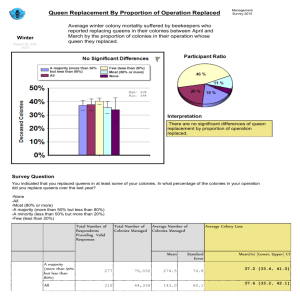
colonization_answers
advertisement

Correct Answers for European Exploration and Colonization Study Guide 1. What did exploration and colonization initiate or begin? 2. What products were exchanged between the Americas and Europe? 3. To what ideas did European colonization in the Americas eventually lead? 1. worldwide commercial expansion or trade 2. agricultural products 3. ideas of representative government and religious toleration that were later copied in other parts of the world 4. that one accepts another person’s religion, even though it is different 5. climate, soil conditions, and other natural resources 6. Africans 4. What does religious toleration mean? 5. What factors shaped regional economic differences in the American colonies? 6. What large group of immigrants to the New World came involuntarily? 7. Why did the Puritans settle New England? 8. Define the term Puritans. 7. They were seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe. 8. Englishmen who believed the Anglican Church should purify or cleanse itself by abandoning its ritual and ceremony. 9. Church of England 9. What was another name for the Anglican Church? 10. Who were the Pilgrims? 11. Where did the Pilgrims settle? 12. What is a covenant? 13. What was the Mayflower Compact? 10. a group of extreme Puritans 11. Plymouth, Massachusetts 12. a promise or agreement 13. an agreement signed by the male passengers on the Mayflower to respect laws agreed upon for the general good of the colony 14. Puritans 14. Who founded the Massachusetts Bay Colony? 15. What basic unit of settlement was used by Puritan church congregations in the Massachusetts Bay Colony? 16. What is the historical significance of the Puritan town meetings? 17. Explain how direct democracy worked at New England town meetings. 15. the town 16. In these town meetings the Puritans practiced a form of direct democracy. 17. Each member of the Puritan church could vote at town meetings and thereby participate directly in making the laws for that town. In other words, each Puritan church member helped make the laws for their town. 18. Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Connecticut, and Rhode Island 19. direct democracy in ancient Athens; the “Athenian” direct democracy model 18. Name the four New England colonies. 19. What ancient model did New England town meetings follow? 1 20. What were the two major reasons why the Puritans settled in New England? 21. What European groups chiefly settled the Middle Atlantic region? 22. Why did European immigrants settle in the Middle Atlantic region? 23. What served as the major reason for the settlement of Virginia and the other Southern colonies? 24. Who were the Virginia “cavaliers”? 20. religious freedom and economic opportunity 21. English, Dutch, and Germans 22) religious freedom and economic opportunity 23. economic opportunity 24. English nobility, who received large land grants in eastern Virginia from the King of England 25. Small farmers or artisans; they settled in the Shenandoah Valley or western Virginia 26. skilled craftsmen 27. people who agreed to work for a master for a fixed period of time in order to pay for passage to the New World 28. poor people from England, Scotland, and Ireland 29. Jamestown; 1607 25. What was the occupation of many poor English immigrants to Virginia and in what part of the colony did many of them settle? 26. Define the term artisans. 27. Define the term indentured servant. 28. Who were these indentured servants and from where did they often come? 29. What was the first permanent English settlement in North America, and when was it settled? 30. What was the Virginia House of Burgesses, and why was it important? 31. What has been the name of Virginia’s lawmaking body, since independence from Great Britain? 32. What regions of the Western Hemisphere did the Spanish explore and settle? 33. How did European colonization affect the American Indians? 30. Virginia’s lawmaking body; it was the first elected assembly in the New World 31. the General Assembly 32. the Caribbean, Central America, and South America 33. 1) Violent conflicts, 2) Indians lost their land, 3) Indians died of European diseases like smallpox 34. Canada 34. What region of the Western Hemisphere did the French explore? 35. How did the effects of French exploration differ from those of English exploration? 36. What institution was introduced into the New World as a result of the agricultural economy which developed in the Southern colonies and the Caribbean Sea? 37. What was the result of European 35. 1) no large-scale immigration from France, 2) French had better relations with the Indians 36. African slavery 37. Europeans forced millions of Africans 2 introduction of African slavery in the New World? 38. What were the three regions of English settlement along the Atlantic coast? 39. What formed the economic basis of colonial New England? to come to the Americas against their will. 38. 1) New England colonies, 2) the middle colonies, 3) the Southern colonies 39. shipbuilding, fishing, lumbering, smallscale subsistence farming, and eventually, manufacturing 40. growing only enough food to feed one’s family 41. Puritans’ strong belief in hard work and thrift 40. Define subsistence farming. 