Mountains and Volcanoes Questions
advertisement

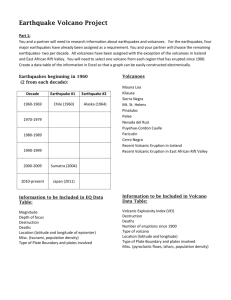
Mountains and Volcanoes – Questions ANSWERS 1. A mountain can be defined as: A natural elevation of the earth’s surface, rising abruptly from the surrounding level. – steep hill. 2. Orogeny means: The name given for the processes of mountain forming 3. An orogenic belt is: Long tracks of highly deformed rock that run in parallel strips exhibiting similar characteristics along the entire length of the belt. 4. How long does it take for a orogenic belt to typically form? It can take tens of millions of years. 5. Identify and describe the two main ways/processes a mountain can form. Deformation – continental collisions resulting in folding and faulting Volcanic Activity – opening in crust which allows magma to escape and form a volcanic mountain. 6. Complete the graphic organizer attached identifying the main type of mountains. 1 7. What are the differences between a shield volcano, a stratovolcano and a cindercone volcano? Fill in chart below. Overall shape: Cindercone Volcano Wide base, gradual slope, small crater Characteristics Lava fragments Magma and are called Lava: cinders Shield Volcano Strato Volcano Wide base, low Wide base, low grade slope, large grade slope, wide crater crater Lava is runny and flows like a river Magma is thick and sticky and easily clogs crater. Type or Lava is ejected Does not explode. Most violent Eruption from one vent Just heads and eruption – and deposits melts the above explodes and around that vent. rock. blows rock and ash everywhere. Typically found Found near Can be found Found near (i.e. on plate subduction zones anywhere on a subduction zones boundaries) (where oceanic plate – does not (where oceanic and continental have to be along and continental plates collide) a boundary plates collide) 8. Where is Mount St. Helens found? What type of volcano is it? How can you tell this? It is found in Washington on the west coast of USA. It is a stratovolcano because when it erupts – it spews rock and ash. 9. How do the formations of mountains and volcanoes relate to the theory of plate tectonics? Both mountains and volcanoes result from tectonic activity. Mountains from collision of continental plates; volcanoes from hot spots or collision of oceanic and continental plates. 2 10. Research the Iceland volcanic eruption that began April 10. 2010 at the Eyjafjallajökull Volcano. Based on your research: identify the type of volcano (be sure to include how you know this (ie. Nature of eruption, etc.) the nature of the eruption, how long the eruption lasted, the impact on humans. Type of Volcano – Stratovolcano Evidence – created a rock and ash cloud that extended over much of Europe for days. Nature of Eruption – violent, and lasted months until the eruption finally stopped in October of that year. Human Impact – loss of homes, airways were blocked: planes could not fly to/from Iceland and many European countries nearby. Farmland and livestock were also greatly impacted. 11. Research how a volcanic eruptions can affect the environment and climate and list below affects below. Volcanoes that release large amounts of ash into the atmosphere can cause sun rays to be reflected away from the earth’s surface causing air temperatures to decrease. Increased amounts of rain are also common in areas with this type of eruption occurs as water likes to attach to these ash particles causing a lot of rain and thunderstorms. 12. Is Halifax located on a foreland or a craton? Explain. Is is located on a craton. Why? Because we are located in the middle of the North America plate. A foreland is the area of land right beside a mountain range and Halifax is not right beside a mountain range. 3 13. Why are there no active volcanoes in the eastern parts of North America? Because there are no: hot spots in the area or subduction zones (collision of oceanic and continental plates) to create volcanoes. 14. What are some benefits to volcanic activity? They produce fertile soil for growing many crops, they can create new land (volcanic islands such as Iceland and Hawaiian Islands), Gems and minerals are found here too. 15. What are the differences between active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes? Active: volcanoes that have at least one eruption during the last 10,000 years. Dormant: volcanoes are active but no eruptions but are expected to. Extinct: volcanoes that have not erupted for over 10,000 years. 16. What are the similarities and differences between mountains and volcanoes? Similarities: both can result from the collision of plates. Volcano – through collision of oceani/continental at a subduction zone. Mountains – though collision of two continental plates Similarities: mouth are sloped, elevated land masses Differences: Mountains wont release magma Differences: Mountains are due to uprising of crust, Volcanoes build due to the release of lava. 4