PS7 - Cornell
advertisement

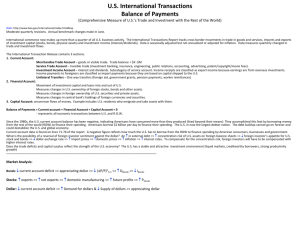
Economics 102 Introductory Macroeconomics Spring 2004, Professor J. Wissink Problem Set 7 NOT DUE, but DO before the final. Multiple Choice 1. Which one of the following will increase the price of the US dollar relative to the Mexican peso? A) An increase in the demand for dollars. B) An increase in the supply of dollars. C) An increase in the demand for pesos. D) All of the above. 2. Consider monetary policy with flexible exchange rates. Assume that the economy is below full employment and the Fed decides to expand the money supply through open market purchases of U.S. government securities. Which one of the following is true? A) This results in an increase in the interest rate. B) A relatively lower interest rate in the U.S. means a higher foreign demand for U.S. securities. C) The quantity of dollars demanded increases. D) A cheaper dollar further stimulates the domestic economy. 3. Imports A) supply us with foreign exchange, and thus they are registered as a credit item in the balance of payments current account. B) supply us with foreign exchange, and thus they are registered as a debit item in the balance of payments current account. C) cause foreign exchange to leave the country, and thus they are registered as a debit item in the balance of payments current account. D) cause foreign exchange to leave the country, and thus they are registered as a credit item in the balance of payments current account. 4. Which one of the following IS NOT included in the current account? A) Exports of services. B) The change in U.S. government assets abroad. C) Net investment income. D) Net transfer payments. E) Imports of goods. 5. More German companies start to invest in the United States. This will lead to A) a decrease in the demand for dollar and a stronger dollar. B) an increase in the demand for dollars and a stronger dollar. C) a decrease in the supply of euros and a stronger dollar. D) an increase in the supply of dollars and a weaker dollar. 6. A high rate of inflation in one country related to another puts pressure on the exchange rate between the two countries, and there is a general tendency for the A) demand schedule of the citizens of the low-inflation country for the high-inflation country’s currency to shift rightward. B) demand schedule of the citizens of the high-inflation country for the low-inflation country’s currency to shift leftward. C) currency of the relatively high-inflation country to appreciate. D) currency of the relatively high-inflation country to depreciate. Short Questions 1. Explain how the following situations affect the United States' balance of payments. a. b. c. d. A U.S. defense contractor sells its consulting services to a company in France. Your investment club decides to buy 100 shares of a promising Korean automobile manufacturer. A consortium of European investors decides to build a large manufacturing facility in Montana. You are from India and you and your parents decide to send you to Cornell. 2. Identify whether each of the following would lead to an appreciation or depreciation of the dollar. In each case, explain why the currency either appreciates or depreciates. a. U.S. citizens switch from buying stock in British companies to buying stock in U.S. companies. b. The inflation rate in the United States increases relative to the inflation rate in England. c. The money supply is increased in the United States. d. Income in the United States increases. 3. Suppose an economy is represented by the following equations: C = 300 + 0.6Yd I = 400 G = 1,000 EX = 400 IM = 0.1Yd Yd = Y-T T = 1,000 a. b. c. d. Find Y* for this economy. Find the value of the government multiplier. What is the value of this economy’s current account in its balance of payments? Without using any explicit numbers, how would a sudden depreciation of the dollar alter Y*? 4. During 1981 and 1982, the president and the Congress were pursuing a very expansionary fiscal policy. In 1980 and 1981, the Federal Reserve was pursuing a very restrictive monetary policy in an attempt to rid the economy of inflation. Ultimately, the economy went into a deep recession, but before it did, interest rates went to record levels. a. Explain how this policy mix led to very high interest rates. b. Show graphically the effect of the high interest rates on the foreign exchange market. What do you think would happen to the value of the dollar under these circumstances? c. What impact was such a series of events likely to have on the trade balances in countries like Japan?