The Power of the Single Number A Political History of GDP
advertisement

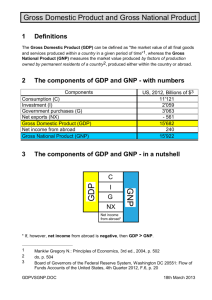
The Power of the Single Number A Political History of GDP Seminar IDDRI / SciencesPo November 19, 2013 Philipp Lepenies, IASS GDP as Phenomenon • • • • • Most powerful statistical indicator in history GDP integral part of our political culture Recently: attempts to surpass or „dethrone“ GDP But: GDP sits firmly in the saddle notable absence of historical dimension in current discussions • Why and how did GDP become the world‘s most powerful number? What is GDP? • GDP is Political Arithmetic: – officially calculated by the State – influences politics directly – allows „governing by numbers“ History of GDP • National Income – Gross National Product – Gross Domestic Product • from account to single number • growth • focus on production • why more than mere statistics? The History of GDP Is a tale of… – two countries: Britain and USA – three men: William Petty, Colin Clark and Simon Kuznets – tragedy: none of them succeeded – triumph: of J. M. Keynes Great Britain (England) William Petty (1623 – 1687) • Land Surveyor and Anatomist • Political Arithmetick • „Express myself in terms of number, weight, or measure …to consider only such causes that have visible foundations in nature“ • „the perplexed and intricate ways of the world are explained by science“ • “The glory of the prince, and the happiness and greatness of the people” • goal of government: peace and plenty The First National Account • THERE are of Men, Women, and Children, in England and Wales, about six Millions, whose Expence at 6l. 13s. 4d. per Annum, or near 4½d. per Diem, for Food, Housing, Cloaths, and all other necessaries, amount to 40 Millions, per Annum. • NOW if the Annual proceed of the Stock, or Wealth of the Nation, yields but 15 millions, and the expence be 40. Then the labour of the People must furnish the other 25 Triumph or Tragedy? • „Had not his doctrines offended France, they had long since seen the light and had found followers as well as improvements…to the advantage … of mankind“ (Petty‘s son, Lord Shelbourne) • „I have no great faith in political arithmetic“ (Adam Smith, Wealth of Nations 1776) Legacy • Interest in „National Income“ – only academically • Discovery of „labour“ as economic value • Political arithmetic becomes „Statistik“ (Achenwall) • problematic: combination and interpretation Colin Clark (1905 – 1989) •Chemist •„inventor“ of GNP and National Income •Member of Papal Commission on Birth Control The National Income 1932 • Three ways of calculation: consumption, production and distribution • Per capita income measure of progress • Estimates macroeconomic aggregates • numbers before theory • National income as historical category Conditions of Economic Progress 1940 • International comparison • Sectoral development: Agriculture Industry Services • Begin of Development Economics • New Picture of the World After Clark The Keynesian System • System of National Accounts following requirements and logic of the Keynesian Theory • Focus on Income (tax base) – not production • No single number • Positive and important role of the state • taken up by the govt. – but very late • No planning • No longer only historical number (quarterly) The U.S.A. Simon Kuznets (1901‐1985) • empirical study before theory • „exemplar empiricist of the century“ Definition of National Income 1932 • start by end of all economic activity provision of goods and services • Moment individuals receive their income • Closely linked to distribution • People‐centred, welfarist approach • Extremely cautious Birth of GNP • Victory Program 1942 Keynes visit to US 1941 Result • Focus on single‐number Gross National Product GNP • Production‐focus ‐ politics of productivity • Based on adapted System of National Accounts • Political Arithmetic – Dept. Of Commerce • Taken up by political rhetoric Production Kuznets 1945 • • • • • Income more important than production Means to an end Goal of economic activity? Market‐based economy Role of state – harmony of accounts critical Internationalization • Assess reconstruction need and strength of European countries • Methodology imposed on Marshall‐Plan recipient countries • Possibility to classify and rank countries – international comparison Growth Traditional View Stagnation or Maturity a cognitive change 1945/1946 1946 • Employment Act : Full Employment • Council of Economic Advisors: growth of GNP • Harrod Domar – Dynamization of Keynes (growth theory – endless growth and GNP planable) – GNP measure of future • Development Economics (Rosenstein‐Rodan) 1947 and beyond • • • • • Truman Doctrine: economic progress 1949 Point Four – geopolitical policy Foster GNP growth around the world and at home (race of the systems) CIA calculation of Soviet GNP Marshallplan and Modernization •Production‐focus •Hoffmann: „You can become like us, this was the original message of the Marshallplan“ •Idea of „catching‐up“ – economically, but also politically – Modernization Theory •Civilizing (becoming Western) is the result of economic growth •Rostow: GNP per stage‐of‐growth – measure of future Erhard 1957 / Galbraith 1958 Ludwig Erhard • Expression of post‐war Germany‘s political „mentalité“ • GNP table at beginning • GNP growth as perpetual government goal – for all socio‐economic worries • Transformation of society • End of fight over redistribution • Bright future of „wealth for all“ – global happiness Problems of Materialism GDP / GNP Result of extreme historic circumstances Political useful in various times of crisis more than economic statistics (always!) defines globally how we view the economy and progress • Political arithmetic • „peace and plenty“ • • • • • But: only one way to explain „the intricate ways of the world“ Lessons learnt • Defenders of GDP: conscious of the historic context in which GNP/GDP emerged • Advocates of alternative measures: conscious of what it took GDP to triumph – and what it might take to establish an alternative political arithmetic Thank you! philipp.lepenies@iass‐potsdam.de