Engineering Glossary: Manufacturing Processes & Materials
advertisement

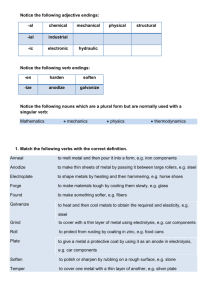
Glossary (1) Engineering the speed at which a manufacturing step is carried out Rate process: Transfer process: a manufacturing process which takes laboratory tastes and applies them to a practical application. Hydraulics: a branch of science that deals with practical applications of water in motion. Annealing: make materials tough by cooling them slowly e.g. glass (ανόπτηση) Anodize: to coat a metallic surface with a protective oxide (car components) ανοδίωση Electroplate: to cover with a thin layer of metal using electrolysis e.g. car components. (Επιμεταλλώνω δια ηλεκτρισμούεπικαλύπτω). Forge: shape metals by heating and then hammering e.g. horse shoes (επεξεργάζομαι μέταλλο -forged σφυρήλατος) Found: to melt metal and then pour it into a form e.g. iron components. ( τήκω- χύνω μέταλλο) Galvanize: to protect from rusting by coating in zinc e.g. food cans Grind: to polish or sharpen by rubbing on a rough surface e.g. stone Harden: to make a material strong e.g. steel (βάφω χάλυβα) Mint: to make a metal piece by stamping e.g. coins Plate: (επιμεταλλώνω ) to cover one metal with a thin layer of another e.g. silver plate Roll: to make flat by pressure applied by a roller e.g. make thin sheets of steel by passing it between large rollers(κυλίνδρωση) Soften: to make sth softer e.g. fibres(μαλακώνω) Temper: to heat and then cool metals to obtain the required hardness and elasticity e.g. steel (ανόπτηση, βάψιμο μετάλλου, σκλήρυνση) Tinplate: to cover a metal with a thin layer of tin e.g. food cans Petrochemical: a chemical derived from petroleum or natural gas