Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles and Birds (Chapter 28
advertisement

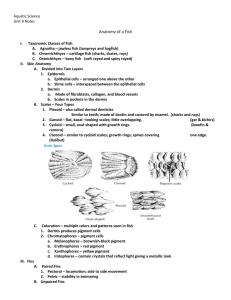
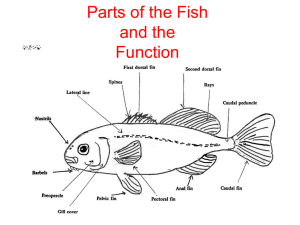
Fish, Amphibians, Reptiles and Birds (Chapter 28-29) Characteristics of Vertebrates - - - Have a backbone Specialized cells that develop into a nerve cord o Neural crest forms – a group of cells that develop form the nerve cord, which portion of the brain, skull and sense organs develop Vertebral Column o Spinal cord o Surrounds and protects the dorsal nerve cord o Replaces the notochord with cartilage (tough flexible material) or bone o Strong flexible rod for muscles to attach to o Allows for increase in speed and strength Closed circulatory system Characteristics of Fish - - - - - Most have a vertebral column Jaws o Allows to prey on larger animals o Defense against predators Paired fins, o Used for balance and steering and propulsion Scales o Ctenoid scales and Cycloid scales are made of bone and skin and are thin and flexible o Placoid scales are made of toothlike materials and are rough and heavy o Ganoid scales are diamond shaped and made of both enamel and bone Gills o Covered with lamellae- folded structures of the gills containing many vessels to diffuse oxygen and carbon dioxide from the blood o About 85% of oxyen is removed o Operculum is a movable flap that covers the gills protecting them and it also aids in pumping water Single looped circulatory system o Heart pumps blood in vessels o Blood passes heart one direction then to gills, then through the body delivering oxygenated blood o Hearts have two main chambers Atrium which receives blood from the body Ventricle which pumps blood from the heart to the gills Feeding and digestion o - - - - Fish swallow food passes through the esophagus to the stomach where digestion begins o Pyloric ceca a small pouch at the junction of the stomach and the intestine that secretes enzymes for digestion and absorption into the blood stream Excretion o Cellular wastes are filtered by kidneys o The main functional unit of the kidney is the nephron, which is a filtering unit that helps maintain the salt and water balance of the body o Some cellular wastes excreted by the gills Brain and senses o Nervous system consists of a brain and spinal cord o Cerebellum is involved in coordinating movement and controlling balance o Receptors that sense smell and detect chemicals in the environment o Olfactory bulbs record and respond to incoming chemical input o Color vision, optic lobes responsible for visual input o Cerebrum coordinates input from other parts of the brain o Medulla oblongata controls the internal organs o Lateral line system are special receptors that enable fish to detect movement and it keeps them upright and balanced Reproduction o External fertilization o Spawning in when females and males release gametes near each other in the water o Sharks reproduce internally Movement o Streamlined bodies o Mucus that lubricates surface to reduce friction o Swim bladder is a gas-filled space that allows fish to control their depth Classes of Fish - - Jawless fish o Class Myxini is the hagfish No scales, eel like shape, no fins, no bony skeleton Have a notocord Live on sea floor and feed on dead fish or invertebrate Produce slime to prevent from being caught by predators o Class Cephalaspidomorphi Lampreys No scales, eel like shape, no fins, no bony skeleton Have a notochord parasitic Cartilaginous fish o o - Body made of cartilage Class Chonodrichthyes Sharks, skates, rays Several rows of teeth Streamlined bodies Sense chemicals in water Lateral lines Whale sharks are filter feeders Bony fish o Class Osteichthyes Rayed fish : most fish today Lobed fish have muscular joints like land vertebrate Use lungs to exchange air like the lung fish Amphibians - - - - Characteristics o Frogs, newts, salamanders, toads, legless caecilians o Four legs o Moist skin with no scales o Gas exchange through skin o Lungs o Double loop circulatory system o Aquatic larvae Feeding/digestion o Frog larvae are herbivores o Salamander larvae are carnivores o Adults in both are carnivores feeding on invertebrates and small vertibrates o Jaws or tongues used to catch prey o Mouth---esophagus----stomach----small intestine----large intestine o Cloaca is a chamber that receives the digestive wastes, urinary wastes, and egg or sperm before they leave the body Excretion o Filter wastes through kidneys o Excrete ammonia or urea as wastes products of cellular metabolism o Ammonia is the end product of protein metabolism excreted by those that live in water o Urea is made from ammonia in the liver and stored in the bladder for those on land Respiration o Through skin and gills Circulation o Double looped - - First loop moved oxygen poor blood from the heart to pick up oxygen in thelungs then back to the heart Second loop moves oxygen filled blood from the heart to the body where diffused out Have a three chambered heart Two atria o Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from body o Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from lungs ventricle Brain and senses o Nictitating membrane is a transparent eyelid that can move across the eye to protect it underwater and keep it from drying out on land o Tympanic membrane is an external eardrum to hear high pitched sounds and to amplify sounds from their vocal cords o Ectotherms they obtain their body temperature from the external environment Reproduction o Lay eggs in water to be fertilized by males Orders of Amphibians o Order Anura these are the toads and frogs Lack tails Frogs have longer and more powerful hind legs than toad Frogs moist smooth skin toads dry and bumpy o Order Caudata these are the salamanders and newts Long slim line bodies Have tails Moist and smooth o Order Gymnophiona these are the caecilians No legs Wormlike Internal fertilization Feed on worms and other invertebrates