Study Guide: Europe - Glynn County Schools

Study Guide: Europe
I.
3 Major Religions
A.
Christianity - Largest following ,based on teachings of Jesus, Bible is sacred text
B.
Islam - fastest growing, based on teachings of Muhammad, Quran is sacred text, Mosque place of worship
C.
Judaism - Abraham is founder, Torah is sacred text, Synagogue is place of worship
II.
Languages
A. Romance - Based on Latin - French, Spanish, Italian
B. Germanic – English and German - largest population
C. Slavic – Russian - uses Cyrillic alphabet
III. History
A.
Crusades: attempt to take back Holy Land from Muslims 1096-1272
B.
Trade with Asia made Italy rich; England ,Portugal, Spain, & France get mad about profits
C.
Prince Henry the Navigator of Portugal set up navigation school 1400s a.
Dias explored to southern tip of Africa b.
Da Gama explored to India
D.
Spain – 3 rd largest empire - sent Columbus to Asia – found “New World” instead; Spain got most of South America and Mexico a.
Portugal – earliest European empire - got Brazil
E.
England (Great Britain) – largest empire - got North America, Australia,
India, and much of Africa
F.
France - 2 nd largest empire – got part of Canada
G.
World War I (aka The Great War - 1914-1918) a.
Causes i.
Colonization – 1 country taking resources from another country ii.
Imperialism -taking over a country to make it part of yours iii.
Militarism – building strong armies
iv.
Nationalism – love of your country – willing to fight and fie for it v.
Alliance System – agreements among countries to defend each other in time of war b.
2 sides: i.
Allied Powers - UK, France, Russia, USA, Italy ii.
Central Powers – Germany, Austria- Hungry, Ottoman Empire
(Turkey and the countries it ruled) c.
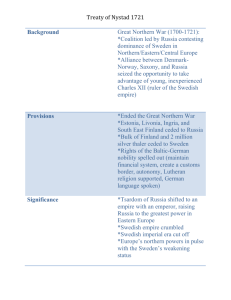
Results: Allied Powers win; make Germans sign Treaty of Versailles which punishes Germany. Treaty takes away Germany’s territories, makes them pay for damages, weakens military, and they have to accept responsibility for WWI.
H.
Russian Revolution a.
Causes: i.
Tsar is an absolute monarch ii.
He is out of touch with people iii.
People have no food, no jobs, and no money iv.
The Great War is a disaster - causes heavy losses b.
Events: Lenin leads a revolution in Russia, which becomes communist
(new name is ‘Union of Soviet Socialist Republics’ or ‘Soviet Union’ or
U.S.S.R.) and gets out of the war with Germany
I.
1920s till 1929 – “Roaring 20s” – time of economic growth (except for
Germany)
J.
1929 – Stock Market Crash; world falls into a worldwide depression.
K.
The stress of the Treaty of Versailles on the German people leads to the rise of Hitler (1933 – becomes Chancellor of Germany) and Nazism (belief that leader should have absolute power, militarism, and belief in German ethnic
& cultural supremacy).
L.
WWII: 1939-1945 a.
Causes i.
Imperialism ii.
Fascism (believe war is good; militarism; leader with absolute power)
iii.
Militarism iv.
Economic problems – The Great Depression v.
Nationalism: Treaty of Versailles angered Germany vi.
Racism b.
2 sides i.
Allies: United Kingdom, France, Soviet Union, United States ii.
Axis: Germany, Italy, Japan c.
Events: i.
Hitler invades Poland - 1939 ii.
1941: Japan attacks United States at Pearl Harbor iii.
Hitler uses genocide (called Holocaust) to eliminate Jews (6 million die) and anybody else he feels threatens Nazi Germany. iv.
1945: United States drops 2 atomic bombs on Japan v.
Germany loses war to USA, United Kingdom, and the USSR;
Hitler dies.
M.
Cold War 1947- 1991. a.
Rise of the USA and USSR as superpowers b.
USA and USSR fight Cold War of government and economic systems - whose is better. c.
NATO is the USA, Canada, western Europe alliance; Warsaw Pact is
USSR (central and eastern Europe) d.
Cold War ends when Soviet Union collapses economically. Germany
(divided after WWII – Berlin Wall built 1961) is reunified (Berlin Wall taken down 1989), and Eastern European countries get right to vote.
IV. Environmental Issues
A.
