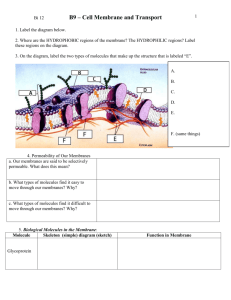
Guided Reading 7-3 Key 1. Name two functions of the cell
advertisement

Guided Reading 7-3 Key Protein Marker with a Carbohydrate Chain Lipid Bilayer Protein Channel 1. Name two functions of the cell membrane: Controls what enters and exits the cell, provides protection and support 2. The cell membrane contains protein molecules that are embedded in the lipid bilayer. 3. Why do scientists call the membrane a "mosaic"? It is made of many different things, proteins, phospholipids, cholesterol 5. What three types of organisms have cell walls? plants, fungi, bacteria 6. What is the main function of the cell wall? to provide support and protection to cells 7. What are plant cell walls composed of? cellulose 8. One of the most important functions of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of dissolved molecules from the liquid on one side of the membrane to the liquid on the other. 9. A solution is a mixture of two or more substances. 10. Define diffusion: when particles, such as solids and gases, move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 11. When the particles are the same throughout, the system has reached equilibrium 12. Diffusion depends on random particle movements, therefore it [ does | does not ] (circle) require energy. 13. If a substance is able to diffuse across a membrane, the membrane is said to be _permeable______________ 14. Define osmosis: ____the movement of water from a high concentration to a low________________________ 15. Isotonic means __equal concentration_____________ Hypertonic means __more solute_________________________ Hypotonic means ____________less solute________________ 16. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water, ___osmosis________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ___swollen_________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmotic pressure? __cell walls_________ FACILITATED DIFFUSION 18. Cell membranes have protein channels that make it easy for certain molecules to cross the membrane. 19. When proteins help molecules move across the membrane, it is called facilitated diffusion ACTIVE TRANSPORT 20. Active transport moves molecules [ with | against ] the concentration gradient. 21. Active transport requires cell energy 22. Changes in protein shape seem to play an important role in the transport process. 23. Define endocytosis: when a cell takes in materials through infoldings or pockets in the cell membrane 24. What are the two types of endocytosis? pinocytosis and phagocytosis 25. How does an amoeba gets it food? phagocytosis 26. Cells release large amounts of material in a process called exocytosis