ArtisticExpression(2.1.5)
advertisement

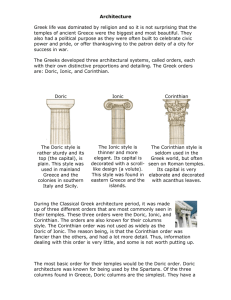
Created by: Amani Gaddy and Ayanna Harrison 4 th period During the 6th century BCE, as Greece awoke from the dark years of illiteracy and cultural deterioration, Greek drama through plays emerged. The origins of Greek drama lie in religious celebrations honoring the Greek deities during festivals or holy days. Many of the celebrations included elements of acting and stagecraft. At some point, the emphasis shifted from reciting stories about the gods to acting them out. According to a Greek legend, a prefamen named Thespis invented the art of acting when he stepped forward from the chorus and sand by himself, not about the god but as the god. Actors today are called thespians to honor his legendary contribution to drama. 3 types of Greek plays: Tragedy- serious playing dealing with the suffering and trials of noble or heroic characters Comedies- humorous plays set mostly in invented situations rather than in the world of myth or legend. Satyr- A blend of comedy and tragedy. The underlying themes of the plays were a serious nature, but their plots and tone were absurd and designed for humorous effect. Order refers to the standard parts of a structure and the arrangement in buildings. The Greeks developed 3 architectural orders. Doric Ionic Corinthian Doric Order: The basic order and first to develop in the early 500 BCE It contains 3 main divisions: stepped platform, columns, and entablature. Ionic Order: Originated in the islands of the Aegean and Asia and was lighter than the Doric. Columns were rested on a carved base and was more slender and graceful than the Doric. It was used to support statues. Corinthian Order: Developed in the late 400 BC. Looks like an upside down bell decorated with carvings of the curly leaves of the acanthus plant. Usually used for the interior of buildings. Romans copied this idea for important monuments. Greco Buddhist is characterized by the strong idealist realism and sensuous descriptions of Hellenistic Art and the first representation of Buddha in human form. The convergence effected the development in which Hellenistic veneration for the body is combined with Buddhist beliefs. It developed over a period of close to 2 years in Central Asia between the conquest of Alexander the Great in the 4th century BCE and Islamic conquest in the 7th century CE. Greco-Roman Used Corinthian, the latest order for their architectural building. Buddhist Buddhists used the typical Buddhist relief in India. Greco-Roman Buddhist Togas were a traditional Buddhists show humans Roman garment in loin cloths.