Families of Elements and Trends in the Periodic Table
advertisement

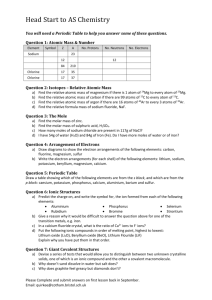
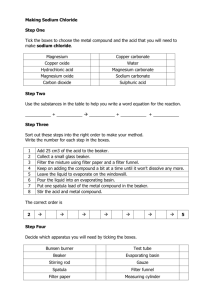
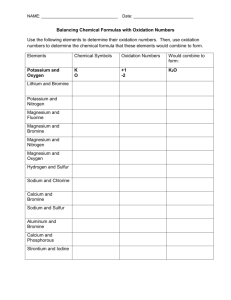
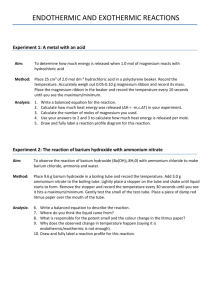
Families of Elements and Trends in the Periodic Table Purpose: To observe the reaction of elements from the alkali family and the alkaline earth family with water, and to predict trends in chemical reactivity. Materials: 250 mL beaker magnesium water calcium safety glasses lithium sodium paper towel potassium WARNING: Wear your safety glasses at all times during this lab Do not touch family 1A, alkali metals with your hands Procedure: 1. Pour approximately 200 mL of water into a 250 mL beaker. 2. Obtain a small sample of magnesium metal on a paper towel. 3. Record physical properties of magnesium in your chart. 4. When instructed, place the magnesium in the beaker of water. Record the reaction of magnesium with water. 5. Write a prediction for calcium, including observations that will be similar to magnesium and different from magnesium. 6. Obtain a piece of calcium on a paper towel. Record the physical properties of calcium in your chart. Pour out the previous sample of water and fill the beaker with about 200 mL of fresh water. 7. When instructed, place the piece of calcium in the beaker and record your observations of the reaction of calcium with water. 8. Obtain a piece of lithium metal with a paper towel. Record physical properties of the metal. Put fresh water in the beaker. 9. When instructed, wipe excess oil from the lithium and place it in the beaker of water. Observe and record the reaction. 10. Make a prediction for sodium, including observations that will be similar to and different from lithium. 11. Obtain a sample of sodium with a paper towel and record physical properties of sodium. Pour fresh water in the beaker. 12. When instructed, wipe the excess oil from the sodium and place it in the beaker of water. Observe and record results. 13. Make a prediction for potassium, including observations that will be similar to and different from lithium and sodium. 14. Obtain a sample of potassium with a paper towel and record physical properties. Pour fresh water in the beaker. 15. When instructed, wipe the excess oil from the potassium and place it in the beaker of water. Observe and record results. 1 Observations: Element Physical Properties Prediction Magnesium Calcium Lithium Sodium Potassium 2 Chemical Properties Analysis: 1. a) As you move down a family (group), does the reactivity of the metals increase or decrease? ___________________ b) As you move across a period (row), does the reactivity of the metals increase or decrease? __________________________ 2. Would you expect barium to be more or less reactive than magnesium and calcium? Explain. ___________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Would you expect cesium to be more or less reactive than lithium , sodium and potassium? Explain. ____________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. a) Draw Bohr-Rutherford diagrams for magnesium and calcium (alkaline earth metals). b) What similarities do you see in the atomic structure (electron arrangement) of the alkaline earth metals?___________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. a) Draw Bohr-Rutherford diagrams for lithium, sodium and potassium (alkali metals). 3 b) What similarities do you see in the atomic structure (electron arrangement) of the alkali metals? _______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ c) Why do you think these elements behave in a similar way when they are placed in water? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ d) What difference in the atomic structure of the alkali metals (Li, Na, K) makes them more reactive than the alkaline earth metals (Mg, Ca)? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4