Subject: Hazardous Drugs Safety and Health Management
advertisement

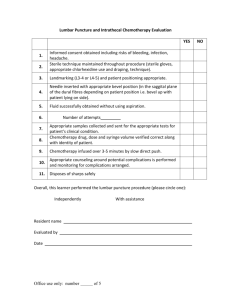
Number: HM 04 Subject: Hazardous Drugs Safety and Health Management Purpose: This policy ensures that employees exposed to Hazardous Drugs (HDs), including Chemotherapy Drugs, have the appropriate understanding of the health effects of exposure to these drugs, understand proper handling techniques for handling and disposal, and understand the use of appropriate Personal Protective Equipment. Policy: All employees working with, or having the potential exposure to hazardous drugs, including chemotherapy agents, will be knowledgeable in the health risks associated with it and understand appropriate safe handling procedures. Related Policy/Procedures: Pharmacy: Toxic and Hazardous Substance Policy Laboratory: LCHP 010: Patient-related Chemical Hazards. "Radiation" and "Ribavirin" Therapy Precautions "Chemotherapy" Specimens Responsibilities: Facility Safety Officer will provide and maintain a program which meets the intent of OSHA Standards and other regulatory guidelines related to Hazardous Drugs, and provide technical services to local management in the implementation of this program. Local Management is responsible for reviewing the specifics of this program with any new staff before handling HD's and providing resources needed to comply with all parts of the program. Employees are responsible for following the Hazardous Drugs procedures. Staff who are attempting to become pregnant are encouraged to discuss how their exposure to HD's might affect their pregnancy with their health care provider and Unit Director and implement changes as necessary to avoid reproductive risks. Staff who are pregnant or breast-feeding should not be involved with the preparation, administration or disposal of chemotherapy drugs/wastes. Pharmacy is responsible for following all applicable regulatory requirements regarding any new hazardous drugs requested. All Hazardous Drugs will be prepared in pharmacy for administration on the nursing units. They will maintain a current listing of HD’s used. The HD’s respective material safety data sheets will be forwarded to MSDS manager. Definitions: Anti-neoplastic drugs are cytotoxins that are used in cancer chemotherapy. These drugs are characterized by interfering with or by preventing the growth and development of malignant cells. Most chemotherapy agents either bind directly to 2/15/2016 1 Hazardous Drug Safety genetic material in the cell nucleus or affect cellular protein synthesis. Cytotoxic drugs may not distinguish between normal and cancerous cells. The growth and reproduction of the normal cells are often affected during treatment of cancerous cells. Corrosive substances have the chemical hazard of visibly destroying or irreversibly damaging living tissue by chemical action (rapid corrosion of living tissue). The main hazards are damage to eyes, skin and tissue under them, but inhalation or ingestion of a corrosive can damage the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Hazardous drugs (HD) are capable of causing toxicity to personnel and others who come in contact with them. Anti-neoplastic/chemotherapy drugs are hazardous drugs. HDs possess any of the following characteristics: genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, teratogenicity and/or fertility impairment (i.e. mutagenic or reproductive toxicant properties) or are acutely toxic to an organ system. These drugs include chemotherapy, hormone agents, bioengineered drugs and some antiviral drugs. HAZARDOUS DRUG SAFETY AND HEALTH PLAN: I. II. III. Effected Departments and Personnel. Preparation, administration, and disposal of HDs may expose pharmacists, nurses, physicians, and other health care workers to potentially significant workplace levels of these chemicals. Risks to personnel working with HDs are a function of the drugs' inherent toxicity and the extent of exposure. The main routes of exposure are: inhalation of dusts or aerosols, dermal absorption, and ingestion. Affected departments may include the following: Nursing Units, Pharmacy, Medical Imaging, Environmental Services and departments that treat patients who have received chemotherapy within the last 48 hours. The following activities can result in exposures to HDs: 1. Reconstituting and compounding powered drugs 2. Counting uncoated pills, crushing pills 3. Breaking open ampules 4. Expelling drugs from syringes 5. Expelling air from a drug-filled syringe 6. Administration by IV, intramuscular or subcutaneous injection 7. Touching drugs on vial exteriors, work surfaces, floors 8. Aerosols generated by IV push or IV infusion 9. Priming IV sets 10. Leakage from tubing, syringe or stopcock 11. Handling contaminated wastes, linens, body fluids, clothing, and dressings 12. Contact with contaminated PPE Health Effects. Published studies have shown that workplace exposures to hazardous drugs can cause both acute and chronic health effects. The health risk depends upon the degree of exposure to these drugs and the toxicity of the drugs 2/15/2016 2 Hazardous Drug Safety themselves. Employees who are pregnant, actively trying to conceive or breastfeeding must understand these