Unit 5.doc - Economics11thgrade
advertisement

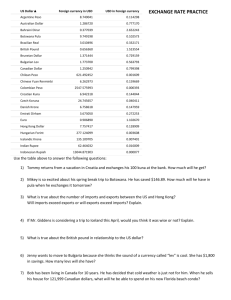
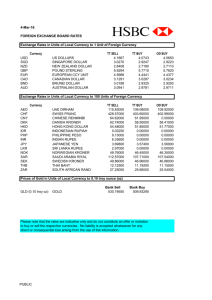
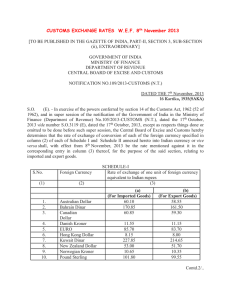
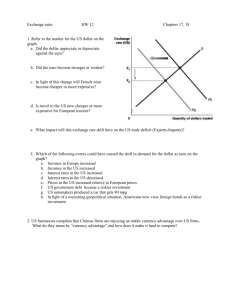
Trading with Other Nations Benefits of Trade -Creates Jobs (when new export industries are created or expanded) -Cheaper (goods created through competition from imported goods) -Efficient use of Resources (specialization) Absolute Advantage-country produces more US Canada Total Shoes Shirts 100 80 180 80 75 155 Comparative Advantage-a country can produce a product at a lower opportunity cost. Example Lance Armstrong Country Wheat Fruit x 100 bags 100 boxes y 1 bag 50 bags Countries will not trade unless a comparative advantage exists. Foreign exchange rate The value of one countries currency in relation to another country’s currency. Fixed-tied to a stable currency like the dollar. (Called hard currency) Floating-based on supply and demand Value of dollar is based on demand for U.S. goods and services Marginal Floating-central bank controls the value if it gets too low or too high. BIG MAC In local IN US US BRAZIL (rael) China (Yen) Mexico (peso) 2.49 3.60 10.50 21.90 2.49 1.55 1.27 1.25 Pricing Country US$ Australia .6478 Brazil .5299 Japan (yen) .00905 Currency 1.5438 1.8870 111.06 Strong vs weak 1.00 US dollar .67 Euro 1.00 US dollar to 86.43yen 1.00 US dollar to 80.00 yen Strong dollar means we import more, our dollar buys more. Makes our trade deficit go up because we are buying more imports. Our dollars leave the US and going to foreign countries. Creates a trade deficit. Because foreign countries have more US dollars they are able to invest more in the US. Balance of Trade- deals with Imports and Exports. How much we are selling and buying. Balance of Payments- deals with imports and exports and money being invested back into the country. Weak Dollar Export more-foreign currency buys more US goods Dollars stay in US Creates trade surplus Because foreign countries have fewer US dollars they invest less. BARRERS TO TRADE Tariffs-taxes that increase the price of imports. Quotas-limits the number of specific goods that can enter the country. Embargo-refusal to trade goods. Standards-all goods must meet certain standards to enter a country. FREE TRADE VS PROTECTIONISM Free Trade-allows for trade without barriers. Protectionism-puts in place. (Protecting US companies) Job security (outsourcing of jobs) Economic Security (depending on other countries put us at a disadvantage) Infant or new Industries (starting new industries is expensive, can’t compete easily) FREE TRADE Improved products (competition makes us better.) Lower prices due to specialization and comparative advantage. Helps exporters (if we place restrictions, what will foreign countries do to us.) GATT-Bilateral agreement WTO-world trade organization NAFTA-north American Free Trade Agreement CAFTA-Central American Free Trade Agreement ASEAN-association south East Asian EU-European union