Pericles` three goals for athens
advertisement

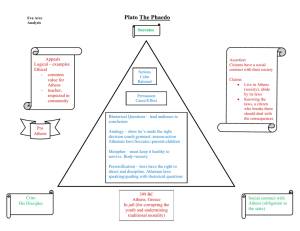
histo notes on the greeks 2 10/21/2010 10:53:00 PM Topic: Ancient Greece- the golden age Time: ca. 480-430 BCE Place: Athens and it colonies Concept: golden age; empire Big Question: How does Athens illustrate the greek principle that hubris leads ate? HUBRIS: ARROGANCE Arachne boasts that she can weave better then Athena and then Athena because of her hubris she gets turned into a spider ATE: RUIN, DOWNFALL GOLDEN AGE: a time when everything is flourishing (really good) in a particular society Pericles’ three goals for athens Pericles led Athens to its golden age 461- 429 BCE 1. To strengthen Athenian democracy 2. To hold and strengthen the empire 3. To glorify Athens Stronger Democracy he increased amount of paid public officials maid more salaries poorest could now serve in politics these reforms made Athens one of the most democratic states in history DIRECT DEMOCRACY- when citizens rule through themselves and not representatives Few other cs practiced this government Athenian Empire He used cash from delian league to fund the 200 ship navy of Athens strongest in the Mediterranean Glorifying Athens He went against the league and to buy gold ivory and marble He spent 15 years of building to build the Parthenon Greek Styles in art Parthenon: 23,000 square foot building like a temple It set the standards for future generations Greek Sculpture In the Parthenon stood a giant statue of Athena goddess of wisdom and protector of Athens Phidias sculpture 38 foot tall sculpture their art values became knows as classical art Greek Drama built first theaters expression of civic pride and a tribute to the gods they wrote two types tragedy and comedy Tragedy serious drama about common themes such as love hate war or betrayal had a hero a defect would cause his downfall often hubris or excessive pride Aeschylus, Sophocles, Euripides were the main play writers Aeschylus wrote more than 80 plays The oresteia based on Agamemnon commander of Greeks at troy Sophocles wrote about 100 plays including Oedipus the king an antigone about a young women from a noble family with 2 bros 1 bro fights against another poleis and 1 fought against their poleis and the king cream announces that one will be buried and one will be left out for the dog she disagrees and fights with her sister and antigone says a law cant be followed if it goes against the gods and my conscious and then that is a bad law in the end buries her brother and and get killed and then her husband the kings son kills himself Euripides author of the play medea Comedy Had humor Satires or works that poked fun at a subject Made fun of customs politics respected people or ideas of the time Aristophanes wrote comedies the birds and lysistrata Lysistrata was women telling their husbands not to fight in the Peloponnesian war Spartans and Athenians Go To War Athens and Sparta had tension wanted to fight and did Peloponnesian war Sparta declares war against Athens in 431 BCE Athens was strongest sea power in Greece Sparta was better on land The Spartans invaded and burned the food supply They went into the guarded city and were safe Sparta gains the edge In the second year of the war (430 BCE) a plague spread out and killed about 2/3 of Athens population Athens second disaster sent 27,000 soldiers to destroy polis of Syracuse one of Spartas wealthiest allies They lost in 413 BCE 404 BCE Athens surrendered War brings political changes after 27 years of war Athens lost its empire they couldn’t figure out what to do Topic: ancient Greece- philosophy: the pre Socratics Time: 6th-5th century BCE Place: Greece Concepts: reason; logic; proof Big Question: Why was Greek Philosophy a revolution in thought? Socrates- morality values meaning good society Presocratics- were like scientists very scientific questions Question: what are the big existential questions that people ask? Why are we alive? How did the world come to be? Why is there good and evil? Why do I suffer? What happens when I die? How did people answer these question in the ancient world? Religion- the gids made it this way/said so Authority- the king (pharaoh, tyrant, nobles) made it this way Tradition- our ancestors have always understood it this way/ done it this way In this sense are the Jews unique? NO. Philosophy: love of wisdom Groundbreaking in the way it answers the existential questions about the world and our place in it. PHILOSOPHY: LOVE OF WISDOM Groundbreaking in the way it answers these existential questions about th e world and our place in it. USE OF REASON: Question: what does this mean??? (Look for evidence t o prove your theory). Rational rather than MYTHOLOGICAL. Earliest philosophers emerge in Greece in the sixth century. Interestingly, they are concerned with the physical world, mostly-what do es it consist