ACEI Journal Member: 4183 8\4\2012 Introduction: In this journal, I

ACEI Journal
Member: 4183 8\4\2012
Introduction:
In this journal, I be will rewriting what we learn in medicinal chemistry lecture.
First mention a rennin-angiotensin pathway and its physiological effect. Then, show the classes of drugs that affecting the rennin-angiotensin system and development of captopril as example on one class of these agents. Finally, therapeutic applications of these drugs.
Body:
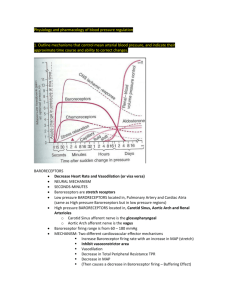
The rennin-angiotensin system is a complex, highly regulated pathway that is integral in the regulation of blood volume, electrolyte balance, and arterial blood pressure. It consists of two main enzymes, rennin and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), the primary purpose of which is to release angiotensin II from its endogenous precursor, angiotensinogen. Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor that affects peripheral resistance, renal function, and cardiovascular structure. Angiotensinogen is an α2- globulin It contains 452 amino acids, is abundant in the plasma, and is continually synthesized and secreted by the liver. Its synthesis stimulated through A number of hormones, including glucocorticoids, thyroid hormone, and angiotensin II. It contains Nterminus as most important portion that cleaved by rennin to produce the decapeptide angiotensin I. The Phe8-His9 peptide bond of angiotensin I is then cleaved by ACE to produce the octapeptide angiotensin II. Angiotensin II can further converted to the active heptapeptide angiotensin III by aminopeptidase through removing the N-terminal arginine residue. Angiotensin II is the most dominant peptide produced by this pathway. It is a potent vasoconstrictor through variety of mechanisms: direct vasoconstriction, catecholamine release and neurotransmission enhancement within peripheral nervous system that lead to rapid pressor response. Also, it has another action that directly increase sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule, aldosterone release from adrenal cortex and degradation of bradykinin which is potent vasodilator to inactive peptides. Since the last action, it will lead to produce dry cough as consequence of edema formation. Finally the results from its action, it will lead to remodeling of both cardiac and vascular cells. Specifically, over-activity of this pathway can result in hypertension or heart failure. Additionally, high levels of angiotensin II can cause cellular hypertrophy and increase both afterload and wall tension. All of these events can cause heart failure at the end. In the level of treatment, since angiotensin II produces the majority of effects attributed to rennin-angiotensin pathway, use of compounds that can block either angiotensin II synthesis or binding of angiotensin II to its receptors should prevent the actions of this
ACEI Journal
Member: 4183 8\4\2012 pathway especially angiotensin II. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are approved for therapeutic use in united state. They are sub-classified into three groups based on their chemical structure. The first group is sulfhydrylcontaining inhibitors like captopril. The second group is dicarboxylatecontaining inhibitors like enalapril. Last group is phosphate-containing inhibitors like fosinopril. Captopril and fosinopril are the lone representatives their chemical sub-groups. The compounds similar in pharmacological action and differ in their potency and pharmacokinetics profiles. Captopril is discovered through rational thinking. Through observation that D-2-benzylsuccinic acid was an inhibit a carboxypeptidase. This binding similar to that seen for substrates with the some exceptions(the zinc ion bind to carboxylate group instead of the labile peptide bond). The first inhibitors to be synthesized and tested was succinyl-L-proline . one of the most modification on succinyl-L- proline was replacement of the succinyl carboxylate with other groups having affinity for zinc atom on ACE. The replacement occur by addition of sulfhydryl group produced 3-mercaptopropanoyl-Lproline. This compound has greater than
1000-fold more potent than succinyl-L-proline. Addition of a D-2-methyl group further enhanced activity. The resulting compound, captopril is competitive inhibitor of ACE and was the first ACEI to be marketed. The sulfhydryl group of captopril proved to be responsible not only for the inhibition action, but also for the two most common side effects, skin rashes and taste disturbance(metallic taste). These side effects will disappear with discontinuation of captopril. They attributed to presence of sulfhydryl group. Therapeutic uses of this agent and other subgroups are treatment of hypertension, heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction and other cardiovascular abnormalities.
Conclusion:
ACEI is the most important and effective class in treatment of cardiovascular diseases. It show specificity in its action through it will targeting the most important enzyme in rennin-angiotensin pathway. This enzyme called angiotensin converting enzyme. It will acquired the importance since it produce angiotensin II which is play important rule in alters renal , electrolytes and cardiovascular hemodynamic changes. Succinyl-L-proline is first inhibitor to be synthesized and tested while captopril is first ACE inhibitor to be marketed.
Another classes of ACEIs are similar in their therapeutic effects but differ in potency and pharmacokinetics.

![Anti-Angiotensin II antibody [BGN/0856/21] ab35643 Product datasheet Overview Product name](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/011980713_1-1b1e68585550d552e091ae57faa2980f-300x300.png)