word - Marric.us
advertisement

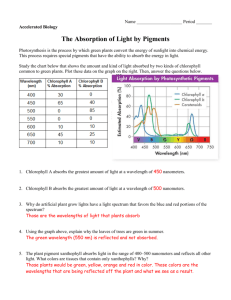
Name_________________________________ Date:_________ Period:____ Respiration Review Questions: Study the diagram of a mitochondrion: 1. Which molecule is represented by A? a. glucose b. water c. CO2 d. chlorophyll 2. Which molecule is represented by B? a. N2 b. Water c. O2 d. O3 3. Cyanide is a powerful poison because it inhibits an enzyme in mitochondria, preventing the transfer of energy during one of the steps in cellular respiration. This poison would directly affect the production of which of the following molecules? a. ATP b. glucose c. oxygen d. RNA 4. The carbon atom in CO2 is “released” from which compound during aerobic cellular respiration? a. water b. glucose c. salt d. chlorophyll Study the diagram below: 5. The amount of ATP produced describes the rate of ___________ in muscle cells. a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c. active transport d. protein synthesis 6. As the amount of sugar is increased ATP production.. a. increases b. stays constant c. decreases d. is NOT affected 7. Which of the following conclusions is best supported by data from this graph? A. ATP production is independent of sugar availability. B. The amount of cellular respiration is constant in muscle cells. C. ATP is only produced when sugar concentrations are above 4 g/L. D. The amount of cellular respiration increases as sugar concentration increases. 8 . A student created the following flowchart to summarize aerobic respiration: Process A represents... a. Glycolysis b. Krebs Cycle Process B represents... c. Fermentation d. Electron Transport Chain Process C represents... 9. A cellular process that uses oxygen as one molecule of glucose is broken down to produce energy in the form of ATP is called ______. a. aerobic respiration b. photosynthesis c. fermentation d. active transport 10. Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert the energy available in food to which energy-rich compound? a. water b. CO2 c. ATP d. DNA 11. Why do eukaryotic cells require mitochondria? a. to package materials inside cells for transport b. to release stored energy for cell activities c. to control cell division for reproduction d. to break down cell debris [wastes] for recycling 12. As respiration begins, glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid and two molecules of ATP are formed. What will happen next in muscle cells if NO [or very little oxygen] is available? a. photosynthesis b. Krebs cycle c. fermentation d. protein synthesis 13. Endoplasmic reticulum is to "highways" as Mitochondrion is to... a. “toll gate” b. "storage tank” c. “power station” d. “city hall” A student created the Venn Diagram below: 14.Which labeled arrow is pointing to erroneous [inaccurate] information? a. W b. X c. Y d. Z 15. SHORT RESPONSE Write in complete sentences: Study the diagram of an experimental set up below- The class sets up an experiment with the four flasks as shown. Flask 1: 100 mL water, 1 mL bromthymol blue, plant Flask 2: 100 mL water, 1 mL bromthymol blue, 2 small fish Flask 3: 100 mL water, 1 mL bromthymol blue, 2 small fish, plant Flask 4: 100 mL water, 1 mL bromthymol blue BTB or Bromthymol blue is a chemical indicator that changes color from blue to yellow in the presence of CO2 [and vice versa when levels of CO2 decrease]. All four flasks are stoppered and placed under the floodlight. a. Flask 1 Flask 2 Flask 3 Flask 4 What color would the solution in each flask be after a few hours? b. Explain how the processes that have occurred in each flask result in the observed color of the bromthymol blue solutions.