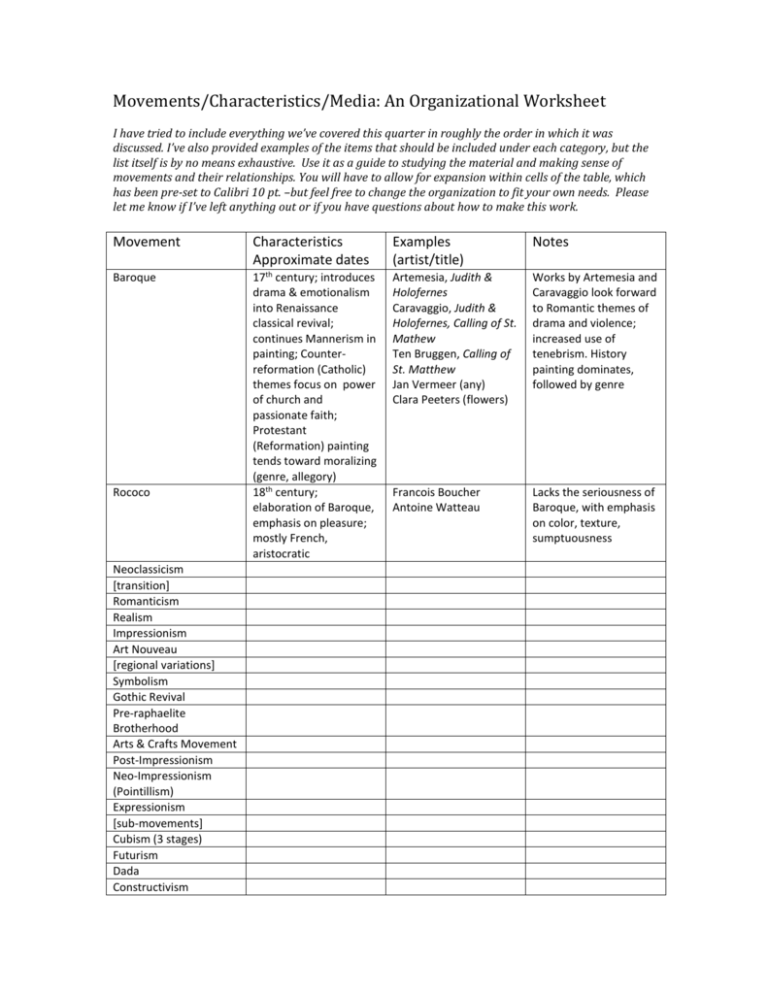
Movements/Characteristics/Media: An Organizational Worksheet I have tried to include everything we’ve covered this quarter in roughly the order in which it was discussed. I’ve also provided examples of the items that should be included under each category, but the list itself is by no means exhaustive. Use it as a guide to studying the material and making sense of movements and their relationships. You will have to allow for expansion within cells of the table, which has been pre-set to Calibri 10 pt. –but feel free to change the organization to fit your own needs. Please let me know if I’ve left anything out or if you have questions about how to make this work. Movement Characteristics Approximate dates Examples (artist/title) Notes Baroque 17th century; introduces drama & emotionalism into Renaissance classical revival; continues Mannerism in painting; Counterreformation (Catholic) themes focus on power of church and passionate faith; Protestant (Reformation) painting tends toward moralizing (genre, allegory) 18th century; elaboration of Baroque, emphasis on pleasure; mostly French, aristocratic Artemesia, Judith & Holofernes Caravaggio, Judith & Holofernes, Calling of St. Mathew Ten Bruggen, Calling of St. Matthew Jan Vermeer (any) Clara Peeters (flowers) Works by Artemesia and Caravaggio look forward to Romantic themes of drama and violence; increased use of tenebrism. History painting dominates, followed by genre Francois Boucher Antoine Watteau Lacks the seriousness of Baroque, with emphasis on color, texture, sumptuousness Rococo Neoclassicism [transition] Romanticism Realism Impressionism Art Nouveau [regional variations] Symbolism Gothic Revival Pre-raphaelite Brotherhood Arts & Crafts Movement Post-Impressionism Neo-Impressionism (Pointillism) Expressionism [sub-movements] Cubism (3 stages) Futurism Dada Constructivism Suprematism De Stijl/Neoplasticism Bauhaus Surrealism Abstract Expressionism (2 variations) Post-painterly Abstraction Pop Art Superrealism Neo-Expressionism Feminist Art Environmental Art (Land Art) Influences from Elsewhere/when Characteristics/Descriptions Examples/Movements Notes Exoticism Interest in the exotic originates in from late Medieval and Renaissance travels (crusades, pilgrimage, trade) and increases as Capitalism rises. Napoleon’s expedition to Egypt, wars, colonialism all bring new objects and ideas into European markets 19th century archaeological expeditions increase interest in very ancient Greece & Mesopotamia Medievalism Japonism/Orientalism Primitivism Harem girls/Odalisques Ingres Grand Odalisque (Neoclassicism/Romanticism) Delacroix Algerian Women (Romanticism) Renoir Algerian Woman (Impressionism) Exotic locales Gros Napoleon Visiting Jaffa (Romanticism) Gauguin Tahitian & Breton paintings (Post-Impressionism) The following table is designed to help you distinguish how various media were interpreted within particular movements. Technologies/ Techniques/Media Associated Movements Examples Notes Prints (etchings, woodblocks, lithographs, posters) Impressionism Art Nouveau Post Impressionism Prints: Mary Cassat Posters: Klimt, Olbrich Posters, Chromolithographs: Toulouse Lautrec Edo period woodblock prints favored by many movements in the 19th century; inspire new perspectives, flat surfaces, simplified compositions Photography Realism Romanticism PRB Gothic Revival Romanticism Architecture Sculpture









