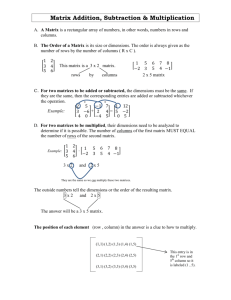
Arrays and the
Commutative Property
CA Standards
AF 1.5 Recognize and use
the commutative and associative
properties of multiplication (e.g.,
if 5 × 7 = 35, then what is 7 × 5?
and if 5 × 7 × 3 = 105, then what
is 7 × 3 × 5?)
AF 2.2 Extend and recognize a
linear pattern by its rules (e.g., the
number of legs on a given number
of horses may be calculated by
counting by 4s or by multiplying
the number of horses by 4).
Also NS 2.0, KEY NS 2.2 ,
NS 2.8, AF 1.0, AF 1.2,
MR 1.2, MR 2.0, MR 2.3,
MR 2.4
Objective Use arrays to multiply numbers in any order.
A rectangular array shows objects arranged in equal
rows and equal columns . Look at the arrays below.
Do the two arrays have the same number of stamps?
1
Multiply to find the total number
of stamps.
6
×
3
=
stamps in
each row
rows
3 columns
18
total number
of stamps
6 rows
array
column
Commutative
Property of
Multiplication
factor
2
6 columns
Turn the page of stamps. The
total stays the same.
product
3
row
×
6
=
stamps in
each row
rows
18
3 rows
total number
of stamps
Solution: Both arrays have 18 stamps.
Commutative Property of Multiplication
Changing the order of the factors does not change
the product .
6
factor
×
3
= 18
factor
102Houghton Mifflin California Math, Lesson Transparency 5.2B
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Use with Chapter 5, Lesson 2
product
3
factor
×
6
factor
= 18
product
• How many rows
are there?
• How many objects
are in each row?
• How can I use
the Commutative
Property?
Write two multiplication sentences for the array.
1.
2.
Find the missing number.
3. 2 × 3 = 6
3× =6
Math Talk
you find 6 × 4?
4. 24 = 8 × 3
=3×8
How can knowing 4 × 6 = 24 help
Houghton Mifflin California Math, Lesson Transparency 5.2B
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
Use with Chapter 5, Lesson 2
5. 18 = 6 × 3
18 = 3 ×