B9-cell membrane and transport
advertisement
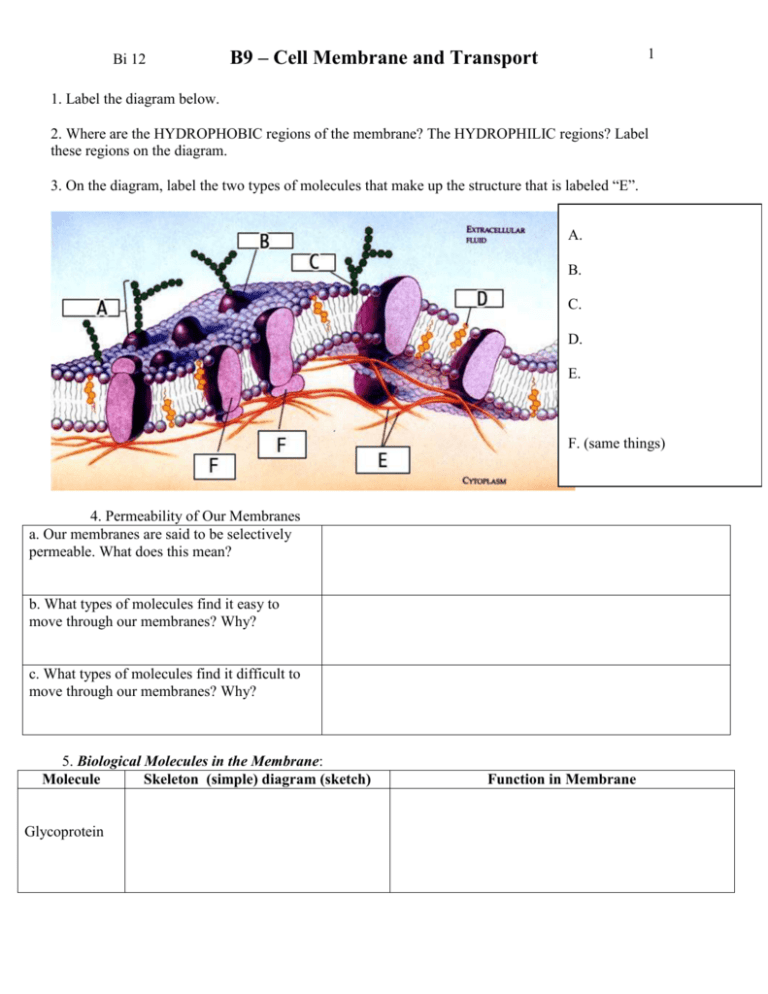
Bi 12 B9 – Cell Membrane and Transport 1 1. Label the diagram below. 2. Where are the HYDROPHOBIC regions of the membrane? The HYDROPHILIC regions? Label these regions on the diagram. 3. On the diagram, label the two types of molecules that make up the structure that is labeled “E”. A. B. C. D. E. F. (same things) 4. Permeability of Our Membranes a. Our membranes are said to be selectively permeable. What does this mean? b. What types of molecules find it easy to move through our membranes? Why? c. What types of molecules find it difficult to move through our membranes? Why? 5. Biological Molecules in the Membrane: Molecule Skeleton (simple) diagram (sketch) Glycoprotein Function in Membrane Bi 12 B9 – Cell Membrane and Transport Glycolipid (Carbohydrate) (not found alone in the membrane, but you need to know this for later anyway – might just as well add it here!) (Function with membrane AND in body) (for comparison to phospholipids) (Function in body) Cholesterol Phospholipids Fatty Acids Proteins Lipids (triglycerides) 2 Bi 12 B9 – Cell Membrane and Transport Channel protein Carrier protein Receptor Protein 6. Describe the differences Processes Endocytosis vs Exocyosis. pinocytosis vs. phagocytosis diffusion vs osmosis Differences 3 Bi 12 B9 – Cell Membrane and Transport 4 9. For each of the next three examples, identify whether the solution is isotonic, hypertonic or hypotonic compared to the “cell”, DESCRIBE what will happen to the cell and explain WHY. 10. Complete the following table: Do the molecules Is the use of Transporter follow their energy process concentration required for gradients with this this process? process? Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Transport Active Transport Endocytosis exocytosis Is a channel or carrier protein used in this process? What types and/or sizes of molecules are transported using this process? Bi 12 B9 – Cell Membrane and Transport 5 11. Describe how the RATE of diffusion across a cell membrane is affected by each of the following factors: Factor How it affects the rate of diffusion. a. temperature b. size of molecule c. charge of molecule d. concentration gradient e. pressure gradient. 12. Identify the type of membrane transport in the diagrams below, and classify them as either passive or active transport. b. a. c. e. d. f. Transport Type a. b. c. d. e. f. Active Or Passive?