A LIVING PLANET
advertisement

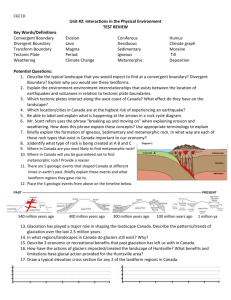
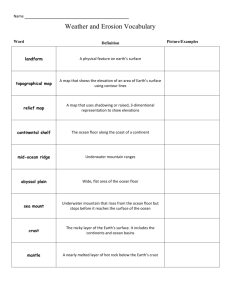
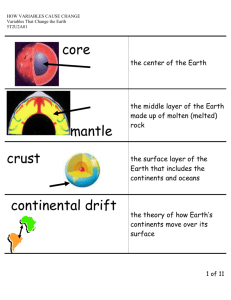
A LIVING PLANET THE EARTH INSIDE AND OUT BODIES OF WATER & LANDFORMS INTERNAL FORCES EXTERNAL FORCES THE EARTH INSIDE AND OUT • Continents – landmasses above water on the earth. • Solar System – consists of the sun and nine known planets and other celestial bodies. THE EARTH INSIDE AND OUT • Core – the center of the earth; made up of iron and nickel. • Mantel – layer surrounding the Core; most of the earth’s mass. • Magma – molten rock. • Crust – thin layer of rock on the earth’s surface. THE EARTH INSIDE AND OUT • Atmosphere –the layer of gases surrounding the earth. • Lithosphere – includes the crust and upper-most mantle. • Hydrosphere – the water on the earth. • Biosphere – the part of the earth where the plants and animals live. THE EARTH INSIDE AND OUT • Continental Drift – the continents have been shifting over millions of years – Pangaea. BODIES OF WATER & LANDFORMS • Hydrologic Cycle – aka the water cycle – the continuous circulation of water on the earth. • Drainage Basin – an area drained by a major river and its tributaries. • Ground Water – the water held in the pores of rock. • Water Table – the level at which rock is saturated with water. BODIES OF WATER & LANDFORMS • Landforms – naturally formed features on the earth’s surface. • Continental shelf – the earth’s surface from the edge of the continents to the deep part of the ocean floor. BODIES OF WATER & LANDFORMS • Relief – the difference in elevation of a landform from its lowest point to its highest point. • Topography – the combination of the surface shape and composition of the landforms and their distribution in a region. INTERNAL FORCES • Tectonic Plate – enormous moving pieces of the earth’s lithosphere. • Fault – a fracture in the earth’s crust. • Earthquake – a violent movement of the earth. INTERNAL FORCES • Seismograph – a special device that detects earthquakes. (Richter Scale) • Epicenter – the location above the focus where the earthquake begins. • Volcano – magma that pours out of a crack in the earth’s surface. (lava) • Tsunami – a giant wave in the ocean; maybe cause by an earthquake. INTERNAL FORCES • Ring of Fire – a zone around the rim of the Pacific Ocean; many active volcanoes. EXTERNAL FORCES • Weathering – physical • Mechanical or chemical Weathering – process processes that that break rock into change the smaller pieces. characteristics of the • Chemical Weathering rock near the earth’s – rock is changed into surface. a new substance • Sediment – smaller because of a pieces of rock created chemical reaction. by weathering. EXTERNAL FORCES • Erosion – occurs when weathered material is moved by the action of wind, water, ice, or gravity. • Delta – when a river enters the ocean, the sediment deposited in a fan-like landform. • Loess – windblown silt and clay sediment. • Glacier – a large, longlasting mass of ice. • Glaciation – the changing of a landform by slowly moving glaciers. • Moraine – hills formed by glaciers. • Humus – the texture of the soil and the amount of organic materials.