risks and respond accordingly. Female personnel who are pregnant or breast-feeding will not be involved with the preparation, administration or disposal of HDs or wastes. Characteristics of HDs that adversely effect health are or cause: 1. Carcinogenic 2. Teratogenic 3. Adverse reproductive effects/fertility impairment a. Mutagencity damage kills somatic cells b.Changes in DNA and reproductive cells 4. Serious organ or other toxic manifestation 5. Physical hazards a. Skin rashes b.Sensitivity IV. V. VI. Types of Hazardous Drugs: The pharmacy will maintain a listing of hazardous drugs. Routes of Exposure 1. Inhalation- airborne is considered the greatest risk according to OSHA. Exposures can occur during the following activities: a. Withdrawing syringe from IV port b.Changing IV piggy backs c. Expelling air from syringe d.Handling waste e. Handling patient excretions f. Spills g.Withdrawing syringe from vial h.Breaking medication ampule 2. Skin contact- HD may settle on surfaces and during the following activities: a. Needle sticks b. Skin exposure to leaks on tubing, syringe c. Handling patient excretions. Precautions should be instituted for at least 48 hours 3. Ingestion- exposures may occur due to the following activities: a. Food/drinks (contaminated) near agent during administration b.Poor hand hygiene c. Poor Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) removal Training 1. Employees who work directly with chemotherapy drugs are required to attend specialized training. These employees must pass the Chemotherapy Competency in order to administer these drugs. 2. All employees who have a potential for exposure to hazardous drugs (preparation, transport, administration and disposal) will receive training on proper handling 2/15/2016 3 Hazardous Drug Safety and disposal techniques. For departments that have extensive preparation or administration of HDs, periodic training along with additional training when new HDs are introduced to the department is required. Department directors shall ensure that this instruction is conducted. This training shall include the following: A. Physical and health hazards of the HD’s in the work area. B. Understanding the preparation, administration, transportation and disposal issues of HDs as it relates to their department. C. Understand the measures staff can take to protect themselves from the hazards, such as PPE, spill procedures, and how to obtain an MSDS for the HDs. D. Periodic observations of drug preparation and administration practices are conducted to determine the need for training in work practices to further reduce exposure. E. Department director will maintain training records. These records will be maintained for three years from the date of training and will include the following: a. The date of training b. Contents/summary of training c. Name and qualification of trainer d. The name and job title of all persons attending the training session VII. Personal Protective Equipment 1. Gloves A. Disposable double gloves will be worn for all procedures involving HDs (including chemotherapy drugs and corrosive agents) including administration of the agents, cleaning of spills and disposing of excreta (urine, feces, vomitus) from a patient who has received chemotherapy within the past 48 hours. B. Change gloves every 30 minutes or immediately after overt contamination C. Care must be taken to avoid puncturing gloves and possible selfinoculation. D. Wash hands with soap and water before and after glove use. 2. Protective gowns A. Protective disposable gowns made of a low-permeability fabric should be worn for all procedures involving HDs. B. Gowns should have a closed front, long sleeves, tight cuff (either elastic or knit), and closed back. Cuffs will be tucked under disposable gloves. C. Gowns are meant for single use and should not be reapplied after removal. D. Gowns should be changed immediately and disposed of into the appropriate chemotherapy waste container if they are torn, punctured or contaminated. E. All potentially contaminated garments or gloves will not be worn outside the work area. 2/15/2016 4 Hazardous Drug Safety 3. Eye and face protection A. Face shields are used for administering chemotherapy agents. B. It is recommended to wear eye protection for all procedures where there is a potential for splash of airborne HDs, chemotherapy drugs, or contaminated wastes. C. Goggles must be worn when handling corrosive drugs. VIII. Hazardous Drugs Specific Procedures 1. Transport: Receiving and Handling The following must be done in the receiving and handling of HDs: A. Transport must be done in sealed container. B. No transport is allowed via the pneumatic tube system. C. Drug packets, bins, shelves and storage areas must bear distinctive labels identifying those drugs requiring special handling. D. Hazardous drugs must be stored in a manner to prevent accidental breakage. E. Hazardous drugs must be separated from regular stock to help prevent errors. F. Double gloves must be worn when stocking or handling hazardous packages. G. Employees must understand proper spill response. 