More about LOD scores
advertisement

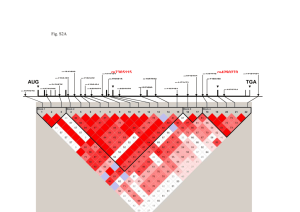
More About LOD Scores 2012 a) Relatedness • Backcross, F2, Recombinant inbred lines • Humans: – Need to be able to compare maps between groups – Need suitable families for analysis - large, multigenerational The Centre d'Etude du Polymorphism Humain (CEPH) b) Viability (polymorphism) Form P Form Q 1% 99% 15% 85% 42% 58% c) Maintenance d) Size The LOD Score Method What is the inheritance of the two traits? • Nail-patella syndrome (affected individuals indicated by filled symbols) - dominant • Blood Type - A and B codominant and each dominant to O Is this cross informative? • Yes - the phase of the alleles at the two loci can be determined by examining the genotypes of the grandchildren. Note: information from the grandparents is useful in determining this. What type of cross is this? • Essentially a test cross AB Npnp x OO npnp (an individual heterozygous at both loci crossed to an individual homozygous at both loci) Are there any linkage associations evident? • Yes - alleles A and Np appear to be linked. Why? Because the 2 alleles are typically present in the same individuals. Are there any recombinant individuals in the pedigree? 1, noted by the asterisk in the figure. Why? He has the A blood type allele but is not affected with Nail patella. What is the percent recombination? • 1/8, or 12.5% THE LOD SCORE METHOD: Z ( ) = log [(1 - )n-r r/ (1/2)n] Z () = (n - r) log [2 (1 - )] + r log (2 ) Z () = (n - r) log [2 (1 - )] + r log (2 ) Z (0.1) = (8 - 1) log [2 (1 – 0.1)] + 1 log (2 * 0.1) Z (0.1) = (7) log [2 (0.9)] + (1) log (0.2) Z (0.1) = (7) log [1.8] + (1) log (0.2) Z q 1 = LOD score based on q 1 Z q 2 = LOD score based on another recombination frequency q 2 Z q 3 = LOD score based on q 3, etc. Calculating LOD Scores Recombination Frequency 0.05 0.10 0.125 0.15 0.20 0.25 LOD score 0.95 1.09 1.12 1.09 1.03 0.92 Z () = (n - r) log [2 (1 - )] + r log (2 ) Z () = (18 - 3) log [2 (1 - )] + 3 log (2 )