PHOTONICS ELE884
advertisement

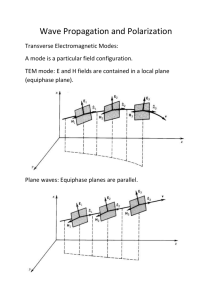
PHOTONICS ELE884 - Problem set A (1) Plane EM wave moving in the r-direction is described by E(r,t) = E0 cos (t - r) where E0 is the amplitude. Using energy arguments, show that the amplitude of a spherical wave must vary as ~1/r and the amplitude of a cylindrical wave must vary as ~ (1/r)-1/2 . (2) A signal of magnitude 0.1095 V/m is received from a radio transmitter 10 km away. The transmitter is radiating uniformly in all directions. What is the EM power radiated by the transmitter ? [Ans: 20 kW] (3) Show that two plane EM waves moving in opposite z-directions with equal frequencies and equal magnitudes E0 produce interference pattern described by the equation E = 2E0 cos (z) cos (t). Sketch a graph of the equation as a function of (spatial domain) for several different times ( t = 0, T/4, T/2, 3T/4) and find the distance z between two consecutive values of the z-coordinate, where E = 0. [Ans: z = /2] (4) Two EM waves in free space with frequencies 6x1014 Hz are incident on a photographic plate. One wave is incident in the normal direction (orthogonally to the plate) and the other at an angle of 30o with respect to the normal direction. The stationary interference pattern is recorded in the photographic emulsion. What is the separation between the recorded interference fringes? (sketch a diagram) [Ans: 1 m] (5) When a pulse of light is emitted from point A in free space it reaches point B in 0.01 sec. When a block of transparent dielectric material 2 m thick is inserted between points A and B, the pulse of light needs 0.0139 sec to reach point B. What is the dielectric constant of the material? [Ans: 2.5] (6) Monochromatic 500 nm light from a distant point source is reflected by a flat mirror whose plane is at some angle ( < 900) with respect to the incident ray. The incident and the reflected wavefronts interfere. What is the alignment of the stationary regions of constructive-destructive interference ? If the separation between the regions of total constructive interference is 5 m, what is the angle of incidence (with respect to the orthogonal direction to the mirror plane) ? [Ans: parallel, 87.13o] (7) A diffraction grating can be produced in a thin photographic emulsion by the interference of two plane waves. When such a grating is illuminated by one of the waves, the other wave is fully recreated. (This demonstrates the principle of holographic imaging). Explain why. (8) A plane light wave penetrates through a circular aperture 0.1mm in diameter. The penetrating light projects a central spot 1.545 cm in diameter on a screen placed 1 m behind the aperture. What is the wavelength of the light ? [Ans: 633 nm] (9) What is the size of the smallest object that can be resolved at a distance of 1 km by a telescopic lens 5 cm in diameter (assume = 550 nm)? [Ans: 1.34 cm] (10) An ordinary 3.0 V flashlight bulb draws current 0.25 Amp., converting about 1 % of the dissipated power into visible light ( ~ 550 nm). The output beam has a cross-sectional area of 10 cm2 . (a) How many visible photons are emitted per second? [2.08x1016 Ph/s] (b) What is the visible irradiance as the light leaves the flashlight ? [7.5 W/m2 ]