of, notions of time and space. Does this sound like a modern discipline to you? [science] Yes-philosophy has always been related to science. Called the “Pre­Socrat ics,” because their work preceded the philosophical revolution started by SOCRATES. T hough they were born observers, the Pre-Socratics rarely undertook deliberate experiment ation. INSTEAD THEY TOOK INDIVIDUAL FACTS AND WOVE THEM INTO THEORI ES. Despite appearance, they believed, the universe was actually simple and subject to natural laws. thales ( 6th c. from miletus) big question: what was the world made of? WATER in Greece there was coast line from all of the water he thought everything was water and there were floating islands flat. Water most important like sustaing thing. It has it 3 states of matter solid liquid gas. Infinite regress: something that cant be proven and cant come to an end. Anaximander (thales student 6th c. miletus) says the world is a circle kept by space and doesn’t move because it is held in palce by other heavenly spheres. Says men come from fish. Democritus- the world is made up of tiny indestructible particles called atoms Pythagoras- math is always true, purly logical, it is eternal and unchanging Pythagorean theorem vegetarian+fenimist hippoctares: (5th c. from cos) Hippocratic oath to sware to be a good doctor “father of medicine” first professional doctore rational empirical (fact- based evidence) epilepsy from brain and that is what he said Topic: ancient Greece- Socrates Time: 469-399 BCE Place: Athens Concepts: inquiry; wisdom Big question: what was Socrates trying to accomplish? AGORA-OPEN PLACE LIKE A MARKETPLACE Inquiry: to inquire to ask Motivation: story of the oracle of Delphi Question: what insight does this story give you into Socrates’ character? Believed that delphiw as the most holy city in the world. Oracle (seer, navi). You would go to Delphi and give a summon to the sun god Apollo and then the oracle would eat it and then give a vision. One story she said they would win the Persian war with wooden walls and they said that it was wooden boats. One story shes asked who was the wisest in Greece and she says Socrates. He gets very mad but then relieazes why she says him. Because he is not arrogant because once you think you are very smart then you are conceded. Philosophers search for truth: Great thinkers in questioning times called philosophers (lovers of wisdom) Based philosophy on2 assumptions: 1. The universe 2. People can understand laws by logic reason Sophists questioned peoples uncontained beliefs and ideas about justice Protagoras who asked about Greek gods Radical and dangerous ideas to Athens Socrates: Believed that absolute standards did exist for truth and justice Concrete vs. abstract concrete: physical things, powerade bottle, table abstact: JUSTICE, GOODNESS, TRUTH, FREEDOM Believed that if you looked into something you will become that ike if you look into goodness then you will become good Relative vs. absolute truth—why Socrates hates the sophists sophists will prove anything that is not absolutely true they will tell you relative to the topic like they could argue something on both sides sophsts just want to persuade you they don’t care if you didn’t like them In athen sophists were very important His method is called Socratic method=dialectic=dialogue Socratic method word: courage bravery but not only battlefied do my own thing does that eman I should listen to anybody no I should face my fears A philosopher should only care about morality and justice Made people think about the process and not the end He also made them question their moral character People who understood him loved him Majority couldn’t understand him 399 BCE Socrates 70 years old. Brought to trial for corrupting youth of Athens and neglecting city gods his trial was a political setup Socrates is a scapegoat One of his famous students alcibiades turned traitor during the war with Sparta Said that if he was offered to live but stop teaching God makes him do it (monotheistic) claimed actions were good because made people look at moral they poisoned him Plato: student of Socrates 28 years when teacher died 385-380 BCE Plato wrote the republic and said his view of perfect government all citizens would be in 3 groups farmers, artisans, warriors, and the ruling class smartest person would be chosen philosopher-king very popular for 1,500 years rivals Socrates and Aristotle Aristotle: questioned world and human belief, thought, and knowledge close to summarizing all knowledge up to his time made method to order logic applied method to field of psychology, physics, and biology his work is the basic building block of the scientific method used nowadays famous pupil Alexander son of king Phillip of Macedonia 343 BCE tutors the son at 13 336 BCE student ended then he became the ruler 10/21/2010 10:53:00 PM 10/21/2010 10:53:00 PM