Week 10 Recap CSE 115 Spring 2007
advertisement

Week 10 Recap
CSE 115 Spring 2007
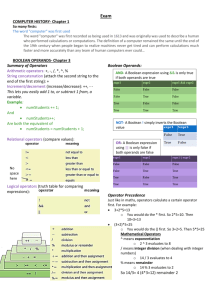
For-each loop
When we have a collection and want
to do something to all elements of that
collection we use the for-each loop to
help us iterate over all elements of
that collection.
For-each loop syntax
for(Type identifier1: identifier2) {
//code to execute for each element
}
Where:
– identifier2 is the name of the collection that you are
iterating over
– Type identifier1 is the creation of a reference to
each element of the collection to use as you are iterating.
If-statements
Selection based on the value of a
boolean expression.
If-statement syntax
if (booleanExpression) {
//code to be executed if
//booleanExpression evaluates to
//true
}
Boolean expressions
Expressions that evaluate to either
true or false
boolean is a type built into Java
However, boolean is not a class
Boolean values and
operators
Methods can return boolean values
Can combine boolean values using
logic operators
&& (logical and)
|| (logical or)
! (logical not)
Operators that return a
boolean value
Comparison operators return boolean
values as well. These operators work
on numeric values.
< (less than)
> (greater than)
<= (less than or equal to)
>= (greater than or equal to)
Operators that return a
boolean value
There are two equality operators in Java:
== (equality)
!= (not equal)
These work on numeric values as you would
expect from arithmetic
But are also defined on references where
they compare if the references are the
same.