Fish Anatomy
advertisement

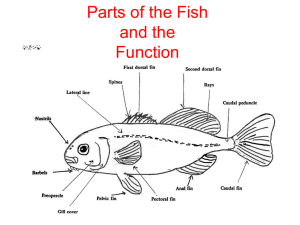
Aquatic Science Unit 9 Notes Anatomy of a Fish I. Taxonomic Classes of Fish A. Agnatha – jawless fish (lampreys and hagfish) B. Chronrichthyes – cartilage fish (sharks, skates, rays) C. Osteichthyes – bony fish (soft rayed and spiny rayed) II. Skin Anatomy A. Divided into Two Layers 1. Epidermis a. Epithelial cells – arranged one above the other b. Slime cells – interspaced between the epithelial cells 2. Dermis a. Made of fibroblasts, collagen, and blood vessels b. Scales in pockets in the dermis B. Scales – Four Types 1. Placoid – also called dermal denticles Similar to teeth; made of dentin and covered by enamel. (sharks and rays) 2. Ganoid – flat, basal –looking scales; little overlapping. (gar & bichirs) 3. Cycloid – small, oval-shaped with growth rings. (bowfin & remora) 4. Ctenoid – similar to cycloid scales; growth rings; spines covering one edge. (Halibut) C. Coloration – multiple colors and patterns seen in fish 1. Dermis produces pigment cells 2. Chromatophores – pigment cells a. Melanophores – brownish-black pigment b. Erythrophores – red pigment c. Xanthophores – yellow pigment d. Iridophores – contain crystals that reflect light giving a metallic look III. Fins A. Paired Fins 1. Pectoral – locomotion; side to side movement 2. Pelvic – stability in swimming B. Unpaired Fins Aquatic Science Unit 9 Notes 1. Adipose – stability 2. Anal – stability in swimming 3. Caudal – tail fin; propels fish 4. Dorsal – stability in swimming C. Supported by Two Types of Rays 1. Soft Rays 2. Spiny Rays IV. Lateral Line A. A series of scales modified by a pore B. Pores connect to a canal system containing sensory cells and nerve fibers C. Easily seen as a dark band running from gills to tail fin D. Serves as an Echolocation device V. Internal Anatomy A. Respiratory System 1. gills remove O2 from H2O (some fish do have lungs) 2. Operculum – the hard bony structure covering the gills 3. Swim Bladder (Air or Gas Bladder) a. Expandable sac similar to a human lung b. Function: buoyancy organ c. Allows fish to change its density B. Cardiovascular System 1. Heart - 2 chambers: Atrium & Ventricle 2. Closed circulation 3. Path of circulation – blood to heart to gills to body 4. Has both red and white blood cells C. Excretory System 1. Consists of gills and kidneys 2. Anterior and Posterior kidney 3. Function: Osmoregulation – process that maintains osmotic pressure of bodily fluids to sustain homeostasis of electrolyte and water content D. Digestive System – Stomach, Intestine, Liver, Pancreas E. Neuro-endocrine System – brain and spinal cord F. Electrical System in Some Fish (electric eel, electric catfish, electric ray) G. Sensory 1. Fish have all 5 senses 2. Fish can detect electrical currents 3. Lateral line plays huge role in the sensory processes of fish