Topic 2 - Gouverneur Central School District
advertisement

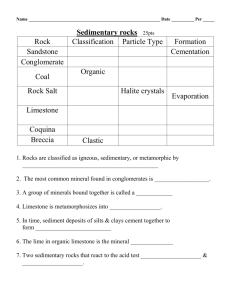
Silicates – are the most abundant family of minerals on Earth They contain the most abundant elements on Earth – silicon and oxygen (page 11 ESRT) Quartz – most common mineral on Earth, you can go anywhere and find quartz *There are 12 common minerals that can be found almost anywhere on Earth.* like: Quartz, mica, feldspar, olivine, hornblende, etc. Silica Tetrahedron – is the basic building block of all silicates 1 silica atom 4 oxygens shaped like a pyramid Differ by internal arrangment of atoms. (how they are put together) Rocks: 3 types I. Sedimentary: A. Clastic: composed of fragments or pieces of rock (sediments) 1. Compression: great force or weight from above (dewatering- water gets squeezed out) ex) shale, siltstone, sandstone 2. Cementation: mineral cement from groundwater ex) conglomerate, breccia, shale, siltstone, sandstone common cements: CaCO3= calcium carbonate (dissolves in acid), FeO2 = iron oxide = rust, Silica B. Non-clastic: chemical 1. Precipitation: mineral comes out of solution, settles to the bottom = called precipitates ex)gypsum, limestone, halite, dolostone 2. Evaporation: mineral is deposited after water evaporates C. Organic / Biologic 1. can be clastic, can form from compression of once living things Ex) coal, peat, fossil limestone (cocina) II. Igneous Rocks: formed by melting, cooling and solidifying A. Intrusive: forms inside the Earth, MAGMA, has large crystals because they cooled slowly a.k.a. plutonic : granite and gabbro B. Extrusive: forms outside the Earth (on the surface), LAVA, has small or no crystals because it cools fast a.k.a. volcanic : pumice, obsidian, rhyolite, basalt Granite = continental crust Basalt = oceanic crust (contains no salt) Crust is mostly igneous with a thin covering of sedimentary rocks. ***As cooling rate increases, crystal size and shape will decrease.**** III. Metamorphic Rocks: form from heat and/ or pressure A. key characteristics Recrystallization Foliation Distortion Banding B. regional: large area Ex) Adirondacks C. contact: small area Ex) where igneous rocks touch other rocks