2. Hazardous Drug Preparation (Pharmacy) A. Chemotherapy agents will be compounded by trained personnel in Pharmacy. Access to the compounding area will be limited to only necessary authorized personnel. All mixing of HDs shall be performed in a Class II biological safety cabinet (laminar Flow Hood- air moves downward) with outside venting. This area will be designated and labeled as a HD preparation area. Special aseptic techniques and precautions must be used because of the downward airflow. B. Except in an emergency, no other IV admixtures will be prepared in the Biological Safety Cabinet designated for the mixing of HD agents, to reinforce the need for special precautions and procedures. C. The biological safety cabinet's ventilation system shall remain on at all times. D. Drug preparations shall be performed only with the viewing window of the hood at the required access opening (8 inches or less). E. All internal surfaces of the biological safety cabinet will be cleaned before and after drug preparation using > 70% alcohol and 4 x 4 gauze. The gauze will be discarded into the appropriate leak-proof waste container. F. The biological safety cabinet will be certified by a qualified technician every 6 months or any time the cabinet is moved. 2/15/2016 5 Hazardous Drug Safety G. Spill kits and clean-up protocol will be available in the HD preparation area. H. At all times staff shall use appropriate personal protective equipment (gloves, gown, mask and eye protection). 3. Compounding Techniques (Pharmacy) A. Double disposable gloves will be worn during drug compounding activities. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. B. Syringes with luer-lock fittings should be used whenever possible. C. A sterile plastic-backed absorbent drape will be placed on the work surface during mixing procedures. The drape will be exchanged whenever substantial spillage occurs or at the end of each production sequence. D. Vials should be vented with a chemotherapy dispensing pin to eliminate internal pressure or vacuum. E. Before opening ampules care should be taken to ensure that no liquid remains in the tip of the ampule. An alcoholed sterile gauze sponge (2X2) should be wrapped around the neck of the ampule while opening. F. Final drug measurement should be performed before removing the syringe from the chemotherapy dispensing pin and vial. G. A puncture resistant "sharps" disposal container, designated for chemotherapy waste, will be available at the biological safety cabinet for the disposal of excess drug solutions. These containers will also be used to dispose of ampules and filter needles. H. During drug preparation, the exact dose is drawn up into a syringe and a "red" syringe cap is attached. The administering nurse will replace the cap with a needle but will not prime the needle. I. The top glove should be removed and placed on the sterile barrier. J. After preparation, the sides and tops of the vials, syringes, and IV bags will be wiped down with an alcohol swab to minimize touch contact with the drug. K. The sterile barrier should be enclosed, taped, and placed in hazardous waste container. Products should be labeled, placed in the sealed container, and the inner gloves removed. L. Special procedures shall be followed for major spills or acute exposures. 4. Dispensing Techniques A. IV solutions are to be labeled as described in the IV policies and procedures. Bag sequence numbers should also be added to the label. B. Syringes and plastic zip-lock bags containing HDs will be labeled with the drug name (generic) and strength, the volume in the syringe, the expiration date and time. The zip-lock bag will also be labeled with patients name and room number, and a chemotherapy caution label. C. IV Bags and syringes will be dispensed in zip-lock bags. a. IV Bags in clear zip-lock bags b.Syringes in amber (light resistant) zip-lock bags 2/15/2016 6 Hazardous Drug Safety c. The zip-lock bags will be dispensed to the nursing units refrigerator, except drugs that require no refrigeration D. Avoid manipulations that can cause splattering, spraying or aerosal generation. Examples include: a. withdrawal of needles from vials b.drug transfers using syringes, needles or filter straws c. breaking open of ampules d.expulsion of air from drug-filled syringes. 5. Hazardous Drug Administration A. Set Up: Patients who are being treated with chemotherapeutic agents will be placed on chemotherapy precautions from the time the chemotherapy is initiated through 48 hours after the last dose is completed. a. A private patient room is preferred. b. A “Chemotherapy Precautions” sign is placed on the patient’s door to inform hospital personnel of the need for use of standard precautions. The sign will state the start and end date precautions need to be implemented. c. The Kardex in Epic will have documentation that patient is on chemotherapy precautions. d. Yellow chemotherapy hazard buckets will be placed in the patient’s bathroom for disposal of chemotherapy tubings, syringes, and IV bags. e. Yellow chemotherapy bags will be placed in the patient bathroom for disposal of any disposable items contaminated with chemo agents or body fluids. f. A chemotherapy drug spill kit will be placed on the nurse server while patient is receiving chemotherapy. Directions for use are included with the kit. B. Administration a. Chemotherapy will be administered with a second nurse to double check calculations of rate and volume. Signing of two nurses will be documented in the Epic MAR. b. The following PPE will always be worn: long-sleeved disposable gowns, double gloves, and face shield. c. Work below eye level. d. Tubing will be primed with normal saline and the chemotherapy bag will be spiked over a disposable, absorbent, plastic-backed liner (chux). e. A guaze pad will be used under the syringe at injection ports to catch droplets during administration. f. Use needles, syringes, and tubing with Luer lock connectors. g. The IV line and IV pump channel will be labeled with a brightlycolored “chemotherapy” sticker. 