Greek Art History: Archaic, Classical, Hellenistic Periods
advertisement
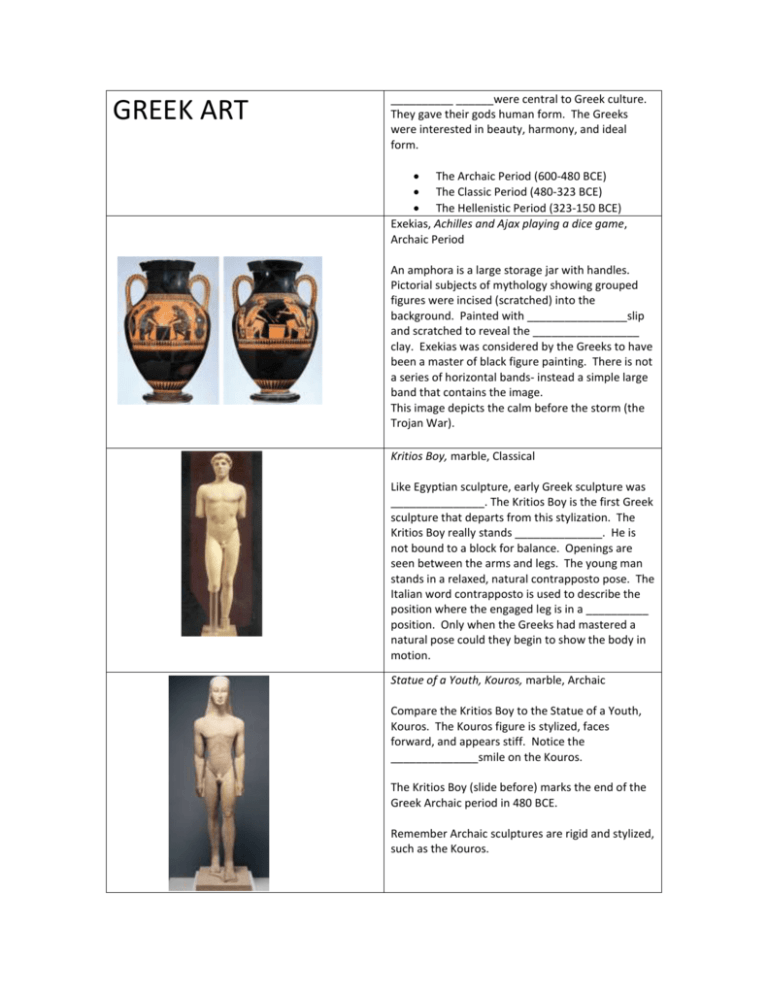
GREEK ART __________ ______were central to Greek culture. They gave their gods human form. The Greeks were interested in beauty, harmony, and ideal form. The Archaic Period (600-480 BCE) The Classic Period (480-323 BCE) The Hellenistic Period (323-150 BCE) Exekias, Achilles and Ajax playing a dice game, Archaic Period An amphora is a large storage jar with handles. Pictorial subjects of mythology showing grouped figures were incised (scratched) into the background. Painted with ________________slip and scratched to reveal the _________________ clay. Exekias was considered by the Greeks to have been a master of black figure painting. There is not a series of horizontal bands- instead a simple large band that contains the image. This image depicts the calm before the storm (the Trojan War). Kritios Boy, marble, Classical Like Egyptian sculpture, early Greek sculpture was _______________. The Kritios Boy is the first Greek sculpture that departs from this stylization. The Kritios Boy really stands ______________. He is not bound to a block for balance. Openings are seen between the arms and legs. The young man stands in a relaxed, natural contrapposto pose. The Italian word contrapposto is used to describe the position where the engaged leg is in a __________ position. Only when the Greeks had mastered a natural pose could they begin to show the body in motion. Statue of a Youth, Kouros, marble, Archaic Compare the Kritios Boy to the Statue of a Youth, Kouros. The Kouros figure is stylized, faces forward, and appears stiff. Notice the ______________smile on the Kouros. The Kritios Boy (slide before) marks the end of the Greek Archaic period in 480 BCE. Remember Archaic sculptures are rigid and stylized, such as the Kouros. Three Goddesses, East Pediment Sculpture of the Parthenon, Classical The Classic Period began after 480 BCE. The Athenians decorated the most prominent building in their city, the Parthenon. Both the east and west ends were filled with sculptures that were larger than life. Sculptures were designed to fill the pediment, or flat rectangular area, at each end of the Parthenon. The clothing of the Three Goddesses falls in_____________ folds and creases, and the drapery seems to cling to their bodies. These folds create visual ____________. Nike of Samothrace, Hellenistic The Hellenistic period came after the Classical period. The art of the Hellenistic period became more concerned with ___________ and ____________. In art of the Classic period, these elements would have been under tight control. The Nike of Samothrace is the symbol of Winged Victory, her great wings spread wide as she lands on the prow of a ship. Old Market Woman, Hellenistic In contrast to the sweeping motion and energetic forward movement of the Nike is the Old Market Woman, whom is bent and almost dragging. The artist portrays her with stark _________________, a painful portrayal of a tired, burdened woman. The focus of Greek art during the Hellenistic period is no longer perfectly beautiful, ideal beings. Iktinos and Kallikrates, The Parthenon, Classic Period, The Acropolis, Athens The Parthenon depicts beautiful proportions and ______________. The columns are equally spaced; with slender shafts that are a more refined version of the earlier squat and bulging Doric columns of the earlier Archaic period. This structure demonstrates the belief that beautiful proportions resulted from strict adherence to harmonious numerical ratios Architecture was based on Egyptian ways, but a difference in materials and tools enabled the Greeks to refine the pure forms and classical designs that have influenced architects ever since. For one, Greek marble was easier to carve then Egyptian sandstone. The Parthenon sits on the Acropolis, which is a hill and the ______________ spot in the city of Athens. The highest point in the city was the preferred location for temples. Most temples had columns around the outside and an inner room (cella) where statues were kept. However, people worshiped outside of the temple. Only priests and priestesses were allowed in the ________________. Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian columns from left to right/ top to bottom Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian Columns. Greek columns were made of drums stacked on top of each other and held together with metal pieces, then ___________________. READ BELOW. Answer the following questions with at least three sentences per topic to receive full credit on this assignment. Which preceding Greek art piece do you find the most interesting or significantly draws you in to its presence? Why? What would say are the most prominent characteristics of classic Greek art, and how might these characteristics be unique to this art movement?











