COMPUTER HISTORY- Chapter 1 BOOLEAN OPERANDS
advertisement
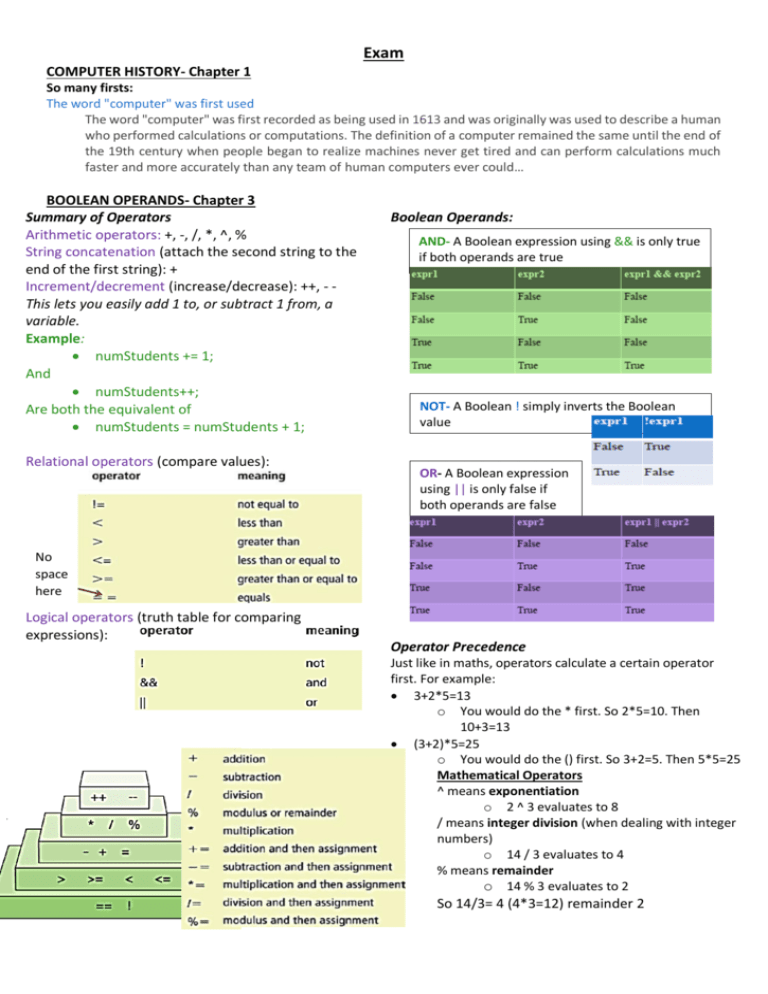
Exam COMPUTER HISTORY- Chapter 1 So many firsts: The word "computer" was first used The word "computer" was first recorded as being used in 1613 and was originally was used to describe a human who performed calculations or computations. The definition of a computer remained the same until the end of the 19th century when people began to realize machines never get tired and can perform calculations much faster and more accurately than any team of human computers ever could… BOOLEAN OPERANDS- Chapter 3 Summary of Operators Arithmetic operators: +, -, /, *, ^, % String concatenation (attach the second string to the end of the first string): + Increment/decrement (increase/decrease): ++, - This lets you easily add 1 to, or subtract 1 from, a variable. Example: numStudents += 1; And numStudents++; Are both the equivalent of numStudents = numStudents + 1; Relational operators (compare values): Boolean Operands: AND- A Boolean expression using && is only true if both operands are true NOT- A Boolean ! simply inverts the Boolean value OR- A Boolean expression using || is only false if both operands are false No space here Logical operators (truth table for comparing expressions): Operator Precedence Just like in maths, operators calculate a certain operator first. For example: 3+2*5=13 o You would do the * first. So 2*5=10. Then 10+3=13 (3+2)*5=25 o You would do the () first. So 3+2=5. Then 5*5=25 Mathematical Operators ^ means exponentiation o 2 ^ 3 evaluates to 8 / means integer division (when dealing with integer numbers) o 14 / 3 evaluates to 4 % means remainder o 14 % 3 evaluates to 2 So 14/3= 4 (4*3=12) remainder 2











