DNA Notes
advertisement

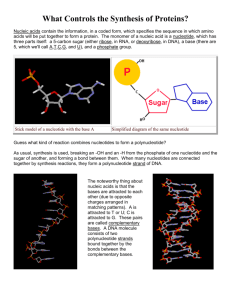
DNA Chapter 13 DNA=Deoxyribonucleic Acid -nucleic acid macromolecule group -makes up chromosomes -a section of DNA = gene DNA Construction: -composed of 4 types of nucleotides --Who was Chargaff? -nucleotides linked into 2 strands by phosphodiester bonds -the 2 strands are held to each other by hydrogen bonds -entire structure then spirally twists = helical shape or Double Helix -Who was Watson & Crick? Nucleotide composed of: 1. Phosphate group (P-group) 2. 5-carbon sugar ring (Ribose=pentose) 3. Nitrogen-base 4 types of bases: 2 Purines 1. Adenine A 2. Guanine G 2 Pyrimidines 3. Thymine T 4. Cytosine C -only one base per nucleotide -DNA composed of 4 types of nucleotides known as A, G, C, or T nucleotides. -nucleotides are linked into two strands by phosphodiester bonds. -each DNA strand has a 3' end & a 5' end -the two strands orient opposite each other. Chargaff’s Rule: -A nucleotides of one strand H-bond with T nucleotides in the opposite strand -G nucleotides of one strand H-bond with C nucleotides in the opposite strand -A bonds with T -G bonds with C -This is termed complimentary base pairing. DNA Replication From one current DNA molecule, two new molecules are formed -parental DNA= template= -daughter DNA= -Semiconservative Replication= Replication Steps: 1. Unwinding -separate parental strands. -Helicase= 2. Complimentary Base-Pairing 3. Joining -Steps 2 and 3 conducted by -DNA Polymerase= -reading direction= -Leading strand= -Lagging strand= -Okazaki fragments= Prokaryotic Replication= Eukaryotic Replication= -replication fork= -replication bubble= Replication errors= -mutation= -Proofreading/repair=