Unit 3 Vocabulary
advertisement
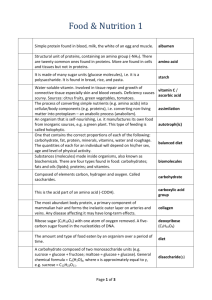
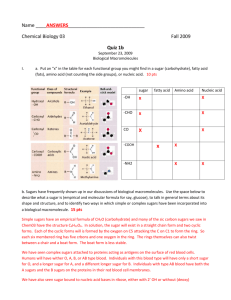
Unit 3 Vocabulary 1. atom 2. element 3. electron 4. neutron 5. molecule 6. compound 7. ion 8. chemical bond 9. chemical reaction 10. pH scale 11. acid (H+ ion)/ acidic 12. base (OHion)/alkaline/basic 13. neutralize 14. buffer 15. buffering capacity 16. catalyst 17. enzyme 18. substrate 19. active site 20. catalyst 21. enzyme-substrate complex 22. randomness/disorder 23. photosynthesis 24. chlorophyll 25. cellular respiration 26. organic compound 27. inorganic compound 28. ATP 29. ADP 30. synthesize (synthesis) 31. decomposition 32. hydrolyze/hydrolysis 33. carbon cycle 34. matter 35. Energy 36. Subunit 37. carbohydrate 38. monosaccharide (simple sugar) 39. disaccharide 40. polysaccharide 41. Starch 42. Cellulose 43. lipid 44. fat 45. fatty acid 46. cholesterol 47. nucleic acid 48. RNA (ribonucleic acid) 49. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) 50. protein 51. amino acid 52. polypeptide 53. poly54. mono55. di- Unit 3 Vocabulary 1. atom- the basic unit of matter; composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons 1. element- pure substance made of one type of atom; more than 100 types; arranged according to properties in the periodic table Unit 3 Vocabulary 3. electron- negatively charged particle around the nucleus of an atom; has very little mass 4. neutron- neutral particle found in the nucleus of an atom Unit 3 Vocabulary 5. molecule- smallest unit of a compound; multiple atoms bonded together (Ex: O2, H2O) 6. compound- two or more elements bonded together (Ex: H2O, CO2, H2O2) Unit 3 Vocabulary 7. ion- an atom with a positive or negative charge; # of e- does not equal # of protons (lost or gained e-) Unit 3 Vocabulary 8. chemical bond- the forces that hold atoms to one another in molecules; represented by lines in models 9. chemical reaction- process that changes one set of chemicals into another (Ex: photosynthesis) Unit 3 Vocabulary 10. pH scale- measure of H+ ions, acidity; ‘power of hydrogen’ 11. acid (H+ ion)/acidicsolution with lots of H+ ions (Ex: HCl) 12. base (OHion)/alkaline/basicsolution with los of OH- ions (Ex: NaOH) Unit 3 Vocabulary 13. neutralize- combining an acid and a base to form water 14. buffer- any substance that resists a change in pH 15. buffering capacity- the ability to resist a change in pH Unit 3 Vocabulary 16. catalyst- substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction 17. enzyme- a biological catalysts that speeds up chemical reactions (Ex: catalase, lactase) Unit 3 Vocabulary 18. substrate- molecule that is changed by the enzyme 19. active site- part of an enzyme that attracts and holds molecules that have the right shape 21. enzyme-substrate complex- when an enzyme is bound to an appropriate substrate and bonds are being broken and reformed Unit 3 Vocabulary 22. randomness/disorder- the idea that non-livings are always moving to a state of randomness while living things, on the other hand, invest energy to create organization Unit 3 Vocabulary 23. photosynthesis- process used by plants to create sugar using light energy 24. chlorophyll- the green pigment in plants that captures light in photosynthesis Unit 3 Vocabulary 26. organic compound- compounds containing C and H; come from living things 27. inorganic compound- compounds that do not contain C and H; don’t come from living things Unit 3 Vocabulary 28. ATP- adenosine triphosphate; important energy transfer compound in organisms 29. ADP- adenosine diphosphate; ATP that has had a phosphate removed to release energy Released Energy Unit 3 Vocabulary 30. synthesize (synthesis)- combine or put together 31. decomposition- breaking down or taking apart Unit 3 Vocabulary 32. hydrolyze/hydrolysis- the breaking of bonds by adding water (Ex: decomposing starch into glucose) Unit 3 Vocabulary 33. carbon cycle- how carbon is exchanged through the environment; includes photosynthesis & cellular respiration Unit 3 Vocabulary 34. matter- a physical substance that has mass and takes up space 35. energy- the ability to do work; stored in chemical bonds or found in light 36. subunit- a part of something (ex: a subunit of a polysaccharide is a monosaccharide) Unit 3 Vocabulary 37. carbohydrate- a macromolecule that has H and O in the same ratio as water, as well as carbon; ‘hydrated carbons;’ (Ex: sugar, starch, cellulose, chitin) Unit 3 Vocabulary 38. monosaccharide (simple sugar)- a single molecule of sugar 39. disaccharide- two linked sugars 40. polysaccharide- many linked sugars Unit 3 Vocabulary 41. starch- complex carbohydrate used for energy storage in plants; long chain of sugars 42. cellulose- complex carbohydrate used as building material in plants; found in cell walls; long chain of sugars Unit 3 Vocabulary 43. lipid- macromolecule that is mostly composed of C and H; includes fats, oils, wax 44. fat- lipid made up of fatty acids and glycerol; used for energy storage, cushioning, insulation 45. fatty acid- chain of linked carbons with many H bonds; component of lipids 46. cholesterol- a type of lipid made by animals; found in cell membranes Unit 3 Vocabulary 47. nucleic acid- macromolecule that carries genetic material; basic unit is nucleotide 48. RNA (ribonucleic acid)- type of nucleic acid used in making proteins; has ribose sugar; singlestranded 49. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)inherited genetic material that contains instructions for life; has deoxyribose sugar; doublestranded Unit 3 Vocabulary 50. protein- macromolecule made of amino acids; contains C, O, H and N; found in muscles; used for growth and repair 51. amino acid- unit of proteins; 20 types; linked together to form polypeptide chain 52. polypeptide- long chain of many linked amino acids; unfolded protein Protein Amino Acids Polypeptide Unit 3 Vocabulary 53. poly- prefix meaning many; ex: polypeptide 54. mono- prefix meaning one; ex: monosaccharide 55. di- prefix meaning two; ex: disaccharide