Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity.doc
advertisement

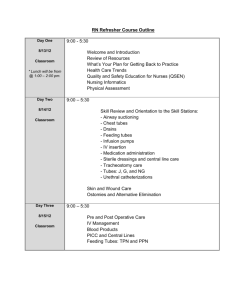
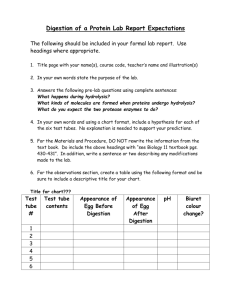
Factors affecting enzyme activity Introduction: An enzyme is a substance which alters the rate of a specific chemical reaction without itself forming part of the final product. One easily observed example of this activity is the effect of the enzyme rennin on milk. The influence the enzyme has on reaction rate is affected by the temperature. Background information: Rennin is an enzyme secreted by the walls of the stomach. It acts on the milk protein casein causing it to clump into a semi-solid curd. The enzyme is readily available in the form of junket tablets. Purpose: To observe the effect of variations in temperature on the action of renin. Equipment: 8 water baths 8 thermometers (0-100°C) Crushed ice Bunsen burner 2 graduated pipettes (10 mL) Milk (60 mL) Marking pen Small beaker Spoon Distilled Water 16 clean test tubes 1 junket tablet 1 eye dropper Stop watch Procedure: Prepare eight, half-filled water baths a temperatures within three degrees of 10°C, 20°C, 30°C, 40°C, 50°C, 60°C, 70°C, 80°C by measuring appropriate amounts of tap water, boiling water and ice. Carefully maintain these temperature throughout the experiment by adding hot water or ice as required. The 70°C and 80°C water baths will have to be maintained with a Bunsen burner. Using the graduated pipette place 3mL of milk in each of the sixteen test tubes. Put two of the test tubes in each water bath, labelling one A and the other B. While the milk is reaching the temperature of the respective water baths, crush the junket tablet with a spoon in 10mL of distilled water in a small beaker. Working quickly, add three drops of junket solution to teach of the test tubes marked A. Shake each tube to ensure contents are mixed and return to the water bath. Immediately record the time. Examine the tubes by tilting gently; do not shake. Do this every minute for the next ten minutes or until clotting occurs. Results Draw up a table similar to the one below and record your results. Temp of bath A B A B A B A B A B A B A B A B Time taken to set Graph these results Further investigation: Continue to maintain the water baths at the required temperature. If there was any temperature at which the enzyme did not act, take that pair of test tubes and place them in the water bath in which the quickest setting occurred. Make sure you label these test tubes with the temperature to which they were originally exposed. Observe these tubes for a further five minute indicating in the table the time taken for the junket (if any) to form. Try to explain what has happened to the enzyme during these experiments. Questions: 1. What is the effect of temperature on enzyme activity? 2. What was the purpose of the ‘B’ test tubes in this experiment?