2/15/2016 7 Hazardous Drug Safety h. After administration, remove the IV container with the tubing attached. Do not remove the spike from IV containers or reuse tubing. C. After Delivery: All chemotherapy items will be removed from the patient's room once date/time has passed. a. Contaminated disposable supplies used to adminster chemotherapy must be discarded into the yellow chemotherapy bucket. These include: i. IV tubings and bags from infused chemotherapy agents. ii. Empty syringes (or other containers) and needles. iii. Excess concentrated chemo drugs. iv. Empty ampules, vials and bottles containing scant amounts of chemo drugs. b. Contaminated disposable PPE and waste will be placed in a yellow chemotherapy bag. These include: i. PPE used during the administration of chemotherapy or in cleaning up of spills/patient body fluids. ii. Plastic backed absorbent liners, hygiene wipes, diapers, gauze. iii. Empty pill wrappers from oral chemotherapy drugs. iv. Any other disposable items contaminated with chemotherapy agents of patients body fluids/excreta. 6. Laboratory A. Specimen containers, containing samples for laboratory analysis, will be handled as follows: a. Labeled with a yellow "chemotherapy" sticker. b.Clean on the outside (not contaminated) prior to being transported to the laboratory. B. Double gloves will be worn by laboratory or nursing personnel when handling a specimen for lab analysis. Hands will be washed upon removal of disposable gloves. 7. Handling a Patient’s Body Fluids: A. Excreta from patients undergoing chemotherapy may contain quantities of cytotoxic drug or metabolic products. The following standard precautions will be followed for 48 hours after the administration of a HD: a. Double gloves and disposable gown will be worn when handling the body fluids and/or excreta of patients who have received antineoplastic drugs within the previous 48 hours. b. Flush the toilet with the lid down after disposing of excreta from patients who have received antineoplastic drugs within the previous 48 hours. If a lid is not present, cover the open toilet with a plastic-backed pad to prevent splashing. 8. Linen Handling 2/15/2016 8 Hazardous Drug Safety A. All non-soiled, non-contaminated linens should be placed in a blue plastic laundry and sent as normal laundry. B. Linen contaminated with chemotherapy agent spills and/or body fluids from a patient who has received chemotherapy within the past 48 hours will be placed into the yellow chemotherapy waste bag. This bag will then be put into the blue plastic bag designated for laundry and sent down the linen chute. Double gloves will be worn by laundry personnel when handling this linen. 9. Hazardous Drug Waste Disposal A. Hazardous drug waste cannot be discarded in the “red” infectious waste containers. B. Access to all areas where cytotoxic drugs are stored will be limited. C. All drug waste will be labeled with a chemotherapy caution label. D. All chemotherapy waste will be placed in either the yellow bags, the yellow sharps containers or in the black hazardous waste containers. a. Yellow bags- All disposable items that have come in contact with HDs during preparation or administration will be discarded the yellow bags. The top will be twisted and the neck of the bag secured with tape when full. Items to be discarded in the yellow bags are: i. PPE used during the administration of chemotherapy or in cleaning up of spills/patient body fluids. ii. Plastic backed absorbent liners, hygiene wipes, diapers, gauze. iii. Empty pill wrappers from oral chemotherapy drugs. iv. Any other disposable items contaminated with chemotherapy agents of patients body fluids/excreta. c. Yellow chemotherapy buckets- Contaminated disposable supplies used to adminster chemotherapy must be discarded into the yellow chemotherapy bucket. The bucket will have the top secured firmly to the base and the access panel secured in place prior to setting aside for disposal. Items to be discarded in the yellow buckets include: i. IV tubings and bags from infused chemotherapy agents. ii. Empty syringes (or other containers) and needles. iii. Excess concentrated chemo drugs. iv. Empty ampules, vials and bottles containing scant amounts of chemo drugs. b. Black hazardous waste buckets- will have the top secured firmly to the base and the access panel secured in place prior to setting aside for disposal. Items to be discarded in the black buckets are: i. Excess concentrated drugs or prepared drug solutions ii. Misformulated drug solutions iii. Expired concentrated drugs iv. Vials & bottles which contain drugs v. Ampules which contain drugs E. Chemotherapy waste containers may not be overfilled. F. Excreta may be disposed of into the sanitary sewer system. 