CHEMISTRY COURSE OUTLINE-YEAR 11
advertisement

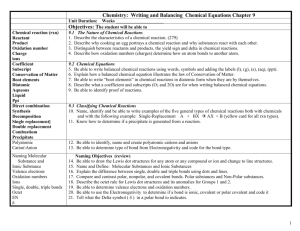
CHEMISTRY COURSE OUTLINE-YEAR 11 SEMESTER 1-2014 UNIT 2A CHE: CHEMISTRY IN AND AROUND THE HOME WEEK 1 WEEK 2 WEEK 3 Physical Properties ORIENTATION 2.1.6 relationship between the and uses of ionic a) Policies and Guidelines number of valence electrons substances. b) course outline and chemical properties of comparison of ionic grade descriptors elements in groups 1, 2 and bond strengths teaching/learning program 13–18 c) assessment outline, 2.1.7 formation of positive Bonding assessment policy and negative ions for formation and d)classroom rules/policies elements in groups 1, 2 and characteristics of: and procedures 13–18. covalent bonds 2 Atomic structure and covalent network Bonding and covalent molecular 2.1 Atomic structure and Bonding formation and substances Periodic Table characteristics of: relationships between 2.1.1 comparison of the metallic bonds and Physical properties and relative charge and relative metallic substances structures of covalent masses of protons, neutrons relationships between molecular substances and electrons properties and structures Names and formulae of 2.1.2 atomic number (Z) of metallic, substances covalent molecular 2.1.3 explanation of isotopes substances 2.1.4 writing the electron Ionic Bonding configurations for the first formation ionic substances writing names and ASSIGNMENT twenty elements (Na 2, 8, 1) 1 formulas of Ionic ANNOUNCED substances 2.1.5 position on the Periodic electron-dot or lewis Table and number of valence structures for Ionic electrons of elements in Substances groups 1, 2 and 13–18 WEEK 6 b) change of phase c) vapour pressure and factors that affect vapour pressure WEEK 7 e) the characteristics of gases d) effect on gases of changes in pressure, temperature and volume d) Boiling point of a substance 1.3 Solutions 1.3.1 saturated, unsaturated and supersaturated solutions 1.3.2 solubility and precipitation reactions 1.3.3 using the WEEK 8 1.3.5 strong, weak and nonelectrolytes 1.3.8 differences between concentrated and dilute solutions of strong and weak electrolytes. 1.3.4 colligative properties of solutions Revision for TEST 2 . WEEK 4 WEEK 5 1.1.2 pure substances, homogeneous mixtures and heterogeneous mixtures representations of covalent molecular substances using electron dot (octet only) or Lewis structure diagrams relationships between physical properties and structures of covalent network substances 1.2 Kinetic Theory 1.2.1. Using the Kinetic Theory of Matter to explain a) TEST 1: Atomic Structure and Bonding relationship between heat and temperature ASSIGNMENT 1 DUE 1.Macroscopic properties of matter 1.1.1characteristics homogeneous heterogeneous mixtures of and WEEK 9 WEEK 10 TEST 2: Macroscopic calculations involving mass to mass properties of matter CHEMICAL REACTIONS Reactions, equations and stoichiometry writing and interpretation of formulae of elements and compounds including molecules that have nonsystematic names including Types of Chemical mass to volume (gases at STP) volume to volume concentration calculations (mol L-1, g L-1 percentage composition by mass stoichiometric problems that interrelate mass, molar mass, number of moles of solute, and colour of ions to identify reactants and the products in chemical processes Reactions equations for simple chemical reactions using state symbols calculations involving molar volume of gases at STP in the evolution of gases simple calculations: molar mass mole to mole mass to mole ) WEEK 11 WEEK 12 WEEK 13 enthalpy (H) in terms of stored chemical energy endothermic and exothermic reactions in terms of bond breaking and bond making enthalpy diagrams and equations that include the heat lost or gained (ΔH). Reaction rates rate of a reaction in terms of rate of change of a measurable quantity with time . collision theory factors affecting rates of reaction: temperature concentration state of sub-division catalysts factors affecting rates of reaction: temperature concentration state of sub-division catalysts TEST 3: CHEMICAL REACTIONS ASSIGNMENT 2 ANNOUNCED ASSIGNMENT 2 DUE WEEK 16 WEEK 17 WEEK 18 FINAL EXAMS FINAL EXAMS energy profile diagrams of reaction relationship between collision theory, kinetic energy distribution graphs and the rate of a reaction. Applied chemistry examples of chemicals and their uses in and around the home including vinegar, bleach, ammonia solution and caustic soda -concentration units used in household mixtures (g 100g-1, mL L-1, g L-1, percentage composition by mass) REVISION FOR TEST 3 WEEK 14 relationships between properties and uses of ionic, metallic, covalent network and covalent molecular substances found in and around the home. WEEK 15 chemical formulae for molecular compounds investigation of real world problems in a laboratory setting common examples of endothermic and exothermic reactions and processes in and around the home including combustion, hot packs, cold packs, change of phase. FINAL EXAMS concentration and volume of solution Energy effects Using Law of Conservation of Energy to explain endothermic and exothermic reactions concepts of system and surroundings to energy transfer CLASSROOM EXERCISE examples where rates of reaction have been altered in and around the home WEEK 19 WEEK 20