Antibody Structure
advertisement

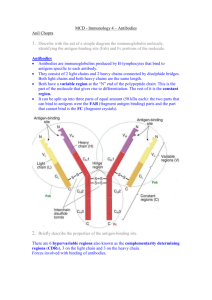
Antibody Structure Introduction Antibodies are immune system-related proteins called immunoglobulins. Each antibody consists of four polypeptides– two heavy chains and two light chains joined to form a "Y" shaped molecule. The amino acid sequence in the tips of the "Y" varies greatly among different antibodies. This variable region, composed of 110-130 amino acids, give the antibody its specificity for binding antigen. The variable region includes the ends of the light and heavy chains. Treating the antibody with a protease can cleave this region, producing Fab or fragment antigen binding that include the variable ends of an antibody. Material used for the studies shown below originated from Fab. The constant region determines the mechanism used to destroy antigen. Antibodies are divided into five major classes, IgM, IgG, Iga, IgD, and IgE, based on their constant region structure and immune function. The variable region is further subdivided into hypervariable (HV) and framework (FR) regions. Hypervariable regions have a high ratio of different amino acids in a given position, relative to the most common amino acid in that position. Within light and heavy chains, three hypervariable regions exist – HV 1, 2 and 3. Four FR regions which have more stable amino acids sequences separate the HV regions. The HV regions directly contact a portion of the antigen's surface. For this reason, HV regions are also sometimes referred to as complementarity determining regions, or CDRs. The FR regions form a beta-sheet structure which serves as a scaffold to hold the HV regions in position to contact antigen. Antibody/Antigen Interaction Click on images to see enlarged view This image represents the structure of an antibody's variable region (Fab) complexed with an antigen, in this case hen egg white The HV regions of a Fab, representing both light and heavy chains, are highlighted in purple. The antigen is green. The part of the antigen in In this view, the HV regions of the Fab have been deleted. The FR regions of the antibody do not contact the antigen. This ribbon structure shows the antibody's HV (purple) and FR (yellow) regions of the Fab, and their interaction with an epitope of the lysozyme. The other images in this section are derived from this structure. direct contact with the antibody is called the antigenic determinant, or epitope. antigen. Animation: FR and HV regions of antibody Animation: Antigen interacts with HV region Antibody/Antigen Interaction – A Closer Look An antigenic determinant, a site on the antigen that the immune system responds to by making antibody, can frequently be one unique structure on the antigen. In hen egg white lysozyme, a glutamine at position 121 (Gln 121) protrudes away from the antigen surface. In this view, Gln 121 is circled. The antibody is not shown. The following images show how this feature is important for the formation of a high affinity antibody-antigen interactions. The antibody's HV region forms an opening to surround the antigen's protruding Gln 121 (green). Hydrogen bonds (yellow) stabilize the antibody-antigen interaction. In addition to hydrogen bonds, other weak interactions such as van der Waals forces, hydrophobic interactions and electrostatic forces improve the binding specificity between antibody and antigen. These interactions occur over large and sometimes discontinuous regions of the molecules, improving binding affinity. The animation shows amino acids of the antibody that interact with Gln 121. Animation: Gln 121 of lysozyme surrounded by amino acid residues of antibody Close-up of a hydrogen bond – The Tyr 101 of the antibody forms a hydrogen bond with the Gln 121 of the antigen. Water molecules (light blue) fill in spaces between the antigen and the antibody. The water molecules contribute significantly to the binding energy by creating additional hydrogen bonds. Molecular structures represented in this tutorial were obtained by X-ray crystallography. The coordinates for these structures are registered at the Protein Data Bank (1FYA and 1FYB).