2/15/2016 9 Hazardous Drug Safety G. Chemotherapy/HD waste will be collected by the Housekeeping Department using the red colored isolation trash carts. H. All chemotherapy waste will be destroyed by incineration. The chemotherapy waste is stored at the MERI facility until it is picked up and transported to a facility having an incinerator approved for this type of chemical destruction. 10. Exposure Incident A. Spills of these agents on skin should be treated immediately. Check the MSDS sheet for the HD for health/physical hazard information. MSDS are available on the St. Mary’s Intranet home page under Policies and Procedures or call pharmacy (Ext. 6551). B. In the event of skin contact with a HD, remove contaminated clothing, flush exposed area with large amounts of water. Wash the area thoroughly with soap and water for five minutes and rinse thoroughly. C. In the event of eye contact with HD drugs, immediately flush the eye (eye lid held open) with normal saline or water for fifteen minutes. D. Obtain medical attention through Employee Heath or the Emergency Room. E. Report exposure to your supervisor. F. Complete an Incident Report for all chemotherapy spills/exposures. 11. Hazardous Drug Spills With all accidental spills, staff must refer to the appropriate MSDS for instruction, notify their site supervisor and document the spill on the Incident Report form. Everyone who works with HDs should be trained in spill cleanup. Yellow chemotherapy bags and containers will be placed in the patient’s room for the entire time the patient is on chemotherapy precautions. Chemotherapy spill kits will be placed at the nurse server until the chemotherapy administration is completed. In the event of breakage of containers of powder or liquid carcinogenic drugs the following procedure will be followed: A. Appropriate safety attire will be worn a. Disposable gown b. Eye protection c. Double gloves d. Surgical mask B. Place chemotherapy sign in the spill kit adjacent to the spill to prevent people from accidently walking through the spill area. C. Use the absorbent towels from the kit to cover and wipe up spills and place the used towels into the yellow chemotherapy bucket. D. Broken glass fragments, sharps, absorbent pads, and any noncleanable contaminated items will be placed into the yellow chemotherapy waste bucket. E. Gloves and outer protective garments used in the cleanup will be removed and placed into the yellow chemotherapy waste bags. 2/15/2016 10 Hazardous Drug Safety F. After the initial clean up, leave the chemotherapy sign in place and contact Environmental Services for a thorough cleanup of the spill area. The area will be cleaned three times with detergent and then the mophead will be disposed of in a yellow chemotherapy bag. G. Chemotherapy Spill Kit Locations: a. Pharmacy in the Ante/Sterile Room (Room #L401C) (Ext. 6551). b.5SW Medical Intermediate/ Oncology Unit in the "Clean" Utility room 5653 (Ext. 6670). 12. Record Keeping. All training records, any exposure monitoring, medical records and disposal manifests should be maintained in accordance with OSHA 29 1910.1020. 13. Monitoring A. The toxicity of antineoplastic and hazardous drugs dictates that the exposure of medical personnel to these drugs should be minimized. B. The personnel working with these agents should be observed regularly by supervisory personnel to ensure compliances. C. Acute exposure episodes must be documented. The employee should be referred for professional examination. D. Employee Health will maintain the confidential employee health file and will include in the employee health file copies of medical surveillance questionnaires and related documentation and any employee exposure records (i.e. Incident Report forms). These confidential records are maintained separate from the individual’s personal medical file. 14. Program Review. This program will be reviewed and updated on an annual basis, or whenever necessary, to reflect changes in regulations by the Facility Safety Officer. REFERENCES: CDC: NIOSH Alert: Preventing Occupational Exposure to Antineoplastic and other Hazardous Drugs in Health Care Setting. DHHS (NIOSH) Publication Number 2004–165 retrieved 2/10/2010 from http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/docs/2004-165/ OSHA Hazard Communication Standard: 29 CFR 1910.1200. Polovich, M., Whitford, J., Olsen, M. (2009). Chemotherapy and biotherapy guidelines and recommendations for practice (third edition). Pitsburgh, PA: Oncology Nursing Society. The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations. Joint Commission 2009 Accreditation Requirements Chapters: Accreditation Program: Hospital, Pre-Publication Version, 2008. 2/15/2016 11 Hazardous Drug Safety REVIEWED BY: *Diana Quinn, Safety Officer Kelly Mitchell, CNS FORMULATED: REVISED: 8/07 9/08, 7/09, 2/10 REVIEWED: 2/10 * Designates who is responsible for review, update, and master/original directive. 2/15/2016 12 Hazardous Drug Safety