41. What Puritan values were reflected in the prosperity of the New England colonies? 42. Name the middle colonies. 42. New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware 43. shipbuilding, small-scale farming, and trading 44. New York and Philadelphia 43. What formed the basis of the middle colonies’ economy? 44. What two cities in the middle colonies began to grow as seaports and commercial (trade) centers? 45. What was the basis of the economies in the eastern coastal lowlands of Virginia and the other Southern colonies? 46. What are Virginia’s eastern coastal lowlands called? 47. Name the Southern colonies. 45. large plantations that grew cash crops (tobacco, rice, and indigo) for export to Europe 46. Tidewater 47. Virginia, Maryland, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Georgia 48. tobacco 48. What was the case crop of colonial Virginia? 49. What were the two cash crops of colonial South Carolina? 50. What formed the basis of the economy of the Southern colonies in the mountains and valleys of the Appalachian foothills? 51. What strong belief regarding property rights was shared by all the English colonies in North America? 52. What two labor systems supplied the labor needs of the plantation economy which developed in the Southern colonies? 53. What was the origin of most of the indentured servants in colonial America? 54. Where and when did the first Africans arrive in colonial America? 55. What is believed to have been the legal status of the first Africans brought to the New World? How did the status of 49. rice and indigo 50. subsistence farming, hunting, and trading 51. a strong belief in private ownership of property and free enterprise 52. indentured servants and African slaves 53. poor people from England, Scotland, or Ireland 54. Jamestown; 1619 55. indentured servants; over time Africans were treated as “servants for life” and later slaves 3 Africans change over time? 56. Define the term Middle Passage. 56. the cruel and inhuman transportation of African slaves by ship from Africa to the New World 57. the African slave trade and a slave labor system 57. What two developments resulted from plantation economies and labor shortages in the English colonies? 58. Eventually what war was caused by the development of a slavery-based agricultural economy in the Southern colonies? 59. What served as the basis of society in colonial New England? 60. What was the Puritans’ attitude towards religious dissenters? 58. the American Civil War 59. religious standing 60. grew increasingly intolerant of (prejudiced against) dissenters who challenged Puritan beliefs 61. people who disagree with the dominant religion 62. Roger Williams; to flee persecution by Puritans in Massachusetts 61. Define the term religious dissenters. 62. What dissenter founded the colony of Rhode Island, and why did he start a new colony? 63. What religious groups settled in the middle colonies and in which colony did each group settle? 64. Who were the Huguenots? 65. What religious groups generally believed in religious tolerance? 66. What socio-economic class developed in the middle colonies and in what ways did members of this class earn a living? 67. Define the term entrepreneur. 68. What formed the basis of the social structure in Virginia and the other Southern colonies? 69. Who dominated the colonial government and society in the Southern colonies? 70. What was the most important church in Virginia and the other Southern colonies? 71. Which region of the American colonies generally maintained stronger ties with Great Britain: the Southern colonies, the New England colonies, or the middle colonies? 72. Who played leading roles in the colonial legislatures of the Southern colonies? 63. Quakers in Pennsylvania; Presbyterians in New Jersey; Jews and Huguenots in New York 64. French Protestants 65. Quakers, Presbyterians, Huguenots, and Jews 66. a middle class of skilled artisans, entrepreneurs, and small commercial farmers 67. business owners 68. family status and land ownership 69. Large landowners 70. the Church of England 71. the Southern colonies 72. planters 4 73. Who made up society in the mountains and valleys of the inland South? 73. small subsistence farmers, hunters, and traders of Scots-Irish and English background 74. Define the term Scots-Irish. 74. Scottish Protestants, who settled in the northern part of Ireland as part of England’s effort to control Ireland 75. What was the “Great Awakening”? 75. a religious movement that swept both Europe and the colonies during the mid1700s 76. Who was the major leader of the “Great 76. George Whitefield Awakening”? 77. What two Protestant denominations 77. Baptists and Methodists experienced rapid growth as a result of the “Great Awakening”? 78. How did the “Great Awakening” relate 78. It laid one of the social foundations for to the American Revolution? the American Revolution, because it had challenged the existing religious and governmental order in the various colonies. 5