unit_1_review
advertisement

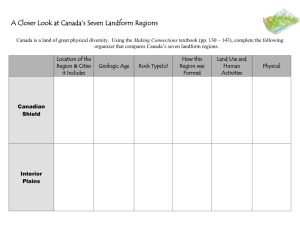
Test Review The earth is made up of a great variety of rock of differing ages. Canada has some of the oldest rock, at about four billion years old. Scientists believe that the earth formed in layers. Over time, the denser materials settled in the earth's centre to form the core, while the lighter materials, including gases, formed its outer layers and atmosphere. At the centre is the core, which has two layers: a solid inner core that is very hot because it is under great pressure, and the liquid outer core. The surface layer, or crust, of the earth is solid. The middle layer, the mantle, is not. The material of the mantle, a type of melted rock called magma, is a hot, relatively dense and slow-moving fluid. What are Landforms? Landforms are the topography, that is, the natural features, of the land's surface. A landscape is an area's landforms together with its cover of vegetation, water, ice, and rock. Landscape also includes the activities of humans and other animals. Cities are often referred to as urban landscapes, while agricultural areas are called rural landscapes. Topography may be described using the following terms: Elevation: is used to describe the height of a landform. It is measured from sea level. Relief: is the difference in elevation between points on the earth's surface. Gradient: refers to the steepness of slopes. Geology: refers to the types of rocks and history of those rocks. Weathering is the decomposing of rocks, soils and their minerals through direct contact with the air. Erosion is displacement of solids (soil, mud, rock and other particles) usually by the agents of currents such as, wind, water, or ice by downward or down-slope movement in response to gravity or by living organisms (in the case of bioerosion). Deposition is the geological process whereby material is added to a landform. This is the process by which wind and water create a deposit, through the laying down of granular material that has been eroded and transported from another geographical location. Canada's Landform Regions A region is an area that is defined on the basis of the presence or absence of certain characteristics. Geographers look for common characteristics or combinations of chracteristics. Regions: Canadian Shield Appalachian Mountains Western Cordillera Innuitian Mountains Arctic Lowlands Interior Plains Great Lakes Lowlands Hudson Bay Lowlands Cardinal Directions In stating directions, it is common to use the terms North(N), South(S), East(E) and West(W) These are the four cardinal directions These terms may also be used in 2 and 3 letter combinations – NW, NE, SE, SSE and so on These combinations are known as inter-cardinal directions Compass Bearings For more precision, it is necessary to state a direction using a compass bearing, given as a number Remember that North has a value of 0° and the numbers increase in a clockwise direction – East is 90° and so on Scale If an object or drawing is made to scale, it means that its dimensions are relative to each other Its proportions are the same as the real thing A scale is a representative fraction (1/87, 1/160, 1/25, 1/700 etc.) giving a size relative to the original An accurate map must be made consistently to one particular scale A common scale used in Canadian maps is 1:50000 1 cm represents 50000 cm (or .5 km) Worldwide Grid Maps showing large areas typically show lines of longitude and latitude Lines of longitude are called meridians Lines of latitude are called parallels They form a grid A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on the Earth to be specified by a set of numbers or letters. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents vertical position, and two or three of the numbers represent horizontal position. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. DDD° MM' SS.S" 32° 18' 23.1" N 122° 36' 52.5" W This is the most common format used to mark maps. It's also the most cumbersome to work with. It's a lot like telling time… There are sixty seconds in a minute (60" = 1') and There are sixty minutes in a degree (60' = 1°). Keeping in mind a few easy conversions between seconds and decimal minutes will help when working with maps that use degrees, minutes and seconds. 15 seconds is one quarter of a minute or 0.25 minutes 30 seconds is one half of a minute or 0.5 minutes 45 seconds is three quarters of a minute or 0.75 minutes