World War 1 - One Bad Ant
advertisement

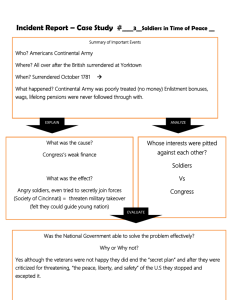
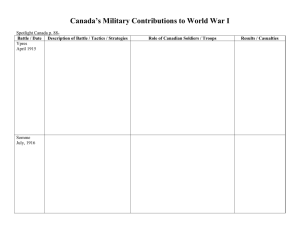
World War 1 “The Great War” 1914 – 1918 Topic DVD “The Great War” notes from film and supplemental material. List the countries in the Allied powers Great Britain, France, Russia later Italy and US List the countries of Central powers Germany, Austro Hungarian Empire, Ottoman Empire (Middle Eastern Countries) How did the assassination of Arch Duke Ferdinand lead to WW1? A series of treaties and alliances required each nation to go to war falling like dominoes. Why was The Arch Duke assassinated? The Black Hand thought the Arch Duke would give Serbs freedoms and more home control thus not have Serbians eager or strongly willing to fight for independence.. Who was the Black Hand and what did they want for Serbia? Secret Serbian Separatists group fighting for Serbian independence. What were new technologies used in this war? (Mechanized Warfare) War Planes, Mustard and Poison Gas, long range artillery, machine gun, tanks. Describe Trench warfare? 25,000 miles of trenches dug from Austria to Belgium. Wet, Diseased, dead bodies, bodies could not be removed while people still fought. Opened land above (No Mans Land) was mined (no mans land) Gas warfare!!! Why was the US hesitant to enter WW1? Policy going back to Washington and the Monroe Doctrine isolationism each hemisphere powers stay out of the others business. Neutrality we were supporting both sides Large population of American immigrants on both sides of the conflict What event changed the US decision to enter the war and what year did we enter the war? U-boat sinking of the Lusitania 1915 Public opinion begins to shift towards war. Sinking of US supply ships to France and England (hoped to roll over Allied powers if US supplies were not provided. US saw Central Powers as not economically viable as trade or political partners. Zimmerman Note: Secret Alliance with Germany and Mexico. If US attacks Germany, Mexico would attack US; Germany would earn back land Mexico land lost during American Mexican War. US enters WW1 in 1917 How did the US pay for the war? Taxes, Income Tax, Liberty Bonds supported by Chaplin and other stars. How did the US control information - Committee on Public Information? Strict control of media and use of propaganda. People would go to movie houses and give “4 min speeches” in movie theaters, anti German sentiment formed. No longer the use of German terms for food such as sour krout or even Germen taught in schools. Even incidents of lynching’s. Nationalism increases! How did Government and Private Sector reorganize the economy during the Wartime? War industries Board – Government and private leaders work to adapt private industry to military economy. Food Administration: Increase food supply with rationing and conservation. Railroad War Board – Mobilizes transportation War labor Board – Creates an 8 hour work day, equal pay for women. What role did women play in the war? Women became industrial workers in huge numbers that would ultimately lead to the 19th Amendment. Following the war women flexed greater confidence and independence. Many became sick from industrial health hazards. What was the Great Migration? 500,000 African American moving to industrial areas to contribute to the war effort. 400,000 African Americans fought in WW1 Describe Wilsons Fourteen Points: 14 points that would eliminate future conflicts and would solve localized disputes. Examples: End to secret diplomacy, Free trade, End of Empires, a League of Nations How did the League of Nations form? Woodrow Wilson’s last point called for an international body to settle disputes between countries. Added as part of the Versailles Treaty ****America does not enter due to Wilson’s Stroke Senate does not ratify our entrance.