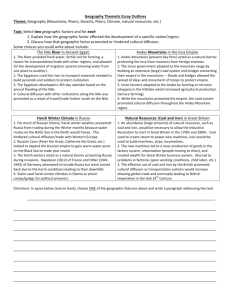
United Kingdom: Air pollution (Smog) [Great Smog of 1952 – lasted 4 days and thousands died] a.
Causes: i.
Burning coal ii.
Car/ diesel exhaust iii.
Weather – high pressure, cold air, high humidity trapped smoke b.
Effects:
i.
Lung illnesses ii.
Blackens buildings iii.
Threatens wildlife c.
Solutions: i.
Smokeless zones (no smoky fuels) ii.
Cleaner coal, taller chimneys iii.
Increased use of electricity & natural gas iv.
Laws to make cars produce cleaner exhaust v.
People drive less vi.
BUT - U.K. still has air pollution from automobile exhaust emissions.
B.
Germany: Acid Rain a.
Causes: i.
Smoke from factories and power plants ii.
Car and bus exhaust b.
Effects: i.
Eats holes in statues and buildings ii.
Damages soil and trees iii.
Pollutes rivers iv.
Kills wildlife c.
Solutions i.
Factories can use water power instead of coal ii.
Laws reduce car & factory emissions iii.
Factories clean smoke that leaves smokestacks iv.
New energy sources – wind and solar power- leading producer in the world
C.
Chernobyl, Ukraine – nuclear disaster a.
What happened – nuclear power station exploded in 1986 b.
Effects: i.
Land and people exposed to radiation ii.
Poisoned land and water iii.
Poisoned air as far away as Scandinavia iv.
Reactor was buried in concrete.
v.
It still is not safe. vi.
28 emergency workers died within months. vii.
Drinking water was unsafe for months. viii.
Cancer rates have increased ix.
Because of wind currents, a mistake in one country can affect other countries!
V.
Economics
A.
Most European countries have a mixed economy lying somewhere on a continuum between command and market – Russia lies closer to command, while Germany is closer to market, and U.K. is even closer to market.
B.
The European Union has 27 members i.
Purpose:
1.
work together to improve …
2.
trade
3.
education
4.
farming
5.
industry ii.
Results:
1.
Euro – currency ($$$) of the EU (makes trade between countries easier)
2.
No taxes on goods traded between EU countries (Freetrade zone)
3.
Citizens can move from 1 EU country to another, live and work in any EU country, and even vote in another EU country.
VI. Geography
A.
Gulf Stream is a current flowing in the Atlantic Ocean that carries warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to northern Europe – makes the climate of U.K. warmer.
B.
Germany: i.
Marine climate (mild – cold winters, warm summer) ii.
Mostly urban population – live in cities along rivers
iii.
Resources: coal, iron…
C.
Italy: i.
Mediterranean climate (warm dry summers, cool wet winters) ii.
Mostly urban population – live along coast and in north iii.
Resources: fish and grapes (wine)
D.
U.K.: i.
Small island ii.
Gulf Stream keeps water warm – ports stay ice-free all year iii.
Marine climate iv.
Mostly urban population in cities along rivers and coasts v.
Resources: fish, coal – big banking/insurance center
E.
Russia: i.
Largest country in the world (land area) ii.
Marine climate near ocean, semi-arid (dry) in south, humid continental (warm humid summers, mild winters)in western, sub-arctic (cold!) in northern iii.
Mostly urban population – mostly in western Russia near the rest of Europe, along rivers and coasts iv.
Ports are frozen much of year v.
Resources: gold, oil, coal – large, cold country makes it hard to get resources out of the ground
VII. Government
A.
U.K.: i.
parliamentary democracy, constitutional monarchy, unitary ii.
bicameral parliament (House of Commons [elected]; House of
Lords [inherited]) iii.
Prime minister is chief executive – chosen from House of commons – leader of political party with most members in
Parliament – runs the government, head of the military iv.
Queen [Elizabeth II] is head of state – mostly symbolic v.
People elect members of House of Commons vi.
Many freedoms
B.
Germany:
vii.
Federal, parliamentary democracy viii.
Bicameral parliament (Bundestag and Bundesrat) ix.
Chancellor – runs the government, head of the military x.
President – head of state – mostly symbolic xi.
People elect parliament; parliament chooses chancellor and president xii.
Many freedoms – Germany is Welfare State – government takes care of those unable to work
C.
Russia: xiii.
Federal, presidential democracy xiv.
Bicameral: Duma and Federation Council xv.
2 chief executives: president (head of state, controls military, more power)and premier (selected by president – runs the government) xvi.
People elect Duma members and president; Federation
Council is not elected xvii.
More freedoms than in the past