Word - ITU
advertisement

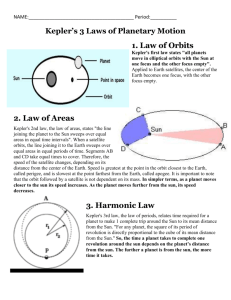
Source: Document 7B/TEMP/93 (2003-2007 study period) Subject: Question ITU-R 235/7 DEFINITION OF VARIABLES APPLICABLE TO FREE SPACE OPTICAL COMMUNICATIONS LINK CHARACTERISTICS Recommendation ITU-R SA.1742 and Draft new Recommendation ITU-R SA.[THz-SPACE-toSPACE] define technical and operational characteristics of free space optical communications links operating around 283 THz and 366 THz. These recommendations provide a number of equations relating to these systems which include parameters unique to optical communications link analysis. This document provides a definition of variables used in calculating key characteristics of free space optical systems. List of variables a: A: Arec: α: b: radius of the telescope mirror (m) area of the telescope aperture (m2) area of the receiving telescope aperture (m2) the ratio, a/ω radius of the secondary mirror (m) B: filter bandwidth (m) BF: filter bandwidth (Hz) c: speed of light (m/s) planet: d: D: Dplanet: : e: Epulse: f: F: bond albedo of a planet diameter of the detector (m) diameter of the aperture (m) diameter of the planet (m) losses due to energy spilling over the edge of the detector (dB) electron charge (coulomb) energy per pulse (J) optical frequency (Hz) focal length of the telescope (m) : field of view of the detector (rad) ': G0: Gr: gt: Gt: solid angle field of view of the detector (srad) maximum on-axis antenna gain (dBi) receiving antenna gain (dBi) gain efficiency transmitter antenna gain (dBi) : obscuration ratio Hsky: radiance of the sky (W/m2/m/sr) -2- ib : is: k: kB: Lt: Lr: Lp: La: Ls: λ: M: N A: N E: Nstar: Nt: Pave: Pback: Ppeak: Pplanet: PS: Psky: Pstar: Pt: θ: θplanet: 1 bulk dark current in the detector (A) surface dark current in the detector (A) electron/hole ionization rate Boltzmann’s constant transmitter losses (dB) receiver losses (dB) pointing losses (dB) atmospheric losses along the space-to-space link (dB) free space loss (dB) wavelength (m) modulation index noise figure of amplifier excess noise factor irradiance of a star (W/m2/m) noise power from all sources average transmitter power (W) total received background power (W) peak power (W) received power from an illuminated planet (W) received signal power (W) received power from the sky (W) received power from a star (W) average laser output power (W) angle off the optical axis (rad) angle subtended by a planet (rad) : angular width of the beam at the 1/e2 point (rad) e 2 'planet: solid angle subtended by a planet (rad) R: distance between transmitter and receiver (m) RD: APD responsivity RL: Rplanet: td : tp : ts: tw : T: ω: J0: resistance of the transimpedance amplifier () distance between planet and receiver (m) transmitter dead time (sec) transmitter pulse time (sec) transmitter slot time (sec) transmitter word time (sec) temperature (K) waist size of the beam at the 1/e2 point Bessel function of the first kind of order zero -3- u: the variable of integration planet: power spectral density of a moon or planet (W/m). ___________