***** How long was Americas time in WW1 how many died how many Americans died? 18 Months 1917 - 1918 120, 000 Dead Americans Directly 50,000 KIA 70,000 indirectly to diseases like typhoid and dysentery 20 million deaths World Wide. What did the Versailles Treaty of 1919 require of Germany? Over 400 clauses requiring Germany to give up land, limited military, take blame, pay reparations. Article 231: The War Guilt Clause—a declaration imposing Germany with the moral responsibility for having started the war. The reparations section and the “war guilt” clause would require reparations of 33. Billion dollars Leaving Germany in ruins and bankrupt with spirts broken. Germany looses much land and former territory. European Allies want revenge for the war. “Revenge never ends” Post War: Economic Disaster and Racial Violence. What was the Red Summer of 1919? Following the war the economy crumbled. At one point 4 out 5 workers went on strike. Returning soldiers and those who came to cities during the Great Migration where no longer welcomed. Tensions rose and race riots broke out in the industrial cities. Especially in Chicago. Lynching’s and violence erupts. Define: Nationalism: Fervent desire for independence. Sense of national superiority Isolationism – Staying out of others conflicts. Progressives – Reformers during the period tried to make changes in social, political and economic changes during the progressive era. Imperialism – One country controlling political and economic policies of another Blockade – Blocking through military force an enemies’ way to deliver needed supplies. U Boat – German Submarine. Sedition Act – Law restricting free speech against the US and urging people not to work or support the war movement. “Fire in a Movie Theater” The Espionage Act - passed by Congress in 1917 after the United States entered the World War 1. It prescribed a $10,000 fine and 20 years' imprisonment for interfering with the recruiting of troops or the disclosure of information dealing with national defense. Additional penalties were included for the refusal to perform military duty. Over the next few months around 900 went to prison under the Espionage Act. Selective Service Act – Required a national draft enlisting over 3 million American. Continues to this day Doughboys – American soldiers fighting over in Europe The Treaty of Versailles ended World War I between Germany and the Allied nations. On 6 October 1918 Treaty of Brest-Litovsk – Upon the Russian Revolution of 1917. The new Soviet Union pulls out of the war signing a treaty with Germany Aftermath Allied Power Losses Britain : 750,000 soldiers killed; 1,500,000 wounded France : 1,400,000 soldiers killed; 2,500,000 wounded Belgium : 50,000 soldiers killed Italy : 600,000 soldiers killed Russia : 1,700,000 soldiers killed America : 116,000 soldiers killed Central Power Losses Germany : 2,000,000 soldiers killed Austria-Hungary : 1,200,000 soldiers killed Turkey : 325,000 soldiers killed Bulgaria : 100,000 soldiers killed Allied Power Losses Britain : 750,000 soldiers killed; 1,500,000 wounded France : 1,400,000 soldiers killed; 2,500,000 wounded Belgium : 50,000 soldiers killed Italy : 600,000 soldiers killed Russia : 1,700,000 soldiers killed America : 116,000 soldiers killed Central Power Losses Germany: 2,000,000 soldiers killed Austria-Hungary : 1,200,000 soldiers killed Turkey : 325,000 soldiers killed Bulgaria : 100,000 soldiers killed The Spanish Flue During mid-1918, Europe was hit by Spanish flu and an estimated 25 million people died. This added to the feeling of bitterness that ran through Europe and this anger was primarily directed at Germany. In America 500,000 died from the Spanish flu Sample thinking Questions 1. How did WW1 continue progressive ideas at home during the war? 2. What does Wilson’s plan and the Versailles Treaty have in common with the political views of the Republicans during post civil war reconstruction? 3. Could the assassination of an “Arch Duke type” figure lead to a World War today? 4. Describe the Symbolism of Armistice Day. Why was this day replaced with veteran’s day? 5. How would you have punished Germany without giving rise to what would become WW2? 6. Why was this called the War to end All Wars? Can any war be so terrible to end all wars?



![vietnam[1].](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005329784_1-42b2e9fc4f7c73463c31fd4de82c4fa3-300x300.png)